Nola Pender is a nursing theorist who developed the Health Promotion Model, a conceptual framework that guides nursing practice and research. Pender's model emphasizes the role of individual behavior and lifestyle choices in determining health outcomes, and it recognizes the influence of social and environmental factors on health.
According to Pender, health is a dynamic state of well-being that is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including physical, emotional, and social well-being. Health promotion, therefore, involves efforts to enhance and maintain these dimensions of well-being by empowering individuals to take control of their own health.
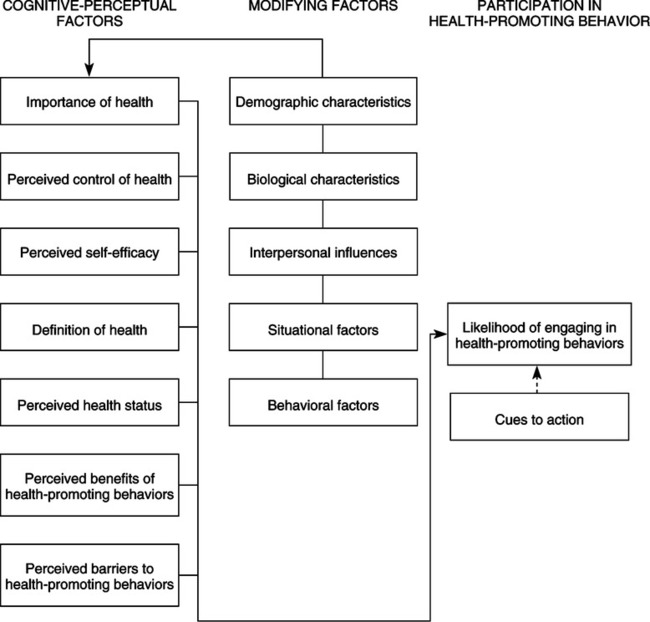
One key component of Pender's Health Promotion Model is the concept of personal factors, which refers to the individual characteristics and experiences that influence health behaviors. These factors include demographic characteristics such as age, gender, and culture, as well as psychological and social factors such as self-esteem, self-efficacy, and social support.
Pender also recognized the importance of environmental factors in determining health outcomes. These factors include the physical and social environments in which individuals live and work, as well as the policies and practices that shape these environments. For example, the availability of healthy food options and access to physical activity facilities can significantly impact an individual's health behaviors and outcomes.
Pender's model also emphasizes the role of health behaviors in determining health outcomes. According to the model, health behaviors are the actions that individuals take to promote or maintain their health, such as exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in stress-reducing activities. These behaviors are influenced by personal and environmental factors, as well as by an individual's knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about health.
Pender's Health Promotion Model has been widely used in nursing practice and research, and it has contributed significantly to our understanding of the complex factors that influence health. The model has also influenced the development of health promotion interventions and programs, which aim to empower individuals to take control of their own health by addressing the personal and environmental factors that shape their health behaviors.
Pender's Health Promotion Model
Pursuing a career in nursing is a calling as evident in the life Nola. At the end of 2014, nearly 1. Cognitions and specific behavioral affects Personal factors are classified as biological, psychological and sociocultural. In summary, the theory takes into account the importance of the social and cognitive process, as well as the relevance that these have in the behavior of the individual, and how all this affects the promotion of health in the person. The Health Promotion Model also takes into consideration the second meta-paradigm of nursing. The environmental factors include social, cultural, and physical aspects. Their establishment and adequate functioning can foster the retention of patients, improve the quality of HIV services, and promote better coordination among social workers, caregivers, and patients.
Nola Pender Health Promotion Model

Examples of the specific theories include the theory of barriers and facilitators and Meleis Theory of care transition. The highly demanded expert, one of our top 10 writers with the highest rate among the customers. The strategy will help to create public health policy, establish supportive environment, strengthen efforts, develop necessary skills, and re-orient health services towards chronic conditions. It defines health as a positive dynamic state rather than simply the absence of disease. During her long career, Nola Pender supported and continues to support different organizations related to nursing, contributing her time, service and knowledge. Pender is presently a Professor Emeritus at Michigan State University.
MIDDLE

It is currently widely utilized in practice, education, and research nationwide and worldwide. In addition, he was a member of the United States Preventive Services Task Force from 1998 to 2002. ADVERTISEMENTS On the other hand, health protection or illness prevention is described as behavior motivated desire to actively avoid illness, detect it early, or maintain functioning within illness constraints. The author begins by examining the health issues affecting many adolescents in every society. The practical application of the abovementioned models will be also realized through various capacity building initiatives as well as functioning of peer-support agencies, peer-based organizations, and engagement of training volunteers. I will also work hard to ensure I become one of the successful nurses as Nola.