Semantic shift, also known as semantic change, is the process by which the meaning of a word or phrase changes over time. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including changes in societal norms and values, technological advancements, and shifts in the way language is used and understood.
One common type of semantic shift is the process of broadening or narrowing. This occurs when a word's meaning becomes either more specific or more general over time. For example, the word "nice" used to mean "foolish or stupid," but over time its meaning has broadened to include positive connotations such as "kind" or "pleasing." On the other hand, the word "gay" used to mean "happy" or "carefree," but its meaning has narrowed to specifically refer to sexual orientation.
Another type of semantic shift is the process of amelioration or pejoration. This occurs when a word's meaning becomes either more positive or more negative over time. For example, the word "savage" used to mean "wild" or "uncivilized," but its meaning has become more negative and is now often used to describe someone as cruel or vicious. On the other hand, the word "awesome" used to mean "inspiring fear or admiration," but its meaning has become more positive and is now often used to describe something as impressive or remarkable.
Semantic shift can also be caused by shifts in the way language is used and understood. For instance, the word "cool" was originally used to describe temperature, but it has since taken on a variety of slang meanings, including "calm" or "unconcerned," and " fashionable" or "trendy." This type of semantic shift is often driven by the way language is used in popular culture, such as music and media.
Semantic shift can have a significant impact on the way we communicate and understand language. It is important to be aware of these changes in meaning to ensure clear and effective communication. Additionally, understanding the history and evolution of words can provide insight into the values and cultural norms of different periods in history.
In conclusion, semantic shift is the process by which the meaning of a word or phrase changes over time. It can be caused by societal changes, technological advancements, and shifts in the way language is used and understood. Understanding these changes can help us communicate effectively and gain insight into the values and cultural norms of different periods in history.
Offences under IPC Section 498A: Bailable or not?

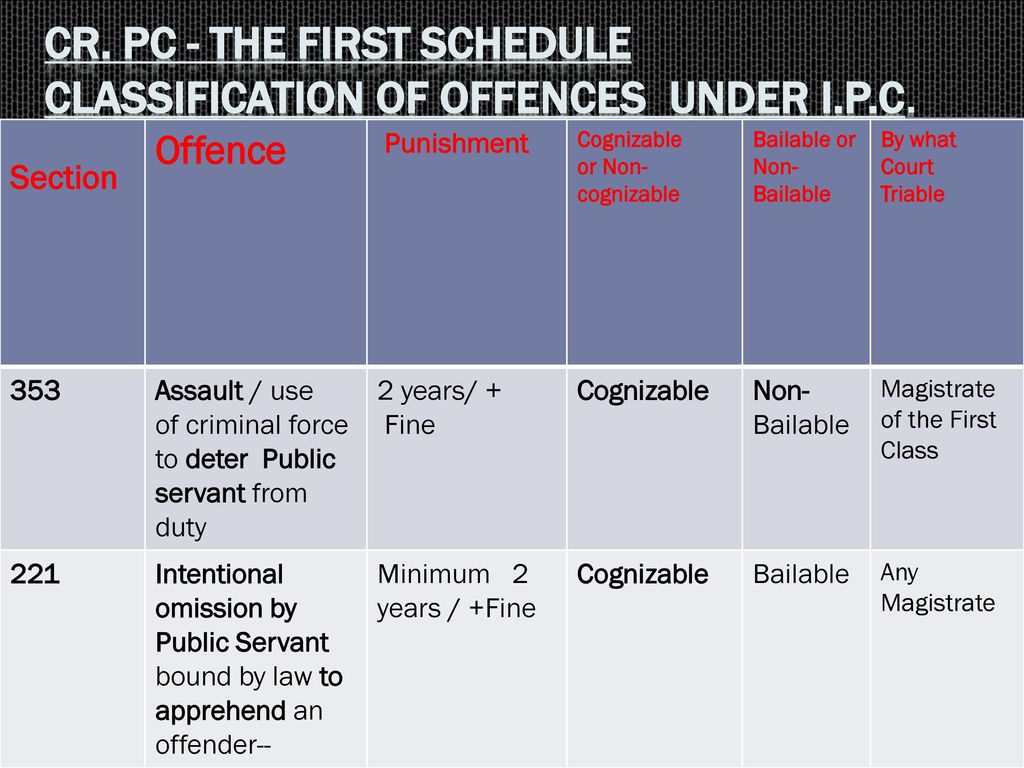
Such forgery may be of many kinds such as forgery of signatures, documents, electronic records, etc. Observing the intensity of the crime, offenses are classified or rather divided as bailable and non-bailable offenses. The bail can only be granted by undertaking a few conditions under section 437 of CrPc. However, the total marks in the forged marksheet contained more marks than that which a student could score even if he secured one hundred per cent marks. Introduction: The crimes and offences and their punishments have been given under the Indian penal code, 1860. If the suspect may not indulge in the non-bailable offence at any stage of the investigation, a person may get bail by the court on the execution of the bond.
List of Bailable and Non

The offence committed under section 420 is a Cognizable as well as a Non-bailable offence. Section 24 of the Standard of Weights and Measures Act, 1976 What are the punishments for the offences contained under Sections 264-267 of IPC? When should bail be denied Philippines? This offence is not against a private individual or family, it is an offence against the State. . The meaning of offenses is that any omission or act made fully punishable by law for certain time during being in force. Under this Section a person may be punished with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to one year, or with fine, or with both. In the event the suspect fails to return to court, the bail will be forfeited. If an individual is in possession of a forged Will wherein they have manipulated certain proceeds of the Will to their benefit, then in such a situation, the law will assume that the Will was forged with a malafide intention to gain wrongful benefit.
IPC Section 300

The severe offenses such as Culpable Homicide, Murder, and Rape are called Non-Bailable. Of course, the appellant cannot disassociate himself from the findings that he was in possession of a loaded firearm in a crowded area where his own guests had gathered to witness the wedding ceremony. State of Andhra Pradesh, 2021 In this Sudha Singh v. How do I fight IPC 406? Thus, it can be understood that an offence committed under Section 471 of the IPC is a cognizable offence. Although in the case of bailable offenses full liberty is not cast upon the accused to get bail, and he may get bail, but if the court thinks fit to commit him to custody, then it can do so while giving justifiable reasons. They are self exclusive.
Offences Related to Weight and Measures under IPC

Why do you need a Lawyer? Moving on to sub-section 6, which is related to trials before a magistrate, it is stated that if in a case triable by a magistrate, the trial of the person accused of any non-bailable offence is not concluded within sixty days from the first date wherein the court sets up for taking evidence, then in such a case, the accused shall be granted bail if he was in custody for the whole period. Instead of exercising any reasonable precautions, such as firing the shot into the air or toward the sky, he took a full risk and pointed the gun at the roof and fired the shot. What began as a gift and promise of protection from one spouse to another quickly turned into a financial demand, resulting in broken engagements or divorce, violence, and even death for unpaid dowries. This implies that the mere possession of such document or legal instrument and the intention to make use of such document or legal instrument is sufficient to convict an individual under Section 467 of the IPC. Section 463 of the IPC states that there must be an intention on part of the offender to establish a case of forgery and the burden of proof lies on the prosecution to prove that the accused has committed forgery.