In psychology, normality and abnormality are complex concepts that are often discussed and debated. Normality refers to behavior that is considered typical or expected within a particular culture or society. It is often associated with concepts such as mental health, well-being, and functionality. Abnormality, on the other hand, refers to behavior that deviates from these norms and is often seen as unhealthy, dysfunctional, or distressing.
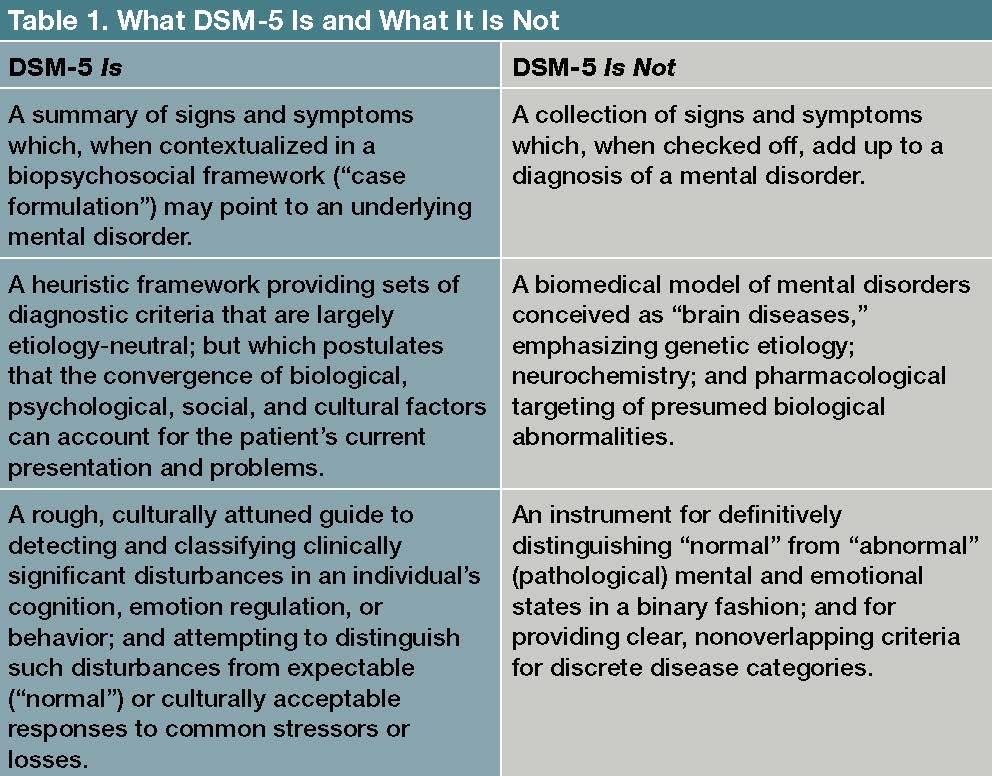
One way that psychologists have attempted to define normality and abnormality is through the use of diagnostic criteria. The DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) is a widely used manual that provides a set of criteria for diagnosing mental disorders. These criteria are based on the presence of specific symptoms, such as abnormal thoughts, emotions, or behaviors, that are considered indicative of a particular disorder.
However, there are several problems with using diagnostic criteria to define normality and abnormality. One issue is that these criteria are often culturally specific and may not be applicable to all societies or individuals. For example, certain behaviors that are considered abnormal in one culture may be considered normal in another. Additionally, diagnostic criteria are often based on the average or typical experience of a particular disorder, which means that individuals who do not meet all of the criteria may still be struggling with mental health issues.
Another problem with using diagnostic criteria to define normality and abnormality is that they do not take into account the context in which a particular behavior occurs. For example, a behavior that may be considered abnormal in one situation may be completely normal in another. This means that relying solely on diagnostic criteria can lead to a one-size-fits-all approach to mental health that does not adequately account for individual differences or the unique circumstances of each person.
A more holistic approach to understanding normality and abnormality involves considering both internal and external factors that may be contributing to a person's behavior. This approach recognizes that mental health is not simply the absence of mental disorders, but rather a complex interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors. By considering these factors, psychologists can develop a more nuanced understanding of normality and abnormality and better support individuals who are struggling with mental health issues.
In conclusion, normality and abnormality are complex concepts that are influenced by a variety of factors. While diagnostic criteria can be useful in identifying mental disorders, they do not provide a complete understanding of mental health and well-being. A more holistic approach that considers the unique circumstances and experiences of each individual is needed to accurately understand and support mental health.