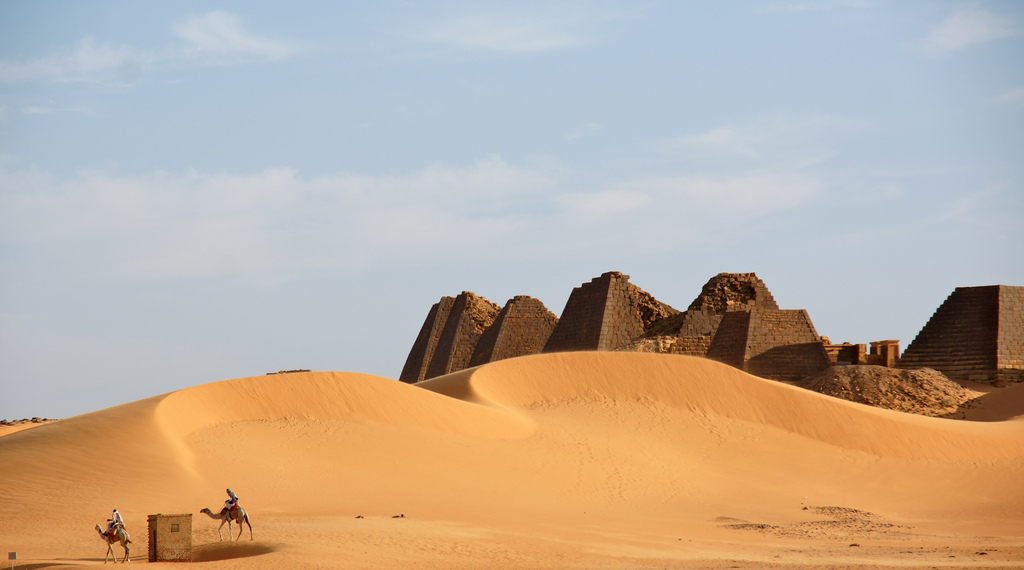
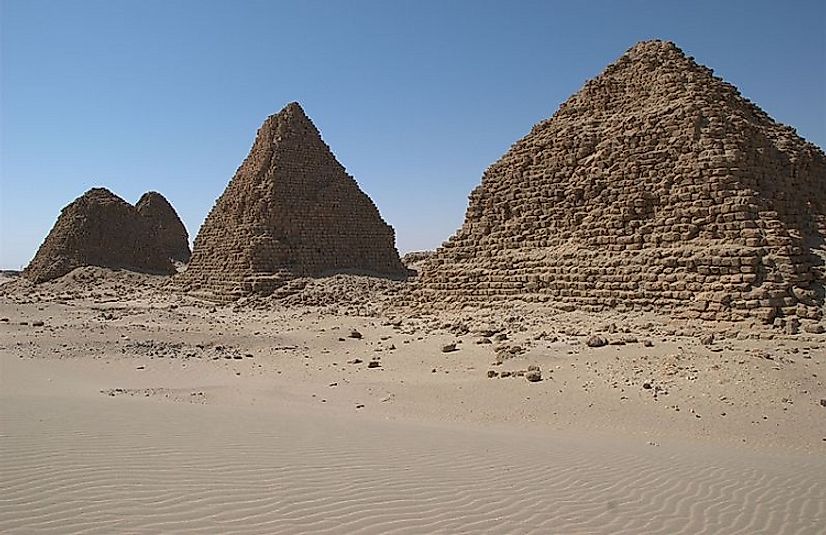
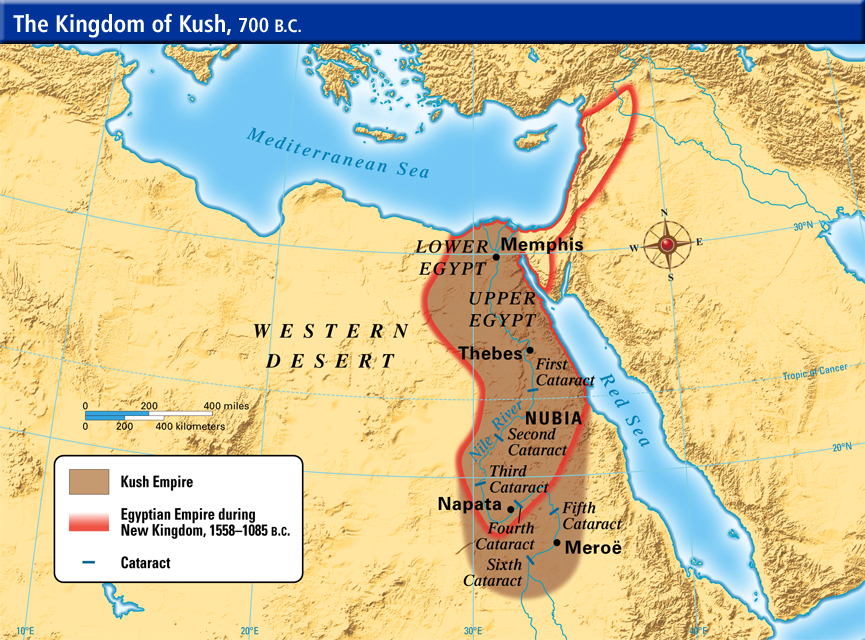
The Nubian Kingdom of Kush was an ancient African civilization located in present-day Sudan and southern Egypt. It emerged as a powerful state around 2000 BCE and maintained its political and cultural influence for nearly a thousand years, until it was conquered by the Kingdom of Aksum in the 4th century CE.
The origins of the Kingdom of Kush are somewhat murky, as the early history of the region is not well-documented. However, it is believed that the Kingdom of Kush arose from the merger of several smaller Nubian states that had developed along the Nile River. The Nubians were a diverse group of people, with a variety of cultures and languages, but they shared a common history and a common set of religious and cultural practices.
One of the most significant achievements of the Kingdom of Kush was its military power. The Nubians were skilled warriors and skilled at building fortifications, and they were able to defend their territory against the frequent incursions of their neighbors. They also established a powerful navy, which allowed them to control trade routes along the Nile and the Red Sea.
The Kingdom of Kush was also a major cultural and intellectual center. The Nubians developed a system of writing, known as Meroitic, which was used to record their history, laws, and religious beliefs. They were also skilled in the arts and crafts, and their pottery, metalwork, and other artifacts are still admired today.
One of the most enduring legacies of the Kingdom of Kush is the royal tomb of King Kashta, which was discovered in the early 20th century. The tomb is decorated with intricate carvings and paintings that depict the King's life and accomplishments, as well as the customs and beliefs of the Nubian people.
Despite its many achievements, the Kingdom of Kush eventually fell to the Kingdom of Aksum, which was a more powerful and technologically advanced civilization. The Nubians were absorbed into the Aksumite Empire, and their culture and traditions were largely lost to history. However, the legacy of the Kingdom of Kush lives on through the rich cultural heritage that it left behind, and it continues to be a source of fascination and inspiration for scholars and historians around the world.