Nursing care plan for myocardial infarction. 170516998 2022-12-31
Nursing care plan for myocardial infarction
Rating:
7,9/10
415
reviews
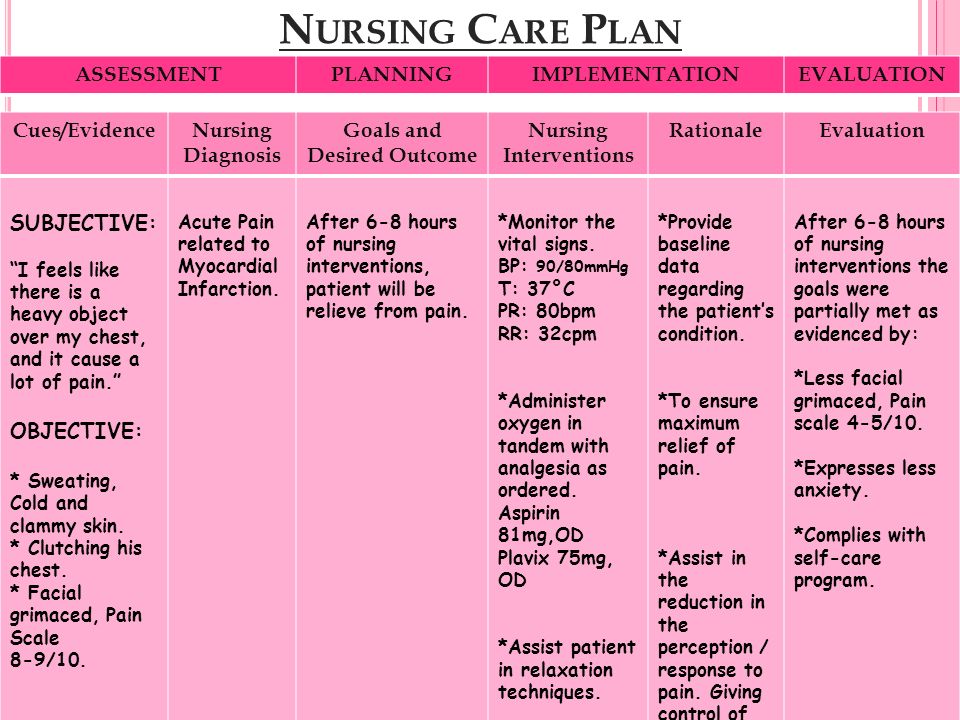
A nursing care plan for a patient experiencing a myocardial infarction, or heart attack, should focus on several key areas to ensure the best possible outcome for the patient. These areas include pain management, monitoring of vital signs and cardiac function, risk reduction and prevention of further complications, and patient education and support.
One of the most important aspects of nursing care for a patient with a myocardial infarction is pain management. The pain associated with a heart attack can be severe and may require the use of strong pain medications, such as opioids. It is important for the nurse to monitor the patient's pain levels and adjust the medication regimen as needed to keep the patient comfortable.
In addition to pain management, the nurse should also closely monitor the patient's vital signs, including blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen saturation. The nurse should also monitor the patient's cardiac function, including their electrocardiogram (ECG) and cardiac enzymes, to ensure that the heart is functioning properly and to identify any potential complications.
Risk reduction and prevention of further complications is also a key focus of nursing care for a patient with a myocardial infarction. This may include educating the patient on lifestyle changes that can help prevent future heart attacks, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. The nurse may also prescribe medications to help lower the patient's blood pressure and cholesterol levels and to prevent blood clots.
Finally, nursing care for a patient with a myocardial infarction should also include patient education and support. This may include teaching the patient about their condition, helping them understand the importance of following their prescribed treatment plan, and providing emotional support and encouragement. The nurse should also work with the patient's family and other healthcare providers to ensure that the patient has the support they need to manage their condition and make the necessary lifestyle changes.
In conclusion, a nursing care plan for a patient with a myocardial infarction should focus on pain management, monitoring of vital signs and cardiac function, risk reduction and prevention of further complications, and patient education and support. By addressing these key areas, the nurse can help ensure the best possible outcome for the patient and support their recovery from a heart attack.
Myocardial Infarction Nursing Care Plan
The receptor is finally discharged into the blood vessels when the muscle tissues are damaged. At times of apprehension, the patient and family can be readily affected if the health care team is also anxious. . Place the patient in supine position during administration to minimize hypotension. Contact your doctor or nursing staff if you develop any symptoms that concern you, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fever. Observe and watch out for the presence of adventitious breath sounds, particularly crackles. To increase the oxygen level and achieve an SpO2 value within the target range.
Next
Myocardial Infarction Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan

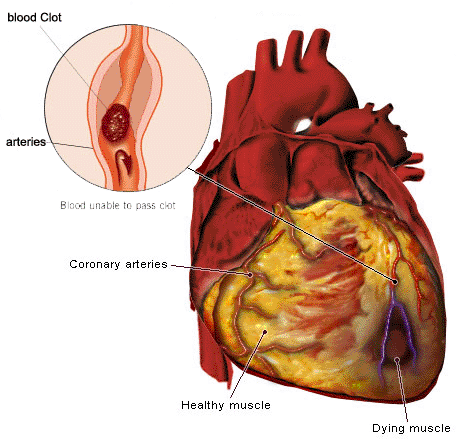
Hypertension and obesity increase the workload of the heart, and diabetes mellitus decreases the circulation to the heart muscle. However, while in the ED, the patient was diagnosed of unstable angina with test to rule out myocardial infarction carried out. This can occur 3 times in total. Administer medications as indicated: Antiplatelet agents, e. An automatic internal cardioverter-defibrillator delivers an electric shock to the heart to terminate episodes of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Option B: Hypertension is usually exhibited by headaches, visual disturbances, and a flushed face.
Next
12 Nursing Diagnosis for Myocardial Infarction

Renal insult is signaled by decreased urine output, and increased BUN and creatinine levels. Quick recognition of any heart change in serial ECG is also the main aspect of nursing care. The cardiac-specific isoenzyme is: A. CAD common cause with plaque formation narrowing vessels and pieces of plaque breaking off, creating emboli b. The first warning may be recurrent chest pain or pain angina that is triggered by exertion and relieved by rest. By decreasing the heart rate and contractility, beta-blockers improve myocardial filling and cardiac output, which are primary goals in the treatment of cardiomyopathy. Application of the TIMI risk score for ST-elevation MI in the National Registry of Myocardial Infarction 3.
Next
Home Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction

Collaborative Administer supplemental oxygen by means of nasal cannula or face mask, as indicated. She has more than 10 years of clinical and teaching experience and worked as a licensed Nursing Specialist in JCI-accredited hospitals in the Middle East. The patient may still show symptoms of a heart attack. Nurses must overcome patient problems and refer them to heart nurses or nutritionists for specialist advice, as well as primary care teams for ongoing secondary prevention. The effects of stress are likely to increase myocardial workload. Refer to ND: Activity intolerance. Nursing Care Plan for Myocardial Infarction 2 Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Desired outcome: The patient will be able to maintain adequate cardiac output.
Next
Nursing Care for Infarction (Hope).docx

They also should think of the 12-lead ECG as a sixth vital sign and obtain it within the first 10 minutes of arrival at the first complaint of chest pain for in-patients. Most hospitals have RRTs that nurses can call for immediate assistance. Some heart attacks strike but individuals have symptoms hours, days or months beforehand and signs. Like all other tissues in the body, the heart muscle needs oxygen -rich blood to function. STEMI, NSTEMI, and other dysrhythmias can be detected. This usually means you will be taken urgently, by ambulance, to a few of those expert centres or the emergency or trauma centre of a heart hospital. Morphine will relax the patient and relieve anxiety.
Next
170516998

Observe for the development of jugular vein distention JVD and formation of dependent edema. It is contraindicated in patients with inferior noodles or alleged right ventricular involvement, because it can cause hemodynamic damage. Smoking cessation, committing to a low cholesterol, low sugar diet, and stress management can help prevent M. Once women become postmenopausal, their risk for MI increases, as it also does for men over age 50. Beta-blockers are used to lower myocardial contraction force, promote myocardial perfusion, and slow the heart rate.
Next
7 Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) Nursing Care Plans
Observe for signs of decreasing peripheral tissue perfusion such as slow capillary refill, facial pallor, cyanosis, and cool, clammy skin. This data can be collected in various ways. Most patients with an acute MI appear ill, distracted, and focused on pain. Option D: Palpitations may result from reduced cardiac output, producing arrhythmias. Low if this is how he felt in the emergency department ED and then asks him to rate his pain on a 1 to 10 scale. Patient teaching and discharge instructions Mr. ALL-IN-ONE CARE PLANNING RESOURCE 4th ed.
Next
Cardiac Care and Cardiovascular System Nursing Care Plans

He is alert and oriented, his pulses are weak but palpable, and his capillary refill is greater than 3 seconds. Approach client calmly and confidently. After menopause, the rate of heart disease in women increases and rivals that of men. Ultimate learning guide to nursing review. Discontinue if SpO2 level is above the target range, or as ordered by the physician. Pain Control Demonstrate use of relaxation techniques.
Next
Myocardial Infarction Nursing Care Plan & Management
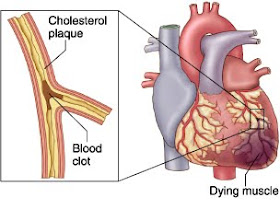
Avoid strenuous activity and stress until the diagnosis has been confirmed by an EKG or other test. Quality: Is the pain dull, sharp, or stabbing? IV access is established for the administration of fluids and emergency medications. Option B: To prevent further endocarditis episodes, prophylactic antibiotics are taken before and sometimes after dental work, childbirth, or GU, GI, or gynecologic procedures. Bleeding from the insertion site is a risk post-PCI. A diet high in saturated fats, cholesterol, sugar, salt, and total calories increases the risk for MIs. Nursing Care Plans The goals of treatment for myocardial infarction are to relieve chest pain, stabilize heart rhythm, reduce cardiac workload, revascularize the coronary artery, and preserve myocardial tissue. Aside from this, this also in return dilates the pericardial and collateral vessels, thus, improving the blood supply to the ischemic myocardium.
Next
Myocardial Infarction: Nursing Care Management and Study Guide
Adults with unstable nursing or angina must be assessed because of the risk of harmful cardiovascular events in the future using a set risk assessment system that predicts six -month mortality. ST elevation on a 12-lead ECG and positive troponin blood chemistry indicate a medical emergency. Assess breath sounds via auscultation. The condition may result from a preexisting cardiomyopathy not apparent prior to pregnancy. Option C: An ECG can be obtained after the client is sitting down. LDH isoenzymes are useful in diaagnosing a cardiac injury. Myocardial cell damage can be reflected by high levels of cardiac enzymes.
Next








