Obesity is a significant public health issue that affects individuals of all ages, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds. It is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, which is calculated by dividing a person's weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. Obesity is a serious condition that can have negative impacts on both physical and mental health.
One of the main causes of obesity is an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure. When a person consumes more calories than they burn, their body stores the excess energy as fat, which can lead to weight gain and eventually obesity. Factors that contribute to this imbalance include unhealthy diet choices, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medical conditions such as hypothyroidism.
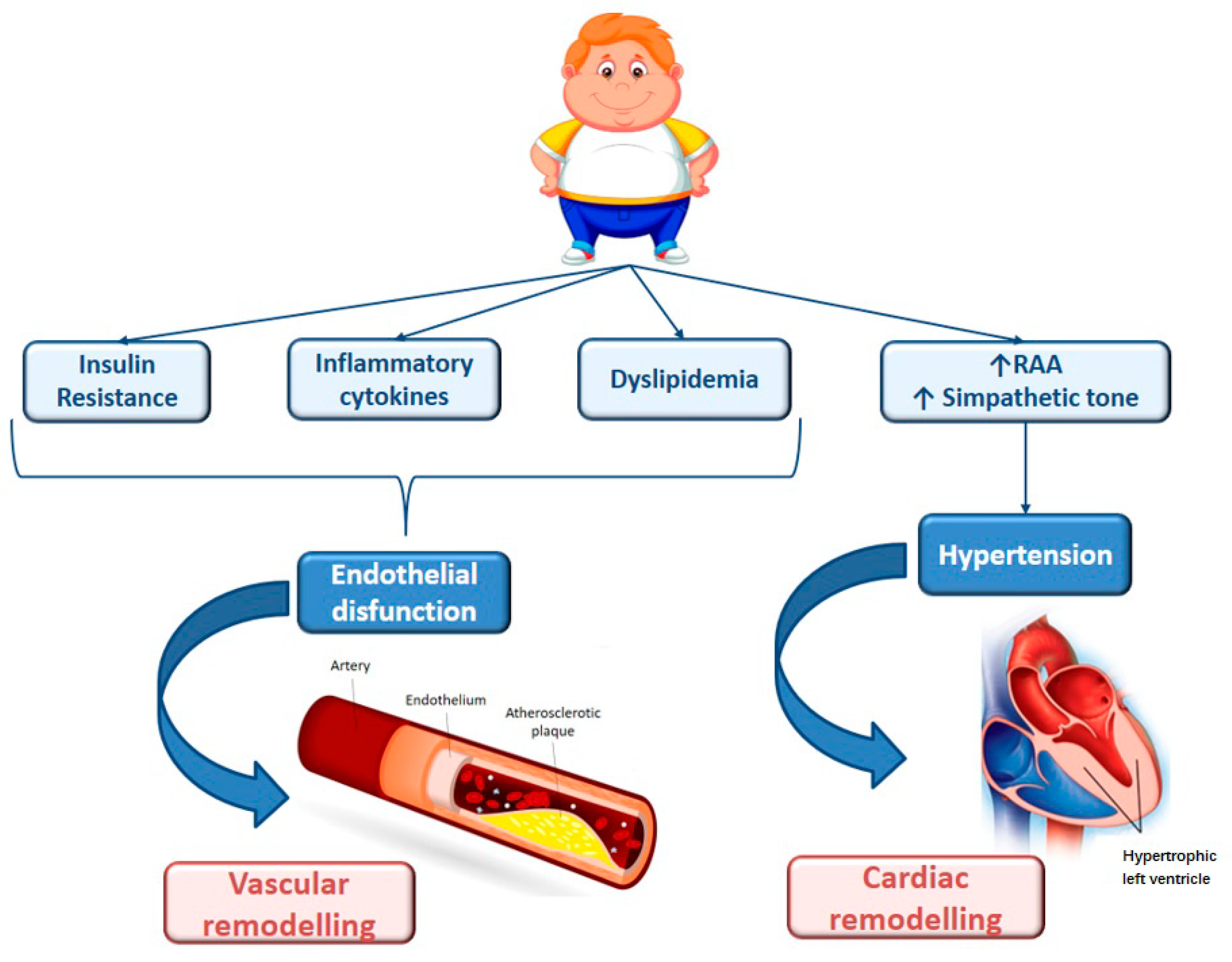
The consequences of obesity are numerous and can be severe. Physically, it can increase the risk of various health problems such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It can also lead to mobility issues and a decreased quality of life. Mentally, obesity can cause or exacerbate mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
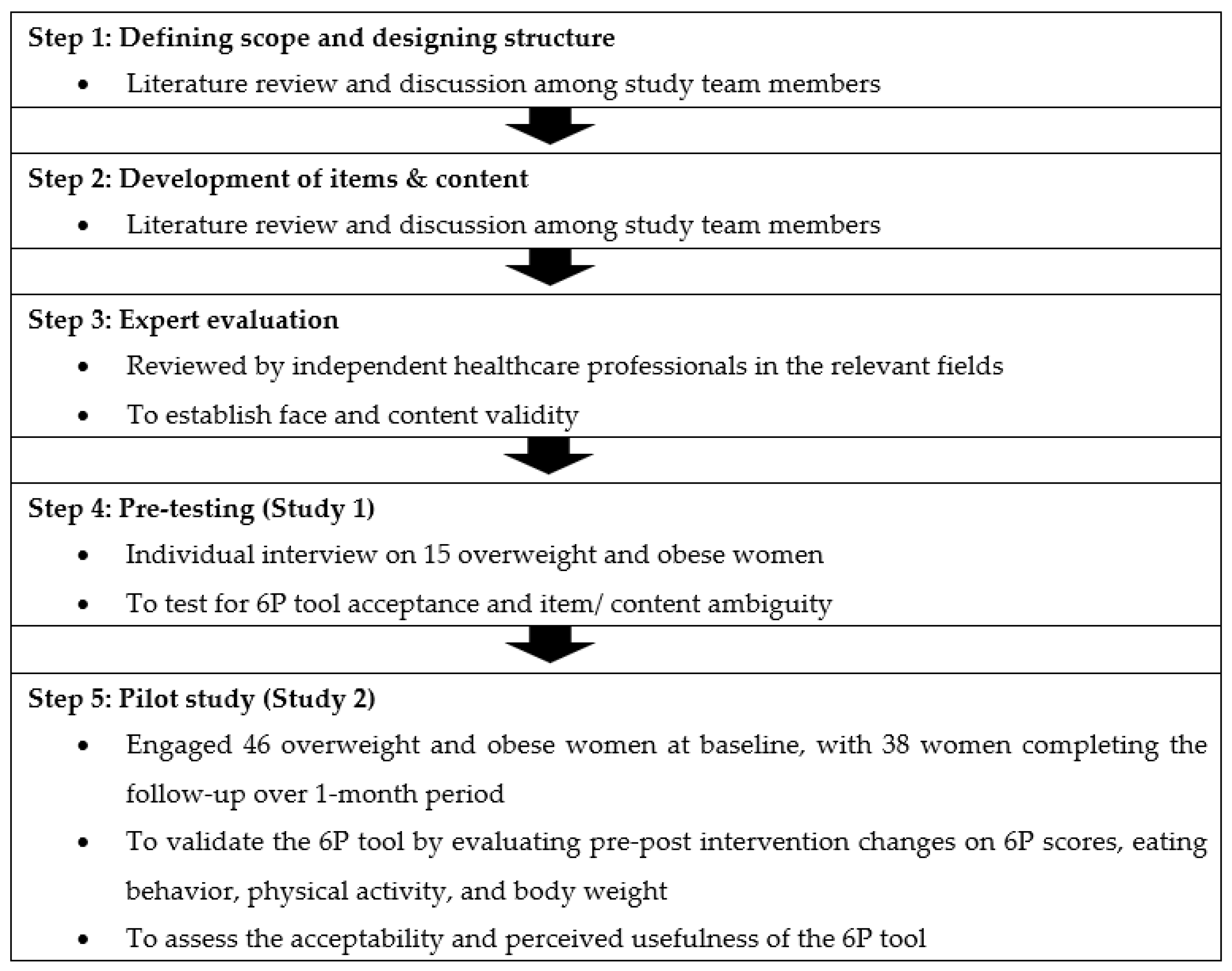
Preventing and treating obesity requires a multifaceted approach that includes individual and societal changes. At the individual level, this can involve making healthy diet and lifestyle choices, such as eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and getting enough sleep. At the societal level, this can involve creating environments that support healthy behaviors, such as providing access to healthy food options and promoting active transportation.
In conclusion, obesity is a significant public health issue that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. It is caused by an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure and can have severe consequences on physical and mental health. Preventing and treating obesity requires a multifaceted approach that involves individual and societal changes.