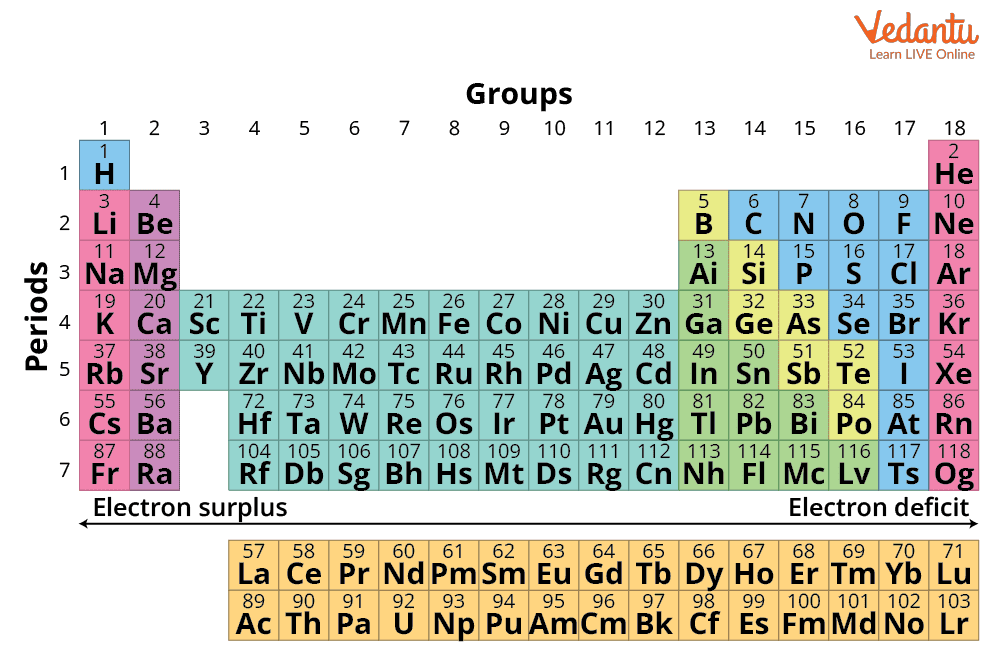A period in the periodic table is a horizontal row of elements. The periodic table is a chart that arranges all of the known chemical elements in an organized way. Each element is represented by a unique symbol, and elements are grouped together based on their similar properties.
One way that elements are grouped together is by their atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. As you move from left to right across the periodic table, the atomic number of the elements increases. This means that elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells, but a different number of protons in their nucleus.
There are seven periods in the periodic table, and each period contains elements with similar properties. For example, the first period contains the elements hydrogen, helium, and lithium, which are all light, reactive gases at room temperature. The second period contains elements such as beryllium, boron, and carbon, which are solid at room temperature and have very different properties from the elements in the first period.
As you move down a period, the elements become more metallic in nature, meaning they are good conductors of heat and electricity and have a shiny appearance. The elements in a period also tend to have similar chemical properties, such as the way they react with other elements.
Overall, the periodic table is a crucial tool for chemists and scientists, as it helps them to understand and predict the properties of different elements. By organizing elements into periods, scientists can better understand how different elements will behave and how they can be used in various applications.
What is a period on a periodic table?

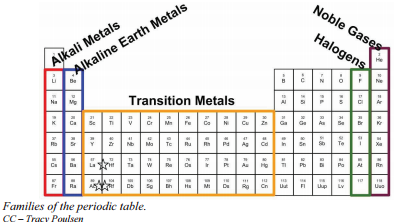
In simple words, electron affinity is the tendency of an atom to accept the electron. Firstly, I want to tell you one property of metals. And along the group, the Valency remains constant, because you know very well that the number of electrons in the outermost orbit remains the same for all the elements of the same group. Some arguments in favour of Sc-Y-La-Ac can still be encountered in the literature, but they are based on false premises or logical fallacies. All elements in a row have the same number of electron shells.
All Periodic Trends in Periodic Table (Explained with Image)

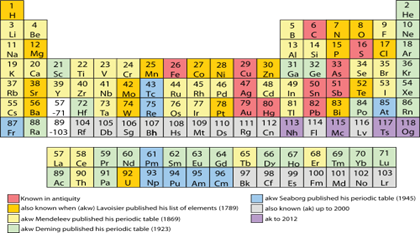
In other words, if the atomic size is less, then it will attract the electron pair and this is termed as Electronegativity. What are the 4 most common atoms? For example, the elements placed in the second period have two shells K, L. What are the 7 groups of the periodic table? So finally we can say that, less the size of atom, more will be the ionization energy energy required to remove the electron. In 1, where the superscript indicates the number of electrons in the subshell. Metallicity A simple substance is a substance formed from atoms of one chemical element. There are 18 groups, and there are 7 periods plus the Periods on the Periodic Table So what is a period on the periodic table? Period 1 has only two elements hydrogen and helium , while periods 2 and 3 have 8 elements.
Periods in Periodic Table (Explained with Images)
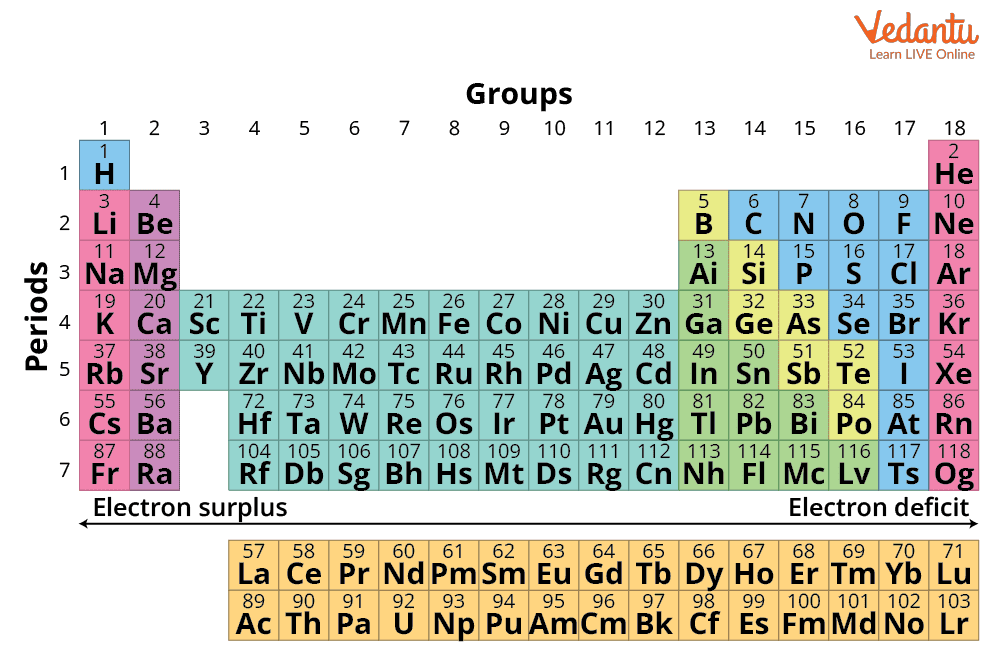
Elements of period 4 and period 5 are given in the tables below. Analogous arguments based on For transition metals, common oxidation states are nearly always at least +2 for similar reasons uncovering the next subshell ; this holds even for the metals with anomalous d x+1s 1 or d x+2s 0 configurations except for 4 , and then to +2 at the end. There are two different numbering systems that are commonly used to designate groups, and you should be familiar with both. In 1869 Russian chemist Group vs Period Groups are the columns of the periodic table, and periods are the rows. Group 13 Fact box Group 13 2077°C, 3771°F, 2350 K Period 2 4000°C, 7232°F, 4273 K Block p 2. There is eighteen groups on the periodic table in total, and each periodic table group contains elements with the same number of The number of valence electrons present dictates the properties of an element. Because of their similarities in their chemical properties, Mendeleev put these elements into the same group.
Period (periodic table)
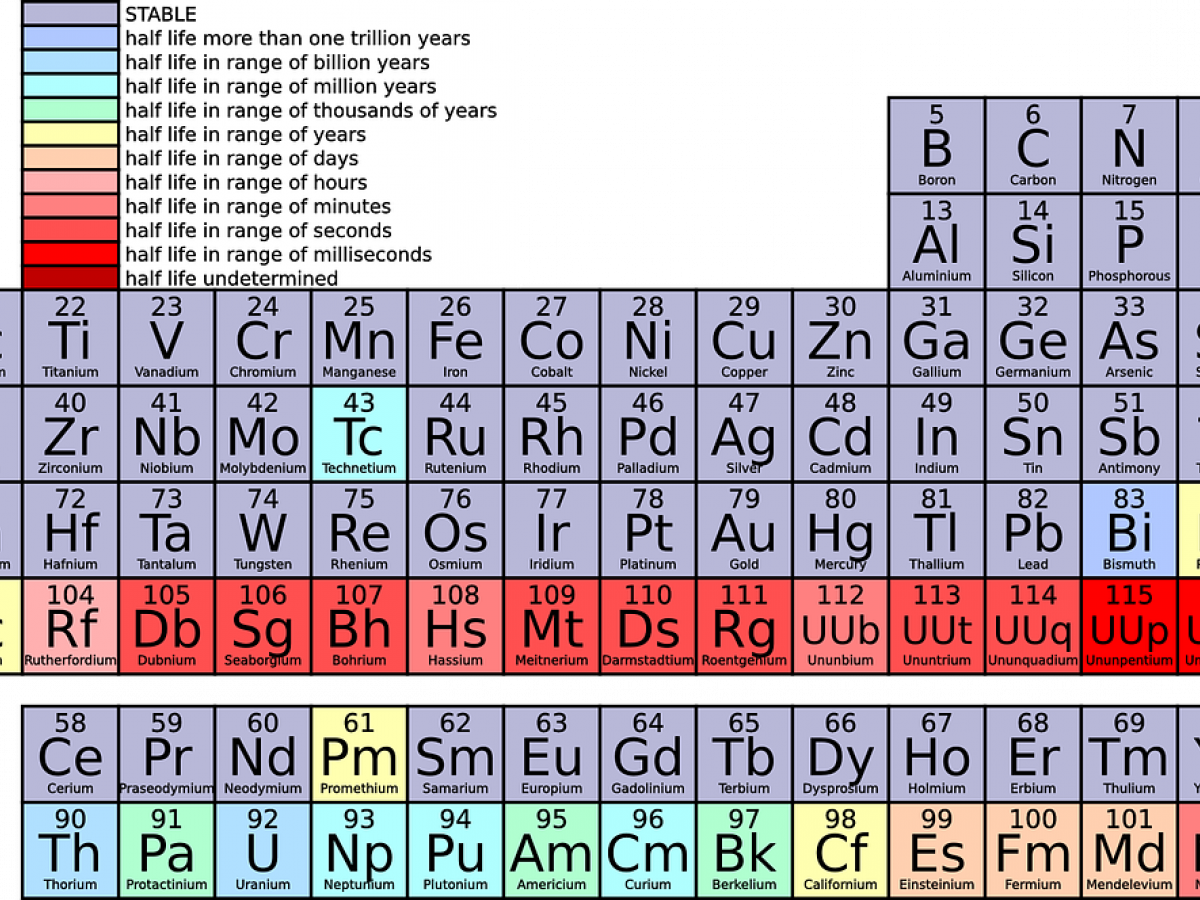
Period 4 elements have 4 energy shells while period 5 elements have 5 energy shells. The same pattern is true of other groups on the periodic table. Since the families of elements were organized by their chemical behavior, it is predictable that the individual members of each chemical family will have similar electron configurations. As it is in the first shell, this is called the 1s orbital. This is because the +, the outermost orbital which determines ionic radius is still 3s, so the hydration enthalpy is small and insufficient to compensate the energy required to remove the electron; but ionising again to Mg 2+ uncovers the core 2p subshell, making the hydration enthalpy large enough to allow magnesium II compounds to form. What is common for periods in periodic table? The 4d and 5d elements exists higher oxidation state than 3d elements. This is expected, as metallicity tends to be correlated with electropositivity and the willingness to lose electrons, which increases right to left and up to down.
2.3: Families and Periods of the Periodic Table
As these structures do not use all their orbitals for bonding, they end up with bonding, nonbonding, and antibonding bands in order of increasing energy. What do the periods have in common? When their outermost electrons are identical, they will be in the same group see Figure 2. For example, the group 1 elements are all soft, reactive metals. The elements lying in the same groups show similar chemical properties and they also have same number of valence electrons. They form either small molecules like hydrogen or oxygen, whose atoms bond in pairs or giant structures stretching indefinitely like carbon or silicon.