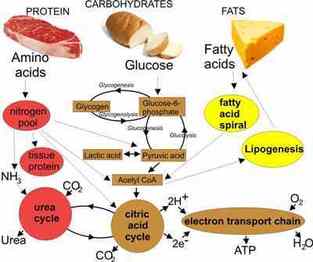
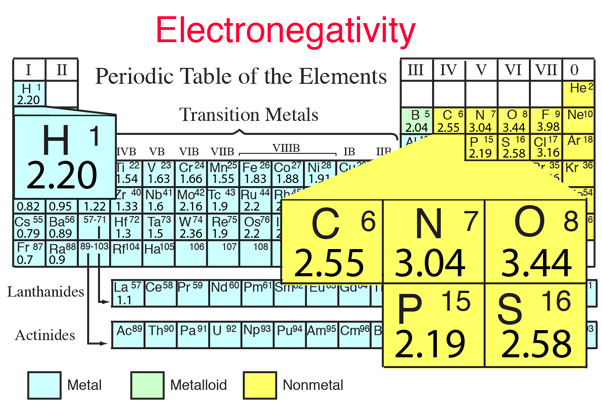
Organic molecules are the building blocks of life, and they play a crucial role in the functioning of living organisms. These molecules are composed of carbon and hydrogen, with smaller amounts of other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. They include a wide range of compounds, including carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Carbohydrates are a class of organic molecules that include sugars, starches, and fibers. They are an important source of energy for living organisms, as they can be broken down into simpler sugars such as glucose, which cells can use for energy. They also play a structural role in cells, serving as a component of cell walls and as a source of energy storage.
Lipids are another class of organic molecules that are important in living organisms. They include fats, oils, and waxes, and they serve as a source of energy, insulation, and protection for cells. They also play a role in the synthesis of hormones and other signaling molecules, as well as in the formation of cell membranes.
Nucleic acids are a class of organic molecules that include DNA and RNA. They carry the genetic information that is passed down from one generation to the next, and they play a crucial role in the process of protein synthesis. DNA stores the genetic information in the form of a code, while RNA carries that information to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
Proteins are another class of organic molecules that are important in living organisms. They are composed of chains of amino acids, and they play a wide range of roles in the body, including structural, catalytic, regulatory, and signaling. They serve as enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions, as structural elements of cells and tissues, and as hormones and other signaling molecules.
In conclusion, organic molecules are essential for the functioning of living organisms. They provide the energy and raw materials needed for growth and development, and they play a wide range of roles in the body, from structural support to catalyzing chemical reactions. Understanding the properties and functions of these molecules is essential for understanding the biology of living organisms.