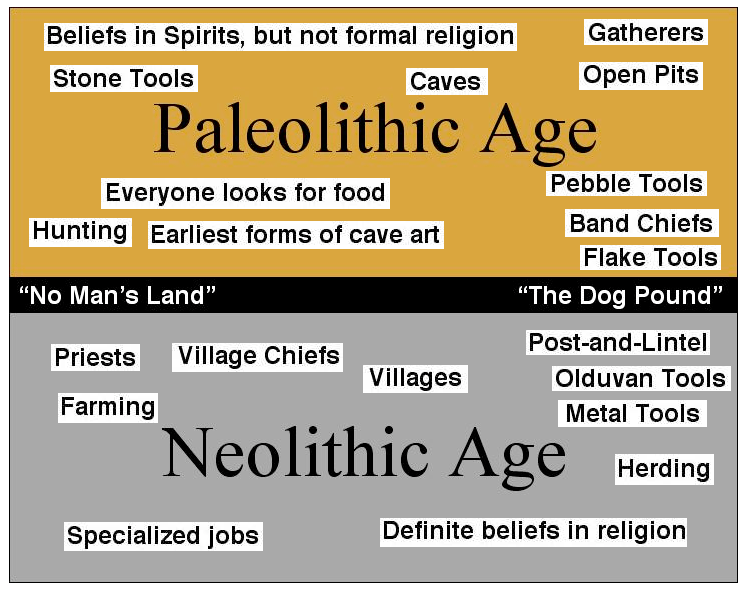
The Paleolithic and Neolithic periods were two significant phases in the development of human history. The Paleolithic, or "Old Stone Age," refers to the period of human history that lasted from approximately 2.5 million years ago to around 10,000 years ago. During this time, humans lived in small, nomadic groups and relied on hunting and gathering for their survival. They made and used simple tools, such as stone knives and spears, for hunting and foraging.
The Neolithic, or "New Stone Age," began around 10,000 years ago and lasted until around 3,000 years ago. This period saw the development of agriculture, the domestication of animals, and the creation of permanent settlements. As a result, Neolithic societies were more settled and less reliant on hunting and gathering for survival. They also made more advanced tools and developed more complex social and economic systems.
One key difference between the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods was the way in which people obtained their food. During the Paleolithic, humans were primarily hunters and gatherers, relying on the resources of their environment to sustain themselves. This meant that their diet was varied and included a wide range of plant and animal products. In contrast, during the Neolithic, people began to cultivate crops and domesticate animals, which allowed them to produce their own food and have a more reliable source of sustenance. This shift in food production had a significant impact on the way that Neolithic societies developed and organized themselves.
Another significant difference between the two periods was the level of technological advancement. During the Paleolithic, humans made simple tools and weapons using materials such as stone and bone. These tools were used for tasks such as hunting, skinning animals, and preparing food. In contrast, the Neolithic saw the development of more advanced tools, including pottery, weaving, and metallurgy. These innovations allowed people to create more complex and sophisticated products, and also facilitated the growth of trade and commerce.
In terms of social and cultural development, the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods also differed significantly. During the Paleolithic, humans lived in small, nomadic groups and had relatively simple social structures. In contrast, the Neolithic saw the development of more complex societies, with more advanced forms of social organization and governance. This was due in part to the development of agriculture and the resulting growth of permanent settlements. As people began to live in one place for longer periods of time, they needed to establish more formalized systems of governance and social organization in order to maintain order and ensure the survival of their communities.
Overall, the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods represent significant phases in human history, marked by significant changes in the way that people lived, obtained their food, and organized themselves. These changes had a lasting impact on the development of human societies and continue to shape the world we live in today.