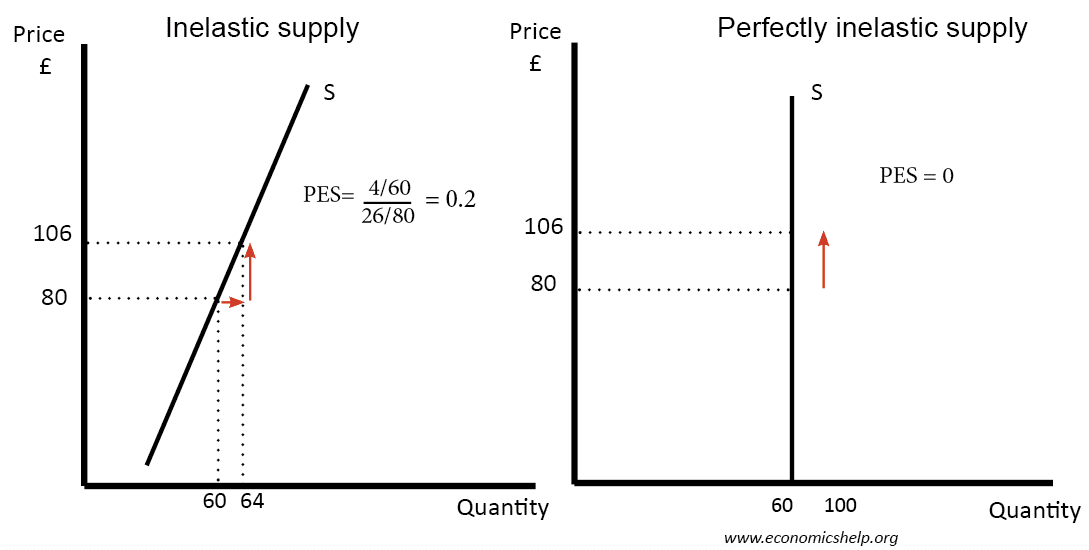
A perfectly elastic curve, also known as a vertical supply curve, is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity of that good or service that is available to be sold. In economics, the perfectly elastic curve is used to illustrate the concept of perfect elasticity, which refers to a situation in which the quantity of a good or service that is demanded is perfectly responsive to changes in its price.
One of the key characteristics of a perfectly elastic curve is that it is a straight, vertical line. This is because, in a perfectly elastic market, the quantity of a good or service that is available to be sold is not affected by changes in its price. For example, if the price of a particular good or service increases, the quantity of that good or service that is available to be sold will remain unchanged.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of a perfectly elastic curve in a particular market. One of the most important factors is the presence of a large number of substitutes for a particular good or service. If there are many substitutes available, consumers will be more likely to switch to a different product if the price of the original product increases. This will cause the quantity of the original product that is demanded to decrease significantly, leading to a perfectly elastic curve.
Another factor that can contribute to the development of a perfectly elastic curve is the presence of a large number of buyers and sellers in a particular market. If there are many buyers and sellers, the market will be more competitive, which can help to keep prices low and make it easier for consumers to find substitutes for a particular good or service.
There are a few key implications of the perfectly elastic curve for businesses and policymakers. First, it is important to note that the perfectly elastic curve is relatively rare in real-world markets. However, understanding the concept of perfect elasticity can be helpful for businesses and policymakers in analyzing and understanding the behavior of certain markets.
For businesses, the perfectly elastic curve can be used as a benchmark for understanding the elasticity of demand for their products. If the demand for a particular product is highly elastic, it may be more difficult for a business to increase the price of that product without experiencing a significant decrease in demand. On the other hand, if the demand for a product is relatively inelastic, a business may have more flexibility to increase prices without experiencing a significant decrease in demand.
For policymakers, understanding the concept of perfect elasticity can be helpful in designing policies that are intended to affect the demand for particular goods or services. For example, if a policy is aimed at reducing the demand for a particular product, it may be more effective if the demand for that product is highly elastic. On the other hand, if the demand for a product is relatively inelastic, it may be more difficult to effectively reduce demand through policy measures.
In conclusion, the perfectly elastic curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity of that good or service that is available to be sold. It is characterized by a straight, vertical line and is used to illustrate the concept of perfect elasticity, which refers to a situation in which the quantity of a good or service that is demanded is perfectly responsive to changes in its price. Understanding the concept of perfect elasticity can be helpful for businesses and policymakers in analyzing and understanding the behavior of certain markets.