Diorite is an intermediate igneous rock that is found in many parts of the world. It is a coarse-grained rock, meaning that it is composed of larger mineral grains than other types of rocks, such as basalt or granite. Diorite has a number of physical properties that make it unique and distinguish it from other types of rocks.
One of the most notable physical properties of diorite is its color. Diorite is typically gray or black in color, although it can also be found in shades of green, pink, or brown. The color of diorite is determined by the minerals that make up the rock, with dark minerals such as hornblende and pyroxene giving it a darker appearance.
Another important physical property of diorite is its density. Diorite is a relatively dense rock, with a specific gravity of 2.8 to 3.3. This means that it is slightly heavier than most other types of rocks, such as granite or sandstone. The high density of diorite is due to the minerals that make up the rock, which are typically denser than the minerals found in other types of rocks.
Diorite is also known for its durability and strength. It is a hard rock that is resistant to weathering and erosion, making it a popular choice for building materials and landscaping. It is also resistant to heat and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for use in ovens and fireplaces.
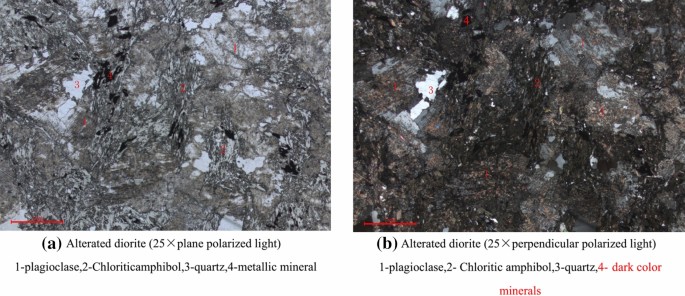
In terms of its mineral composition, diorite is composed primarily of plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene, and hornblende. It may also contain other minerals such as quartz, biotite, and muscovite. The combination of these minerals gives diorite its unique physical properties, such as its color, density, and strength.
Overall, diorite is a distinctive and valuable rock that is used in a variety of applications due to its physical properties. Its durability, strength, and resistance to weathering and heat make it an ideal choice for a wide range of uses, from construction and landscaping to decorative uses in art and jewelry.