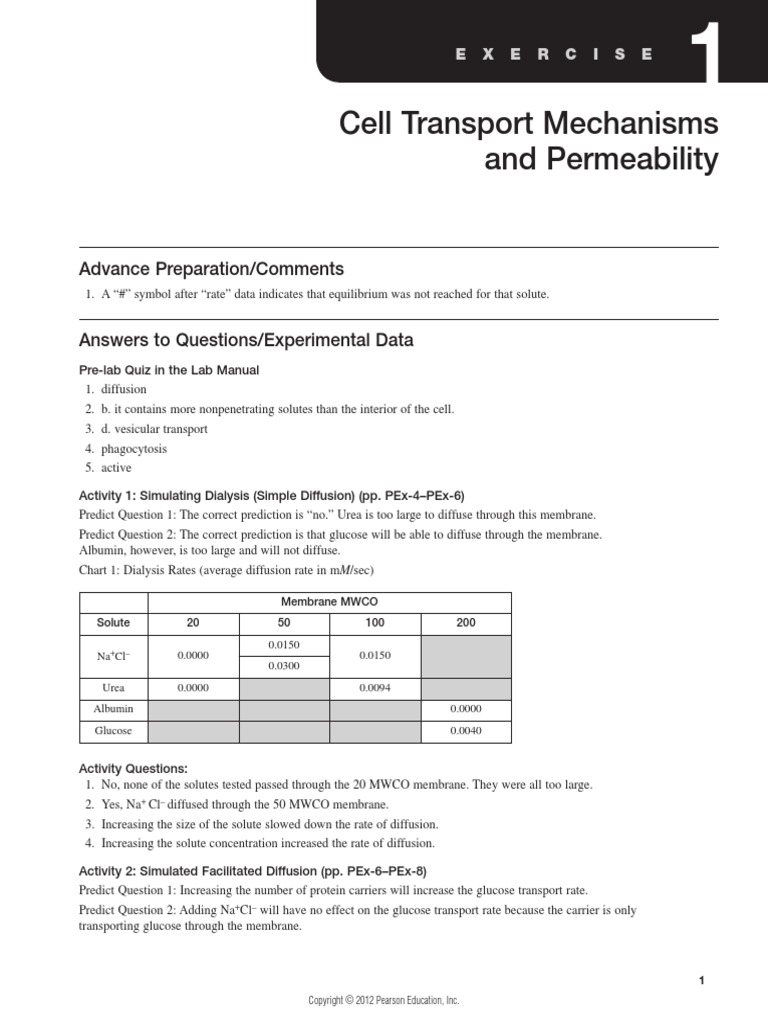
Physioex exercise 12 is a laboratory exercise that focuses on serological testing, which is a type of laboratory test that involves the use of antibodies to identify specific proteins or substances in a sample. Serological testing is often used in the diagnosis of infections, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions that involve the production of antibodies.
In this exercise, students are introduced to several different types of serological tests, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), Western blotting, and agglutination tests. These tests are all based on the principle of antigen-antibody reactions, in which a specific protein or substance in a sample (the antigen) reacts with a specific antibody produced by the body.
One of the key concepts in this exercise is the use of controls, which are samples that are used to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test results. For example, a negative control is a sample that is known to be free of the antigen being tested for, while a positive control is a sample that is known to contain the antigen. The use of controls helps to confirm that the test is working properly and that the results are not due to some other factor.
Another important concept in this exercise is the use of reagents, which are substances used in the testing process to detect or measure specific substances in a sample. Reagents can include enzymes, dyes, and other chemicals that are used to visualize or quantify the presence of a specific substance.
Overall, the goal of physioex exercise 12 is to provide students with a hands-on understanding of how serological testing works and how it is used in the diagnosis of various conditions. By performing the various tests and analyzing the results, students can gain a deeper understanding of the principles behind serological testing and how it is used in the field of medicine.