Physiological motives. 8 Examples of Physiological Needs (Maslow’s Hierarchy) 2023-01-02
Physiological motives
Rating:
9,1/10
485
reviews
Coparcenary is a term that is commonly used in Hindu law and refers to a system of joint ownership and inheritance. It is a type of joint family system that is traditionally found in India, Nepal, and other countries where Hindu law is followed.
In a coparcenary system, property is owned jointly by all the members of a family, and each member has an equal right to inherit and manage the property. This system is different from the Western concept of individual ownership, where property is owned by a single person or entity and can be inherited by their heirs.
The coparcenary system is based on the principle of ancestral property, which means that property is passed down through the generations within the family. Under this system, property is not divided among the heirs, but rather is held in common by all the members of the family. This system is intended to promote unity and cooperation within the family, as all members have a stake in the property and a responsibility to maintain and manage it.
There are several key features of the coparcenary system in Hindu law. First, it is based on the principle of joint ownership, which means that all members of the family have an equal right to the property. Second, it is based on the principle of ancestral property, which means that property is passed down through the generations within the family. Third, it is based on the principle of joint management, which means that all members of the family have a responsibility to manage and maintain the property.
In recent years, there have been efforts to reform the coparcenary system in order to address some of its perceived shortcomings. For example, some have argued that the system is unfairly biased against women, as women are not traditionally considered coparceners and therefore do not have the same rights to inherit and manage property. However, despite these criticisms, the coparcenary system remains a significant and influential part of Hindu law and continues to be followed by many families in India and Nepal.
What is psychological motives in psychology?

How we eat, when we eat, what we eat is determined by the group in which we have been brought up. Punishment informs the individual that his response is not correct. Similar to opioids, cocaine is extracted from a South American plant- the coca plant- and produces feelings of energy and euphoria. These types of needs are hardwired into our brain telling us we need them to survive. The Warmth and Colddrive means the need to be comfortable with the temperature in the environment. Thus, we see that even in prison and solitary confinement, toilets are provided for the prisoners. Say you are washing your hair and get shampoo in your eye.
Next
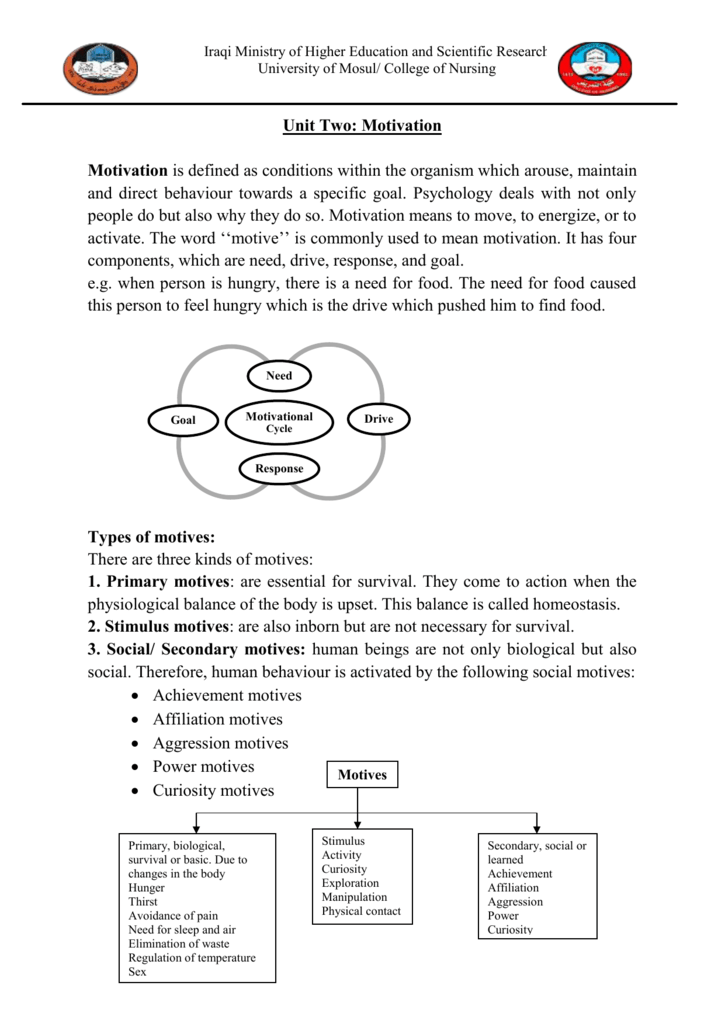
Concept of Motivation: Meaning & Importance
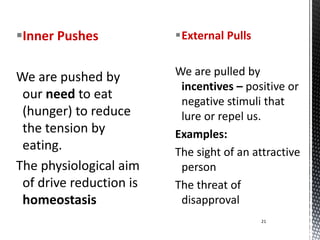
What does this mean? Hence, we can conclude that achievement is not a physiological motive. Not getting enough exercise can lead to obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. More commonly, cannabis has been known to have stimulant and depressive effects, thus classifying itself in a group of its own due to the many different effects of the substance. Module Recap Module 14 presented you with a second way that internal forces motivate behavior. . Pain Reduction Hunger and thirst signal something we want more of, but pain reduction signals when we want to get far away from something. Many psychologists use a biopsychosocial model to understand sexual orientation.
Next
What are basic Types of Motivation? Physiological, Psychological & Social

Hunger The biological drive of hunger, or desiring to eat, relates to the end of this motivated behavior once we are full, called satiety. If you wish to see the entire module, please visit: 14. If you eat a salty meal, you experience the first type called intracellular thirst. Self-assertion also takes the form of domination. Body temperature can be affected by having a fever, working out, using drugs, digesting food after dinner, or drinking alcohol. The key psychological factors to understand when considering consumer behavior are motivation, perception, attitudes and beliefs, along with lifestyle. According to the 2015 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, approximately 70% of individuals drank an alcoholic beverage in the last year and nearly 56% of individuals drank an alcoholic beverage in the past month SAMHSA, 2015.
Next
8 Examples of Physiological Needs (Maslow’s Hierarchy)

What is physiological motive? Even people that live in the most remote areas of the world wear some kind of clothing. Sex Sexual behavior is an interesting type of motivated behavior as it is not needed for survival in the same sense as hunger or thirst but is needed for reproduction and continuation of the species. This is a theory of psychological health predicated on fulfilling innate human needs in priority, culminating in self-actualization. In rare cases, individuals develop psychotic symptoms or schizophrenia following cannabis use Donoghue et al. Another sociocultural view on substance abuse is stressful life events, particularly those related to financial stability. Considerations about career aspirations or long-term goals are simply put on the shelf until these fundamental needs are met. More specifically, recent consumption of food, particularly food high in fat and carbohydrates, slows the absorption rate of ethyl alcohol, thus reducing its effects.
Next
Module 14: Motivation and Physiological Psychology

The thermostat compares the ideal temperature to the actual temperature. Currently, the most common amphetamines are prescription medications such as Ritalin, Adderall, and Dexedrine prescribed for sleep disorders. This is a basic physiological need because it helps to keep the body clean and healthy. Understanding these factors will assist any marketer in understanding the behavior of their consumers in order to successfully appeal to them. However, these symptoms will disappear when normal sleep and rest is taken.
Next
18 Physiological Needs Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy) (2022)
For example, people who live close to the equator generally have less need for clothing than those who live further away. The body need to restore it making the stomach hungry for food. When a man feels that he is not needed by anybody, when nobody wants him, nobody loves him, he feels that life is not worth living. These incentives aid the learning process. Definition of Physiological Needs These are biological needs required to preserve human life.
Next
physiological motive

Of course, even this periodicity may be affected by social influences. Thus we find that dominance-submission behaviour is not peculiar to the human beings. Substance intoxication symptoms vary greatly and are dependent on the type of substance ingested. Low motivation can be remedied with activities that increase dopamine output, like physical exercise, behavioral activation, mindfulness, psychotherapy, and for some, medication. In India also, a new system of awards for distinction has been developed.
Next
Psychological Motives and Psychological Needs

What are biological influences? For example, the ringing of the bell may be used as a punishment if it is rung whenever there is an error. Increased discussion about the effects of marijuana use, as well as psychoeducation about substance abuse in general is important in preventing marijuana use during adolescence. Incomes are taxed and inheritance of wealth is taxed. Pain reduction is an important concept of motivation because who likes pain? What is the study of motivation in psychology? It is well known that there are rivalries based on the need for recognition not only among the individuals but also among groups. There are different physiological drives or motives that are inborn and present at birth. We looked at addiction from the perspective of clinical psychology and you could re-examine the process of change, and what DiClemente had to say, from Module 6.
Next
What is a biological motive in psychology? [Updated!]
Going back to our discussion of behavioral change from Module 6, if we are trying to get in shape by reducing our caloric intake, we need to take into consideration temptations that could lead us to engage in undesirable or problem behavior. The biological need turns into a psychological motive when the drive to satisfy it interferes with our normal functioning by causing us to feel increasing tension until the need is satisfied. This is because our bodies need to move in order to stay healthy. Each person has a goal, a wish, a purpose in life to achieve and succeed. Activation involves the decision to initiate a behavior, such as enrolling in a psychology class.
Next







