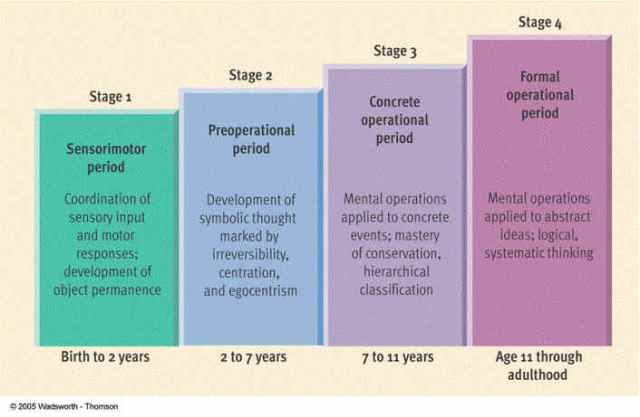
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on the cognitive development of children. He proposed that children go through four stages of cognitive development, the final of which is the operational stage. This stage typically occurs during the school-age years, from around 7 to 11 years of age.
During the operational stage, children develop the ability to think logically and systematically. They are able to perform mental operations, such as classifying, seriating, and reasoning through problems. They also begin to understand abstract concepts, such as time and quantity, and can engage in hypothetical thinking.
One key characteristic of the operational stage is the development of the ability to conserve. This refers to the understanding that certain physical characteristics, such as volume or mass, remain the same even if the appearance of an object changes. For example, a child in the operational stage will understand that a lump of clay will still have the same mass even if it is shaped into a different form.
In addition to the development of logical thinking, the operational stage is also marked by the emergence of egocentrism. This is the tendency to view the world from one's own perspective and to believe that others see things the same way. While this can be helpful in understanding and predicting the actions of others, it can also lead to misunderstandings and conflicts.
One way that Piaget's theory of cognitive development has been influential is in the field of education. His work has helped educators to understand the cognitive abilities of children at different ages and to design age-appropriate activities and tasks. For example, an educator may use Piaget's theory to create activities that challenge a child's ability to perform mental operations and think abstractly, rather than providing tasks that may be too simple or too difficult for the child's level of development.
Overall, the operational stage is an important part of Piaget's theory of cognitive development and is marked by the emergence of logical thinking, the ability to perform mental operations, and the understanding of abstract concepts. It is a critical period in a child's development and has significant implications for education and child development more broadly.