Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky were two influential psychologists who developed theories on the development of children's cognitive abilities. While both theories have had a significant impact on our understanding of child development, they differ in several important ways.
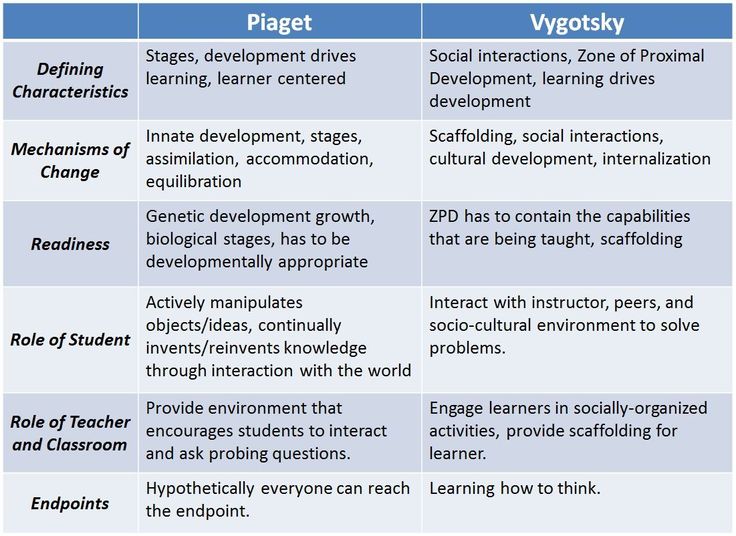
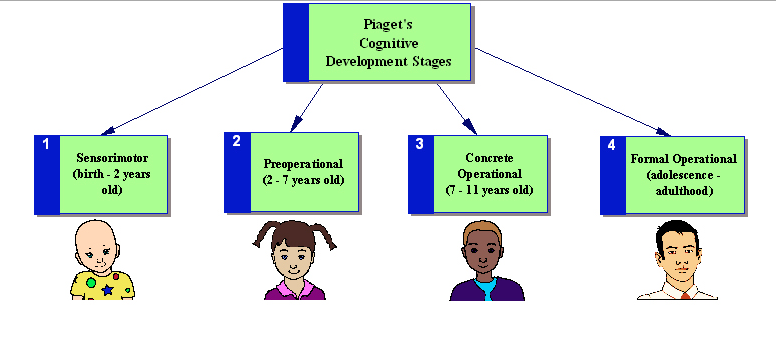
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist who is best known for his work on the cognitive development of children. He proposed that children go through a series of stages as they develop their cognitive abilities, and that each stage is characterized by a different set of cognitive processes. Piaget believed that children are born with a basic set of mental structures that allow them to process information and make sense of the world around them. As children interact with their environment, these mental structures are refined and developed, leading to increasingly sophisticated cognitive abilities.
Piaget's theory emphasizes the role of children in their own development. He believed that children actively construct their understanding of the world through their own experiences and interactions with their environment. According to Piaget, children are not passive learners, but rather they are active explorers who are constantly seeking out new information and experiences.
Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist who developed a theory of cognitive development that focused on the role of social interaction in child development. Vygotsky believed that children learn best through social interaction with more skilled individuals, such as parents, teachers, and peers. He called this process "scaffolding," and believed that it was essential for children to develop higher-level cognitive skills.
Vygotsky's theory emphasizes the importance of language and culture in cognitive development. He believed that children learn through communication and interaction with others, and that language is a key tool for this process. Vygotsky also believed that culture plays a significant role in cognitive development, as it provides children with a shared set of meanings and understandings that they can use to make sense of the world.
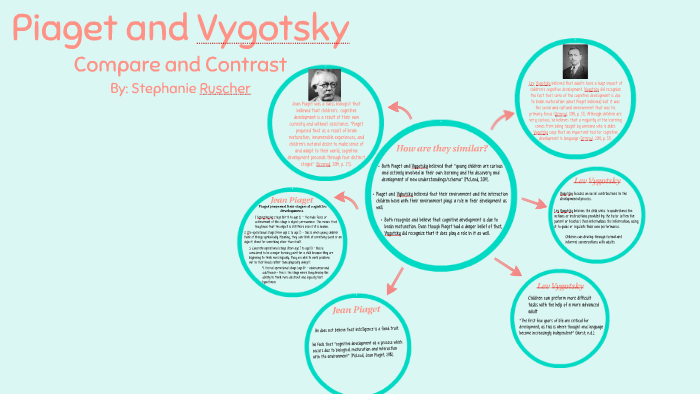
While both Piaget and Vygotsky's theories have had a lasting impact on our understanding of child development, they differ in several important ways. Piaget's theory is more focused on the individual child and their internal cognitive processes, while Vygotsky's theory emphasizes the role of social interaction and language in cognitive development. Additionally, Piaget's theory is more linear, with children moving through a series of predetermined stages, while Vygotsky's theory is more flexible and allows for more individual variation in the development process.
Overall, both Piaget and Vygotsky's theories have contributed important insights into the cognitive development of children. While they differ in their emphasis and approach, they both provide valuable frameworks for understanding how children acquire and use knowledge and skills as they grow and develop.