A duty of care is a legal obligation that is imposed on an individual or organization to take reasonable measures to protect the safety and well-being of others. This duty is owed to anyone who may be affected by the actions or inactions of the individual or organization.
For example, a doctor has a duty of care to their patients to provide an appropriate standard of care and treatment. This means that the doctor must take reasonable steps to diagnose and treat the patient's medical condition, and must act in the patient's best interests. If the doctor fails to meet this duty of care and the patient is injured as a result, the doctor may be held liable for medical negligence.
Similarly, a company has a duty of care to its employees to ensure that the workplace is safe and free from hazards. This means that the company must take reasonable steps to assess and manage risks, and must provide appropriate training and protective equipment to employees. If the company fails to meet this duty of care and an employee is injured or becomes ill as a result, the company may be held liable for a breach of duty.
The duty of care also extends to the general public. For example, a property owner has a duty of care to ensure that their property is safe for visitors. This means that the property owner must take reasonable steps to identify and fix any hazards, such as broken steps or loose railings. If the property owner fails to meet this duty of care and a visitor is injured as a result, the property owner may be held liable for a breach of duty.
In summary, the duty of care is a legal obligation that requires individuals and organizations to take reasonable measures to protect the safety and well-being of others. This duty is owed to anyone who may be affected by the actions or inactions of the individual or organization, and failure to meet this duty can result in legal liability.
Metabolism of aromatic amino acids, PKU/ albinism; catabolism of branched chain Flashcards

The disease is not detectable by physical examination at that time, because no damage has yet been done. Most often, PKU is passed to children by two parents who are both carriers of the changed gene, but don't know it. The provider will likely order an eye exam and closely follow any changes in your child's skin color and vision. Overview What is phenylketonuria PKU? Complications Albinism can include skin and eye complications. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Overview Phenylketonuria fen-ul-key-toe-NU-ree-uh , also called PKU, is a rare inherited disorder that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body.
Phenylketonuria

Complications Untreated PKU can lead to complications in infants, children and adults with the disorder. Without the enzyme necessary to break down phenylalanine, a dangerous buildup can develop when a person with PKU eats foods that contain protein or eats aspartame, an artificial sweetener. Nam risus ante, dapibus a molestie consequat, ultrices ac magna. Such patients also suffer from vision problems. Healthcare providers confirm a diagnosis of phenylketonuria PKU shortly after birth as part of routine newborn screening via a blood test.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)

Babies born to women with high phenylalanine levels don't often inherit PKU. Fusce dui lectus, congue vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio. Electroencephalography EEG , computed tomography of the brain CT , phoniatric and audiologic evaluations were also done. Before becoming pregnant or during your first prenatal examination, you can ask your doctor about testing called carrier screening to determine if you and your partner are at risk for having a child with PKU. Symptoms of infants with classical untreated PKU include: severe mental retardation and developmental delays, musty or "mousy" urine, skin, and , and hair odor due to accumulation of phenylacetate autistic symptoms, hyperactivity and gait abnormalities, loss of motor response, pale-skin, and white blonde hair with blue eyes A two-old baby was kept in the intensive care unit in a pediatric ward due to unexplained clinical problems. This is called autosomal recessive inheritance.
Phenylketonuria Alkaptonuria Albinism
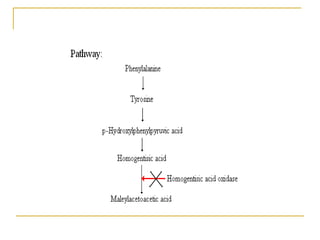
They have a 50% chance of having an unaffected child who also is a carrier middle. Nelson essentials of pediatrics. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. For those who are on a restrictive diet, many people benefit from working closely with a dietician who can advise on the best foods to eat, what to avoid and how to get all the nutrients you need to stay healthy. When low phenylalanine levels are maintained for the duration of pregnancy, there are no elevated levels of risk of birth defects compared with a baby born to a non-PKU mother. Types of phenylketonuria with their defects Types of PKU Defects Classic phenylketonuria or Hyperphenylalaninemia type-I Defect in phenylalanine hydroxylase Atypical phenylketonuria or Hyperphenylalaninemia type-II and III Defect in dihydrobiopterin reductase Hyperphenylalaninemia type-IV and V Defect in dihydrobiopterin synthesis Cause PKU is an inherited condition and is caused by a defective PAH gene. Archives of Disease in Childhood.
[Solved] PKU and albinism are two autosomal recessive traits. If two people...
Fusce dui lectus, congue vel laoreet ac, dictum vitae odio. The enzyme defective in the baby is A. Children presented to the Pediatric Department, or Pediatric Neurology Clinic, Sohag University Hospital in whom the diagnosis of Pheylketonuria was established based on measuring phenylalanine level in blood samples were eligible for this study. Tyrosinosis: Accumulation of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid usually leads to an enlargement of the liver and spleen. Using the term "person with albinism" is preferred to avoid the negative impact of other terms.








