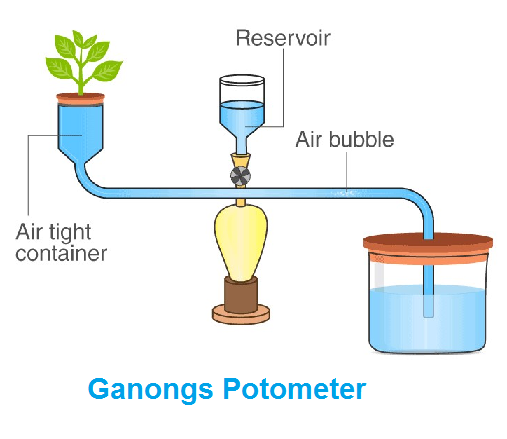
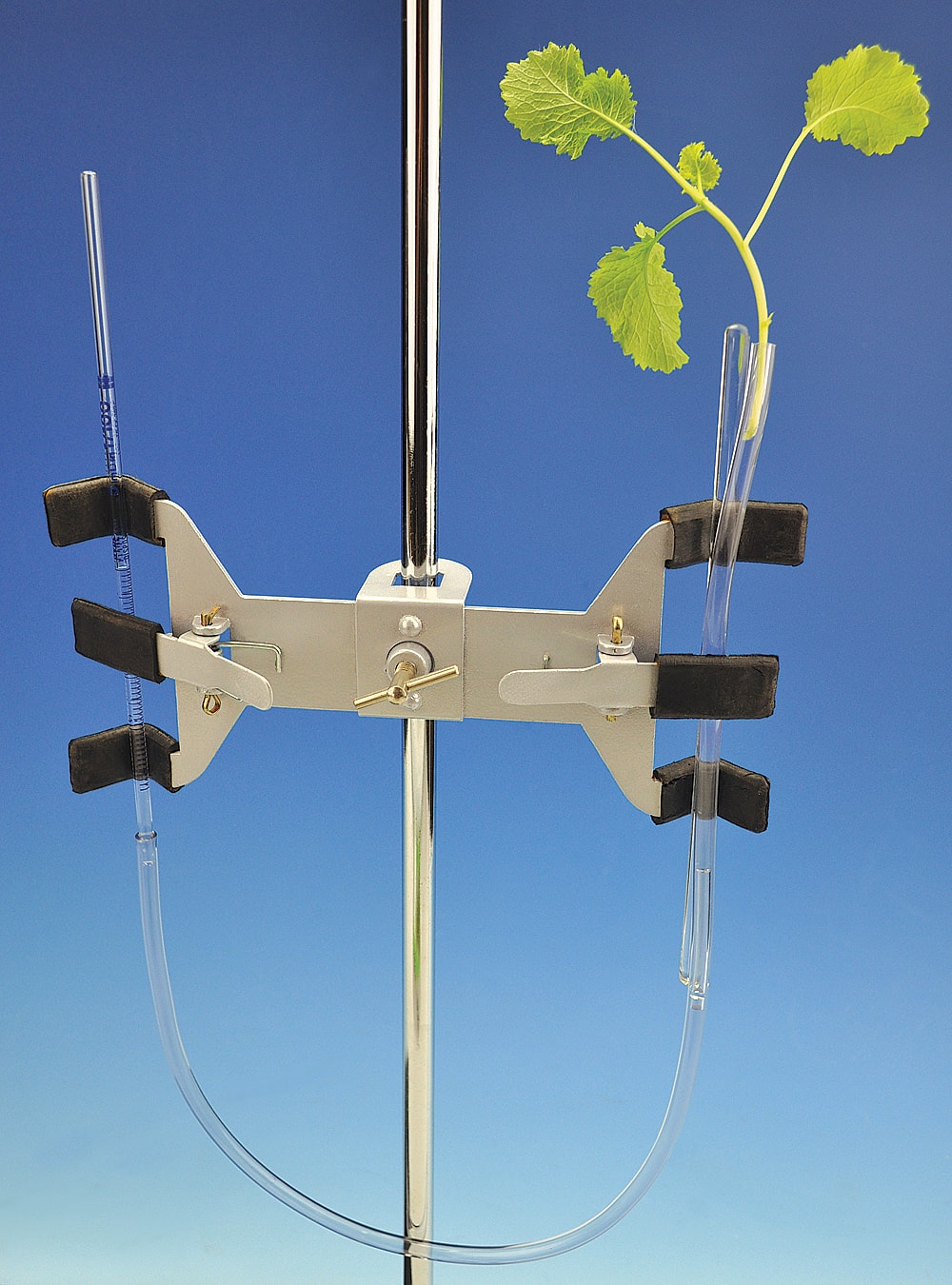
A potometer, also known as a transpiration apparatus, is a device used to measure the rate of transpiration in plants. Transpiration is the process by which water is evaporated from a plant's leaves and stem, and the potometer allows scientists to quantify this process.
To use a potometer, a small branch or stem from a plant is placed in a container of water and sealed with a rubber stopper. A tube is then attached to the stem, and a scale or ruler is used to measure the movement of the water through the tube as the plant transpires.
There are several factors that can affect the rate of transpiration in a plant, including humidity, temperature, and light intensity. By measuring the rate of transpiration in a controlled environment, scientists can determine how these factors affect the plant's water uptake and overall health.
One common application of potometers is in studying the effects of air pollution on plants. By exposing plants to various levels of pollutants and measuring their transpiration rates, scientists can gain insight into how pollution affects plant growth and health.
Potometers can also be used to study the effects of different watering regimes on plant growth. By watering plants at different intervals and measuring their transpiration rates, scientists can determine how much water a plant needs to thrive.
In addition to their scientific applications, potometers can also be used in educational settings to teach students about plant physiology and the importance of water in plant growth. By conducting experiments and measuring transpiration rates, students can gain a deeper understanding of how plants function and the role that water plays in their survival.
Overall, the potometer is a valuable tool for studying plant physiology and the factors that affect plant growth and health. It allows scientists to quantify the process of transpiration and provides insight into how plants interact with their environment.