King Ashoka the Great was an Indian emperor who ruled from 273 to 232 BCE. He is remembered for his military conquests, as well as for his efforts to spread Buddhism and promote nonviolence throughout his empire. Ashoka is often depicted in various images as a powerful, wise, and compassionate ruler.
One common image of Ashoka is that of a strong, imposing figure. He is often depicted with a muscular build and a regal bearing, symbolizing his power and authority as a ruler. This portrayal is further emphasized by his royal attire, which often includes ornate robes, crowns, and other symbols of his status.
Another image of Ashoka that is commonly seen is that of a wise and thoughtful ruler. This is often depicted through images of Ashoka seated on a throne, with a calm and contemplative expression on his face. In these depictions, Ashoka is often shown surrounded by advisors or scholars, symbolizing his interest in learning and his desire to seek out the best counsel for his empire.
A third image of Ashoka that is often seen is that of a compassionate and caring ruler. In these depictions, Ashoka is often shown surrounded by the people of his empire, with a compassionate expression on his face. This image is meant to convey Ashoka's concern for the well-being of his subjects, and his desire to see them thrive and prosper.
Overall, the images of King Ashoka the Great that have been passed down through the ages convey a sense of his power, wisdom, and compassion. These qualities, combined with his efforts to promote Buddhism and nonviolence, have made Ashoka a beloved and revered figure in Indian history.
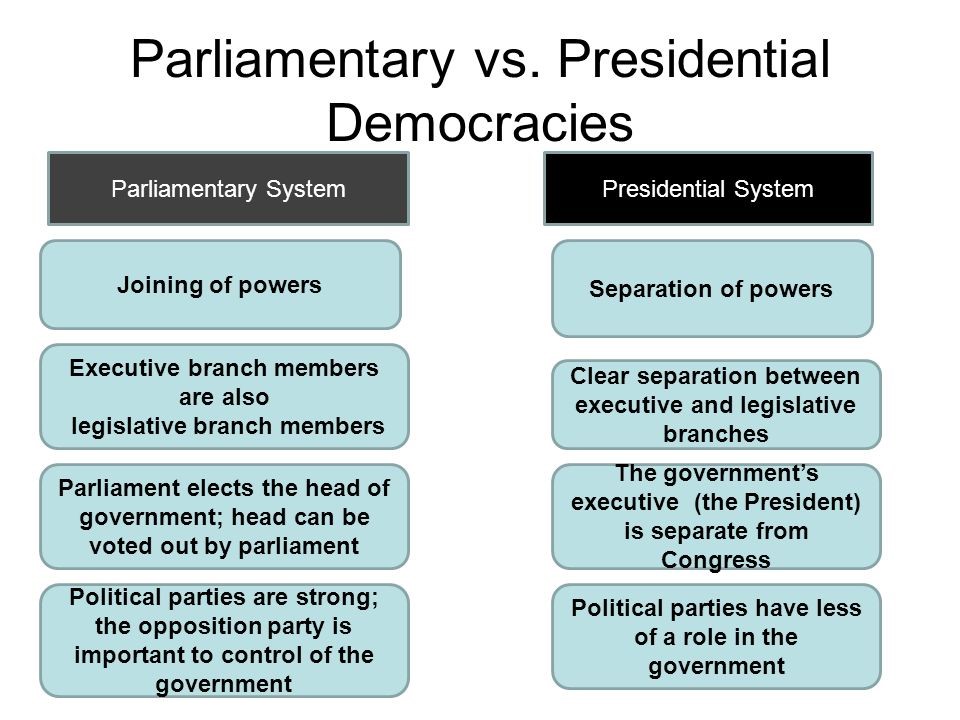
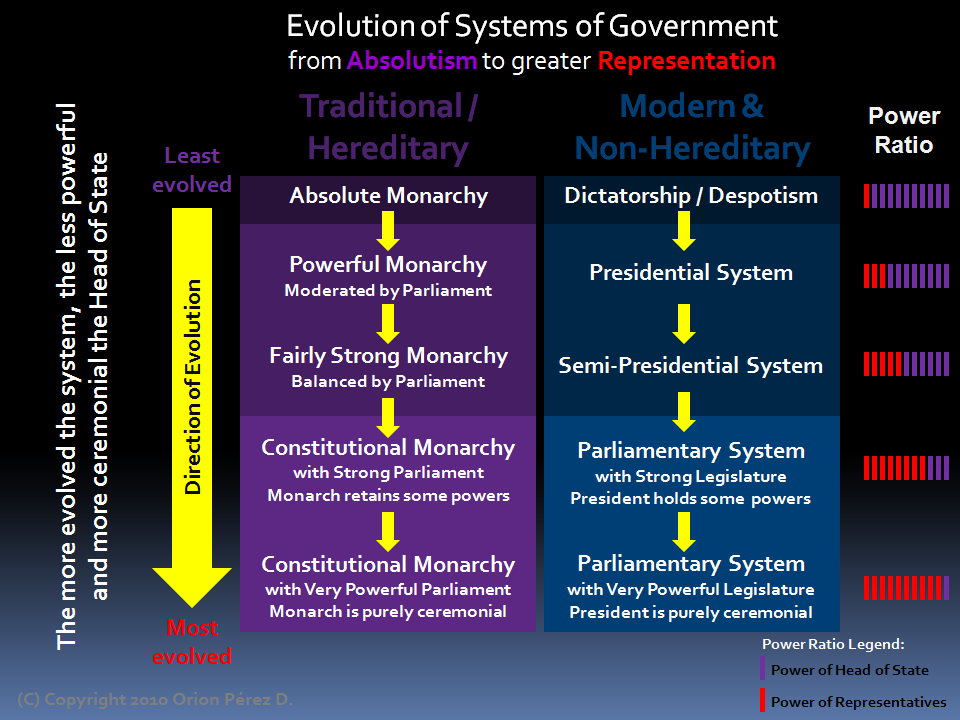
The presidential and parliamentary systems of government are two distinct forms of democracy that are used by different countries around the world. Both systems have their own unique features and advantages, and the choice of which system to adopt is often a matter of political and historical context.
The presidential system is a form of government in which the president is both the head of state and the head of government. This system is characterized by a separation of powers between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government. The president is elected by the people and serves as the chief executive of the country. The president has the power to appoint and remove government officials, including judges, and is responsible for enforcing the laws of the land.
One of the main advantages of the presidential system is that it provides a clear chain of command and decision-making authority. The president has the power to make decisions and take action without the need for the approval of the legislature or other branches of government. This can be particularly useful in times of crisis, when quick and decisive action is needed.
However, the presidential system also has some drawbacks. One of the main criticisms of this system is that it can lead to a concentration of power in the hands of the president. This can lead to abuses of power and a lack of accountability, as the president is not directly accountable to the legislature. Additionally, the separation of powers can lead to gridlock and political polarization, as different branches of government may have conflicting priorities and agendas.
The parliamentary system, on the other hand, is a form of government in which the head of government, known as the prime minister, is chosen by the legislature. The prime minister is responsible for leading the government and setting its agenda, and is typically the leader of the political party that holds a majority in the legislature. The head of state, usually a ceremonial figure such as a king or queen, is separate from the head of government and does not have any executive power.
One of the main advantages of the parliamentary system is that it allows for more collaboration and consensus-building between the different branches of government. The prime minister and other government officials are accountable to the legislature, which means that they must work with members of other parties and factions to get their legislation passed. This can lead to more moderate and centrist policies, as parties must work together to get things done.
However, the parliamentary system also has its drawbacks. One of the main criticisms of this system is that it can lead to instability and frequent changes in government. If the prime minister loses the support of the legislature, they may be forced to resign, leading to the appointment of a new prime minister and potentially a new government. This can lead to a lack of continuity and a lack of long-term planning.
In conclusion, both the presidential and parliamentary systems of government have their own unique features and advantages. The choice of which system to adopt depends on the specific political and historical context of a country. Ultimately, the goal of any system of government should be to promote the well-being and prosperity of the citizens it serves.
A presidential system of government and a parliamentary system of government are two different forms of governance that a country can adopt. Both systems have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which system to adopt often depends on the country's political and cultural context.
In a presidential system, the president is the head of state and government, and is directly elected by the people. The president has a fixed term of office and is not accountable to the legislature. The president is responsible for executing the laws and policies of the government, and has the power to appoint and remove ministers and other officials. The president is also the commander-in-chief of the military.
In a parliamentary system, the head of government is the prime minister, who is appointed by the legislature. The prime minister is responsible for leading the government and for carrying out its policies. The prime minister is accountable to the legislature and can be removed from office by a vote of no confidence. In a parliamentary system, the head of state is typically a ceremonial figure, such as a king or queen, or a president who is elected by the legislature.
One advantage of a presidential system is that it allows for clear lines of authority and responsibility. The president is directly accountable to the people and has the power to take decisive action on issues facing the country. This can be particularly useful in times of crisis, as the president can act quickly to address the problem.
However, a presidential system can also lead to gridlock if the president and the legislature are controlled by different parties. In such a scenario, it can be difficult for the president to get legislation passed, as the opposition party can block his or her proposals.
A parliamentary system, on the other hand, allows for greater flexibility and cooperation between the different branches of government. The prime minister is accountable to the legislature and must work with other parties to pass legislation. This can lead to more consensus-based decision-making and a more stable government.
However, a parliamentary system can also be less stable, as the prime minister can be removed from office by a vote of no confidence. This can lead to frequent changes in government and a lack of continuity in policy-making.
In conclusion, both presidential and parliamentary systems have their own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of which system to adopt depends on the specific political and cultural context of a country. Ultimately, the success of any system of government depends on the ability of its leaders to work together and address the needs and concerns of the people they serve.