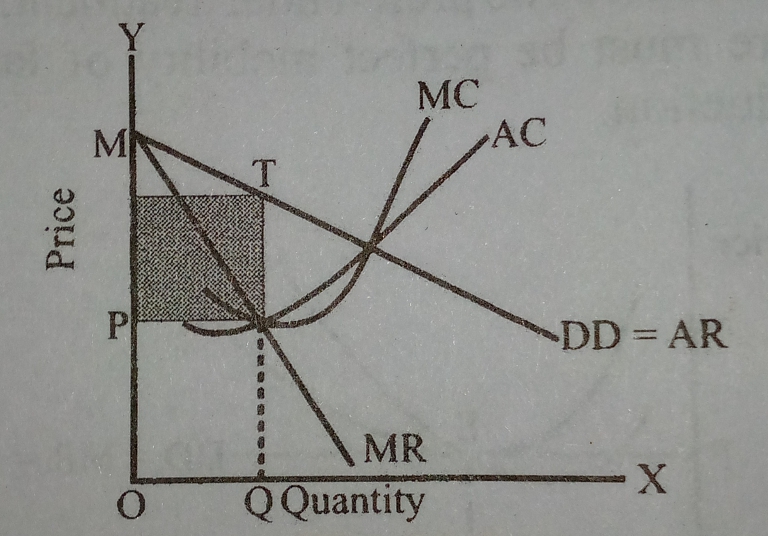
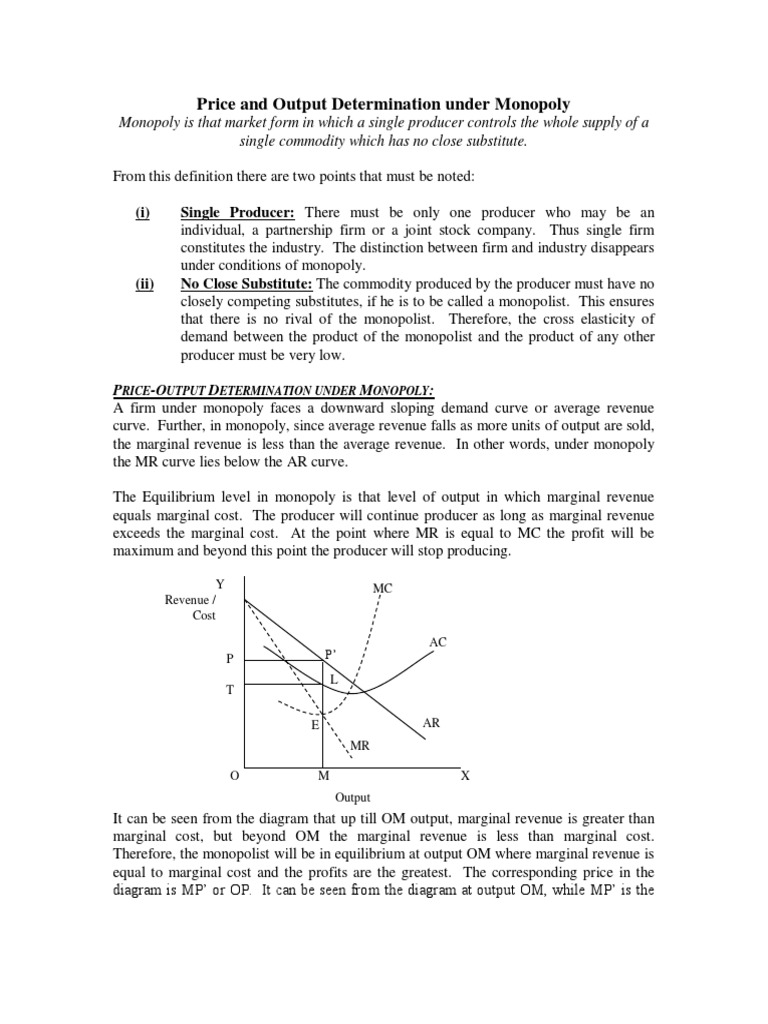
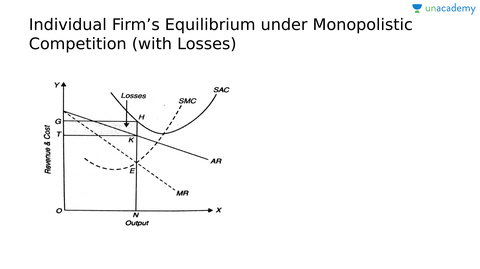
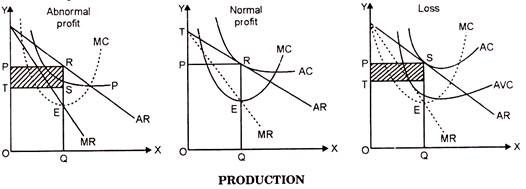
Monopolistic competition is a market structure that falls between perfect competition and pure monopoly. In monopolistic competition, there are many firms selling differentiated products, but each firm has some degree of market power. This means that each firm can charge a price higher than the marginal cost of production, but they must also take into consideration the prices and product offerings of their competitors.
The determination of price under monopolistic competition is influenced by both the demand for the firm's product and the cost of production. The demand curve for a firm under monopolistic competition is typically downward sloping, but not as steep as it would be under perfect competition. This is because the firm has some market power and can charge a higher price for its product without losing all of its customers.
The cost of production also plays a role in price determination under monopolistic competition. A firm will need to consider its fixed costs, variable costs, and marginal cost when setting a price. The marginal cost is the cost of producing one additional unit of the product, and it is important because the firm will want to set a price that covers the marginal cost and earns a profit.
In order to determine the optimal price and quantity to sell, a firm under monopolistic competition can use a diagram similar to the one shown below. The diagram shows the demand curve for the firm's product (D), the marginal cost curve (MC), and the average total cost curve (ATC). The intersection of the demand curve and the marginal cost curve represents the profit-maximizing price and quantity, known as the equilibrium point.
[Insert diagram here]
At the equilibrium point, the firm is able to charge a price that covers the marginal cost of production and earns a profit. If the firm were to charge a higher price, it would decrease the quantity demanded and potentially lead to losses. On the other hand, if the firm were to charge a lower price, it would increase the quantity demanded but also decrease the profit earned.
In summary, the determination of price under monopolistic competition is influenced by demand for the firm's product and the cost of production. Firms must consider the prices and product offerings of their competitors and aim to set a price that covers the marginal cost and earns a profit. The use of a diagram can help firms understand the trade-offs involved and determine the optimal price and quantity to sell.