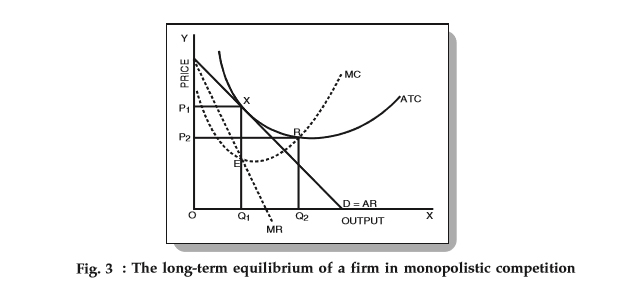
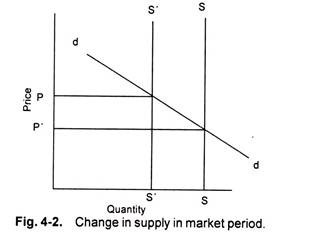
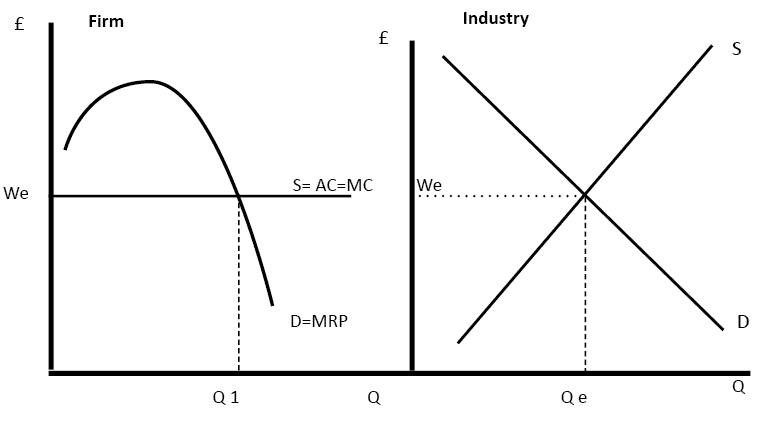
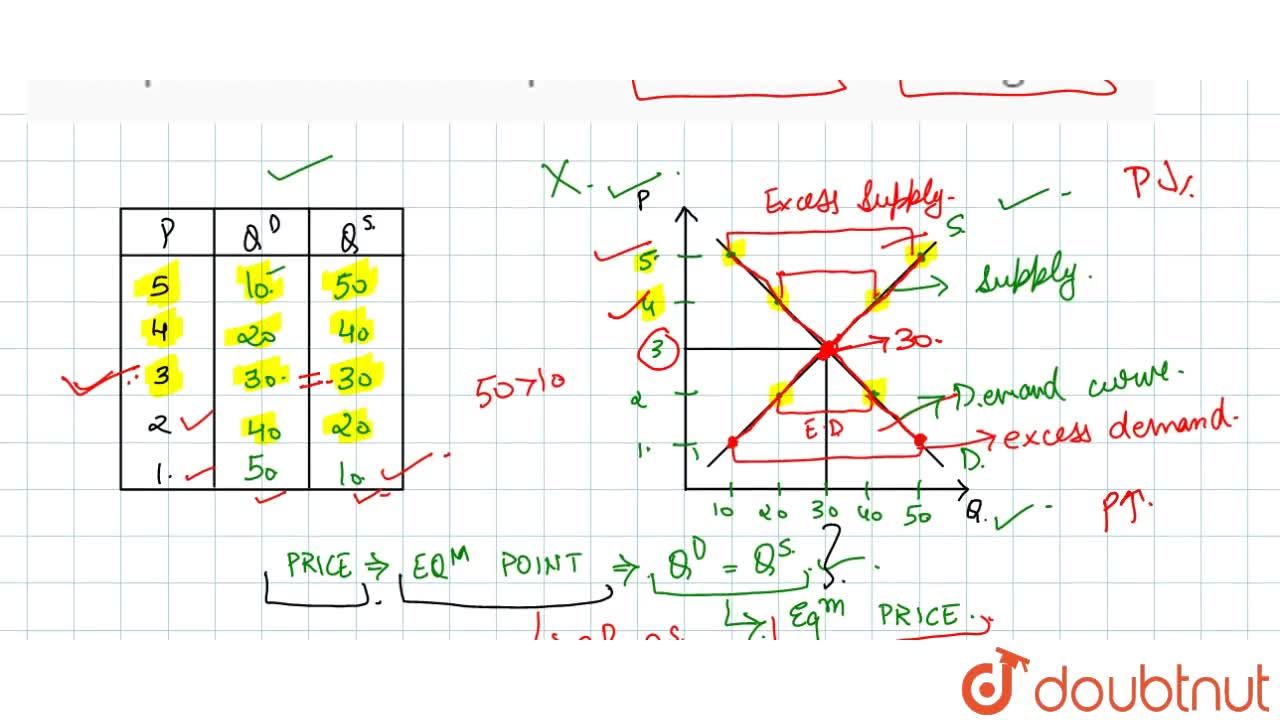
Under perfect competition, firms face a horizontal demand curve and must accept the market price for their products. This is because in a perfectly competitive market, there are many firms producing identical products and many buyers with perfect information about the availability and price of the product. As a result, each firm has a very small market share and cannot significantly influence the market price.
In order to determine the market price under perfect competition, we must consider both the supply and demand for the product. The intersection of the supply and demand curves determines the market equilibrium price and quantity.
On the demand side, the quantity of the product that buyers are willing to purchase depends on the price. As the price increases, the quantity demanded will decrease, and vice versa. This relationship is known as the law of demand.
On the supply side, the quantity of the product that firms are willing to produce depends on the price. As the price increases, firms will be willing to produce and sell more of the product, and as the price decreases, firms will be less willing to produce and sell the product. This relationship is known as the law of supply.
When the market is in equilibrium, the quantity of the product that firms are willing to produce at the market price is equal to the quantity of the product that buyers are willing to purchase at that price. If the market price is higher than the equilibrium price, firms will produce more than what buyers are willing to purchase and excess supply will result. This will lead to a fall in the price until the market returns to equilibrium. On the other hand, if the market price is lower than the equilibrium price, firms will produce less than what buyers are willing to purchase and excess demand will result. This will lead to an increase in the price until the market returns to equilibrium.
Under perfect competition, the market price is determined by the interplay between supply and demand, and firms have no control over the price they receive for their products. They can only choose how much of the product to produce, given the market price. Firms that are unable to produce at a low enough cost to earn a profit at the market price will exit the market, leading to an increase in supply and a decrease in the market price. This process of entry and exit ensures that the market price remains at the lowest level possible to cover the cost of production for the firms that remain in the market.
In summary, under perfect competition, the market price is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves, and firms have no control over the price they receive for their products. They must accept the market price and can only choose how much of the product to produce given the market price.