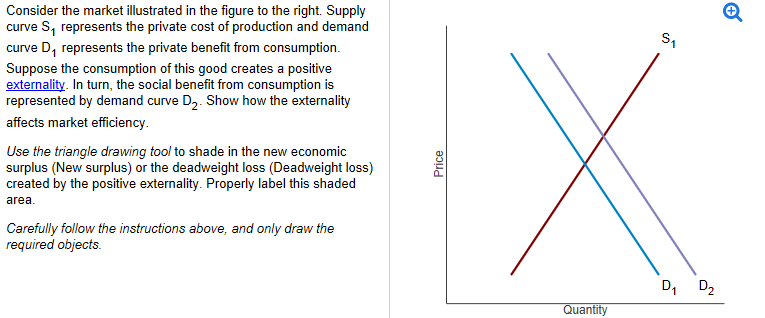
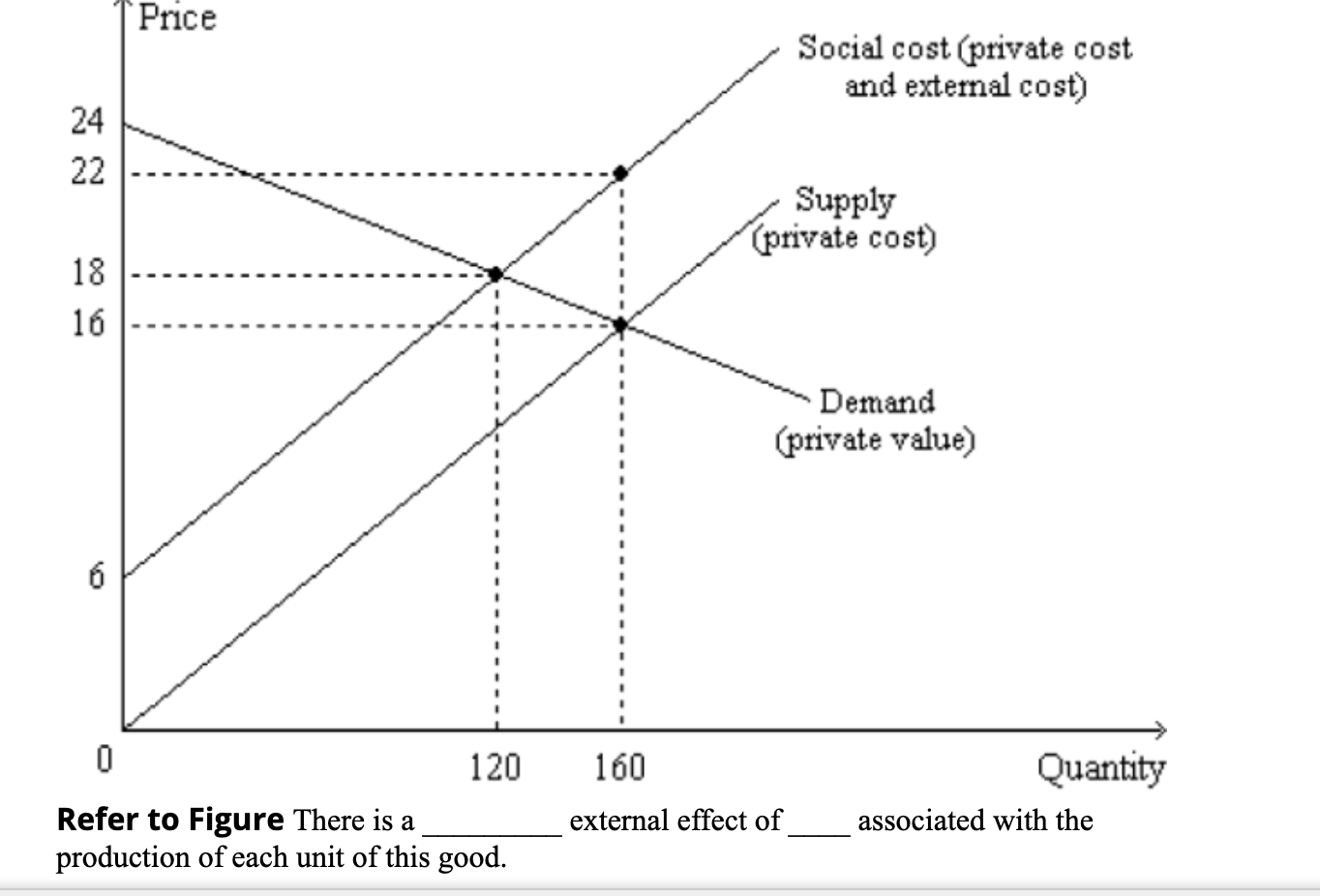
Private cost of production refers to the costs incurred by a firm in producing a good or service. These costs are typically classified into two categories: explicit costs and implicit costs.
Explicit costs are those costs that involve a direct financial outlay by the firm, such as the cost of raw materials, wages paid to employees, and rent or mortgage payments on the firm's production facilities. These costs are easily quantifiable and can be accounted for in the firm's financial statements.
Implicit costs, on the other hand, are the opportunity costs associated with using the firm's own resources for production. For example, if the owner of a firm uses their own money to finance the production of a good, the opportunity cost is the return they could have earned by investing that money elsewhere. Similarly, if the owner of a firm uses their own time and labor to produce a good, the opportunity cost is the wages they could have earned by working for someone else. Implicit costs are not directly observable or quantifiable, and are therefore not reflected in the firm's financial statements.
In addition to explicit and implicit costs, firms may also incur external costs, which are costs that are not borne by the firm itself but are instead imposed on third parties. These can include environmental costs, such as pollution or deforestation, or social costs, such as congestion or noise. External costs are not typically included in the private cost of production, as they are not directly incurred by the firm.
The private cost of production is an important concept in economics, as it determines the minimum price at which a firm must sell its goods in order to cover its costs and earn a profit. If the market price for a good is lower than the private cost of production, the firm will not be able to cover its costs and will eventually go out of business. On the other hand, if the market price is higher than the private cost of production, the firm will be able to earn a profit.
In conclusion, private cost of production refers to the costs incurred by a firm in producing a good or service, including explicit costs such as raw materials and wages, and implicit costs such as opportunity costs. External costs, which are imposed on third parties, are not typically included in the private cost of production. Understanding the private cost of production is important in determining the minimum price at which a firm must sell its goods in order to cover its costs and earn a profit.