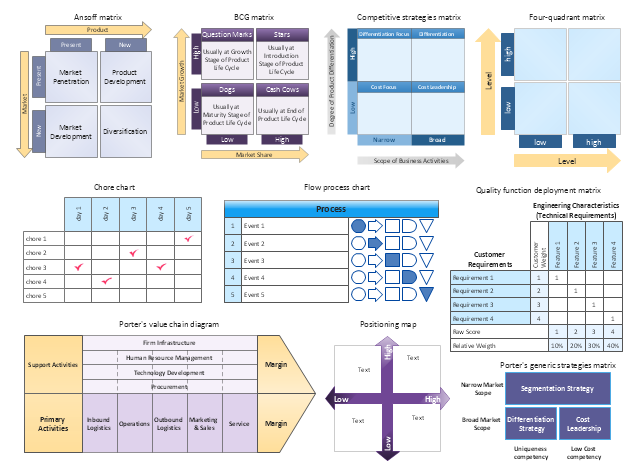
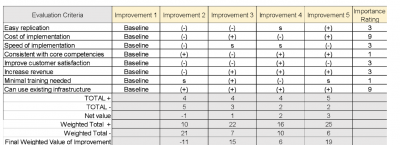
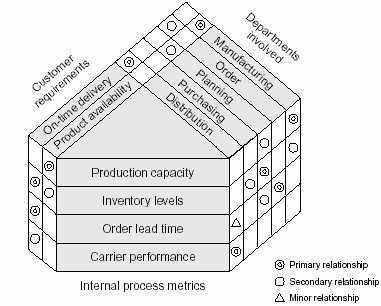
A process design matrix is a tool used to systematically analyze and improve business processes. It provides a visual representation of a process, highlighting its key components and the relationships between them. By using a process design matrix, organizations can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement, as well as develop strategies for optimizing the process.
To create a process design matrix, the first step is to identify the process being analyzed. This could be a process within a single department, or it could be a cross-functional process that involves multiple departments. Once the process has been identified, the next step is to map out the steps involved in the process, starting with the input and ending with the output. Each step in the process should be clearly defined and the relationships between the steps should be identified.
Once the process has been mapped out, the next step is to analyze the process to identify any inefficiencies or areas for improvement. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as time studies, process flow analysis, and value stream mapping. By analyzing the process, organizations can identify bottlenecks, unnecessary steps, and areas where automation could be used to improve efficiency.
Once the process has been analyzed, the next step is to develop strategies for optimizing the process. This could involve streamlining the process to eliminate unnecessary steps, implementing automation to improve efficiency, or reorganizing the process to better align with business goals.
As an example, consider a manufacturing process in which raw materials are transformed into finished products. The process design matrix might include the following steps:
Receiving raw materials: This step involves receiving the raw materials needed for the manufacturing process, such as steel, plastic, and paint.
Preprocessing: In this step, the raw materials are prepared for the manufacturing process. This might involve cutting the materials to size, cleaning them, or performing other preparatory tasks.
Assembly: This step involves assembling the raw materials into the finished product. This could involve using machines to assemble the product, or it could involve manual assembly by workers.
Quality control: In this step, the finished products are inspected to ensure that they meet the required quality standards. Any products that fail the inspection are either repaired or rejected.
Packaging: This step involves packaging the finished products for shipping to customers.
By using a process design matrix, the organization can identify any inefficiencies in the manufacturing process and develop strategies for improving efficiency. For example, they might identify that the preprocessing step is a bottleneck in the process, causing delays in the assembly line. They could then develop a strategy to streamline the preprocessing step, such as by automating certain tasks or reorganizing the workflow to better align with the assembly line.
In summary, a process design matrix is a valuable tool for analyzing and improving business processes. It helps organizations identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement, and provides a visual representation of the process that can be used to develop strategies for optimization. By using a process design matrix, organizations can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the overall effectiveness of their processes.