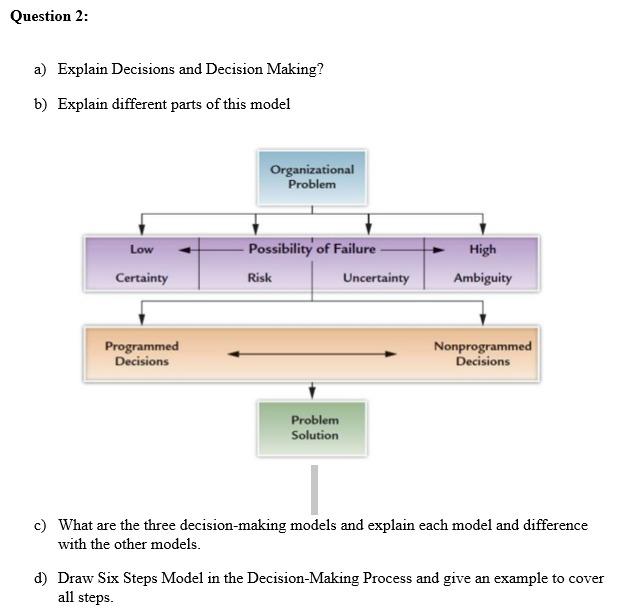
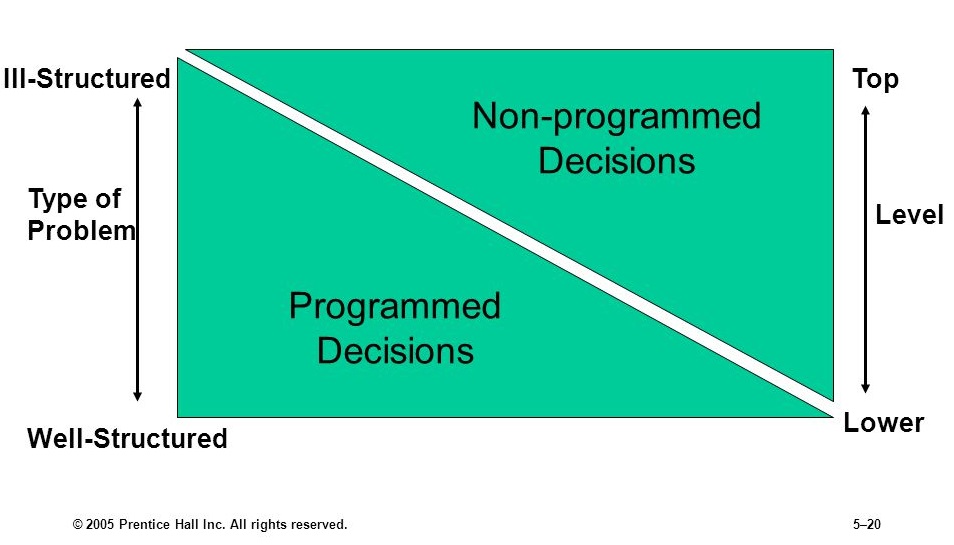
Programmed decision making refers to the use of algorithms and other automated processes to make decisions without human intervention. This approach to decision making has become increasingly prevalent in recent years, as advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning have made it possible for machines to analyze large amounts of data and make decisions based on that analysis.
One of the main benefits of programmed decision making is that it can be faster and more efficient than human decision making. Because algorithms can process large amounts of data quickly, they can make decisions much faster than a human could. This can be especially useful in situations where time is of the essence, such as in emergency response or financial transactions.
Another benefit of programmed decision making is that it can be more accurate than human decision making. Because algorithms are not subject to human biases or emotions, they can make more objective decisions based on the data they are given. This can lead to more consistent and fair outcomes, as the algorithms will not be influenced by personal feelings or subjective opinions.
However, programmed decision making is not without its drawbacks. One concern is that it can be difficult to understand how an algorithm arrived at a particular decision, as the processes it uses may be complex and opaque. This can make it difficult for people to trust the decisions made by algorithms, as they may not understand the logic behind them.
Another concern is that programmed decision making can perpetuate existing biases and inequalities. If the data used to train an algorithm reflects the biases of the society in which it was created, the algorithm may amplify those biases in its decision making. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, and it is important for companies and organizations to be mindful of this issue when implementing programmed decision making systems.
Overall, programmed decision making has the potential to be a powerful tool for improving efficiency and accuracy in a variety of contexts. However, it is important for companies and organizations to carefully consider the potential risks and limitations of this approach, and to take steps to address any potential biases or issues that may arise.