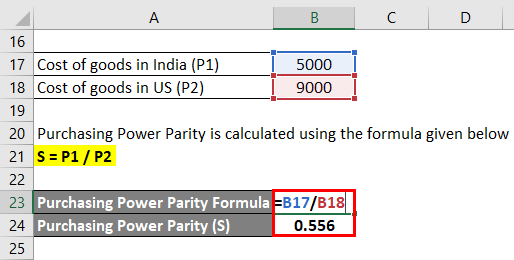
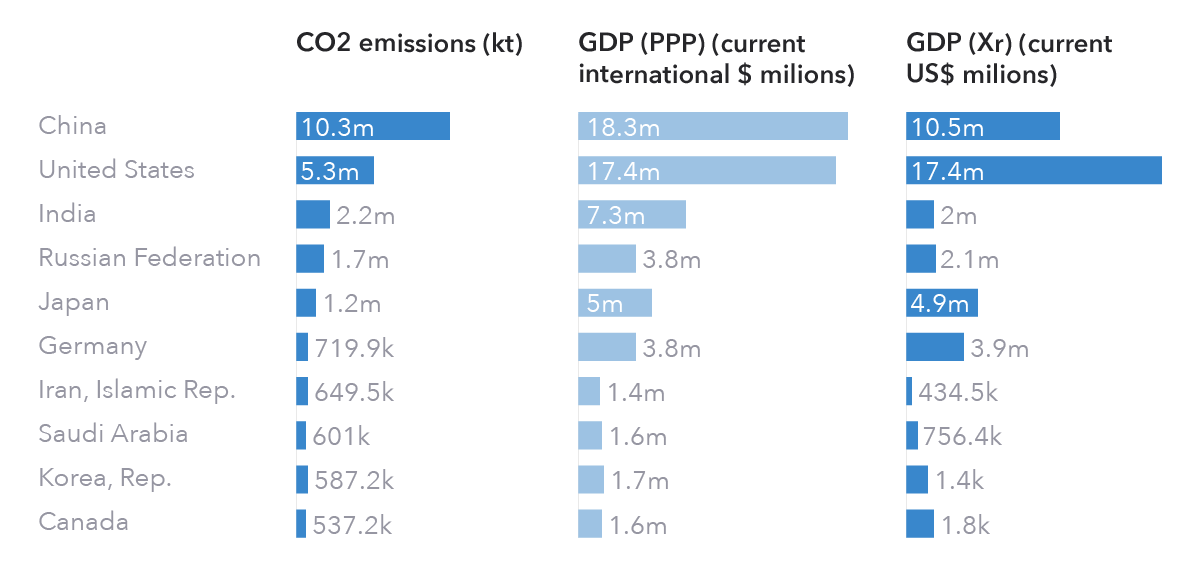
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) is a theory of exchange rate determination that suggests that the exchange rate between two currencies should be equal to the ratio of the prices of a basket of goods and services in each country. According to this theory, the exchange rate between two countries should adjust to reflect the relative differences in the cost of living between the two countries.
The idea behind PPP is that, in the long run, the exchange rate between two countries should adjust to ensure that the price of a basket of goods and services is the same in both countries, after accounting for the exchange rate. For example, if a basket of goods and services costs $100 in the United States and £50 in the United Kingdom, the exchange rate between the two countries should be $1 = £0.50. This is because, at this exchange rate, the cost of the basket of goods and services in the United Kingdom would be $100, the same as in the United States.
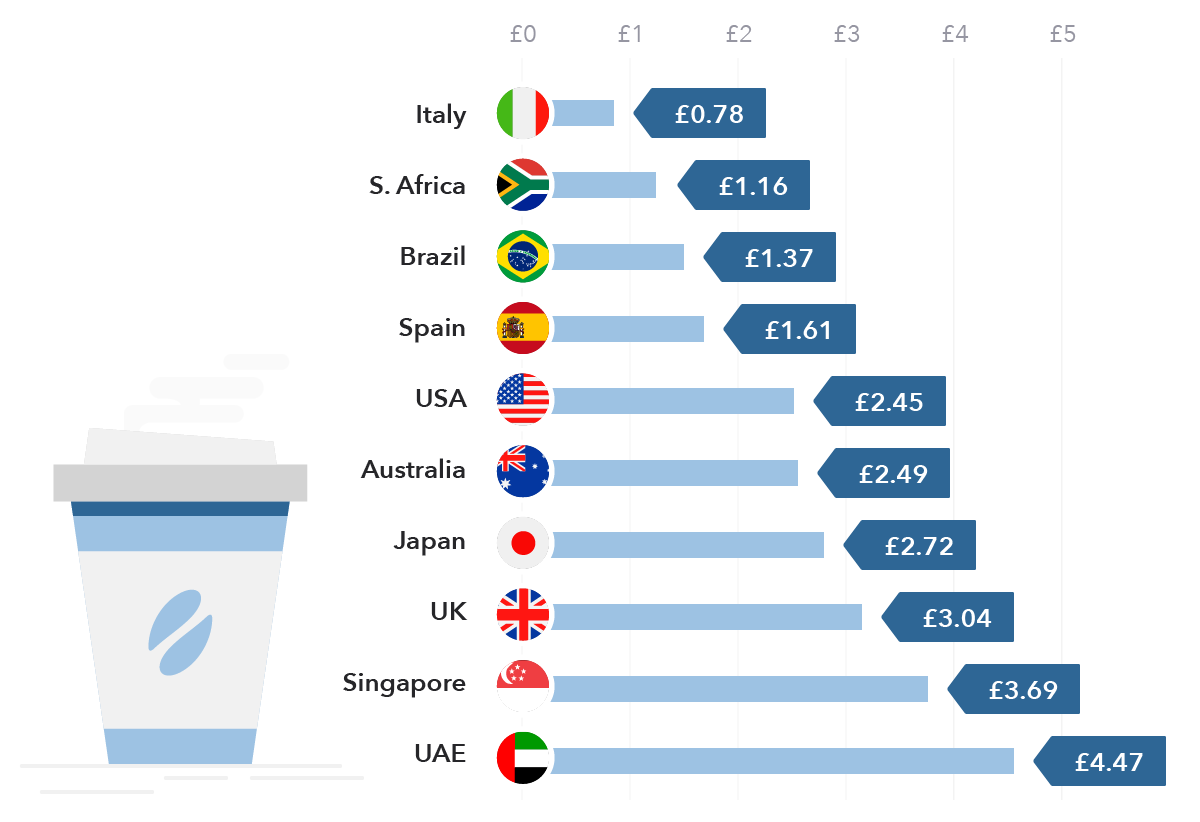
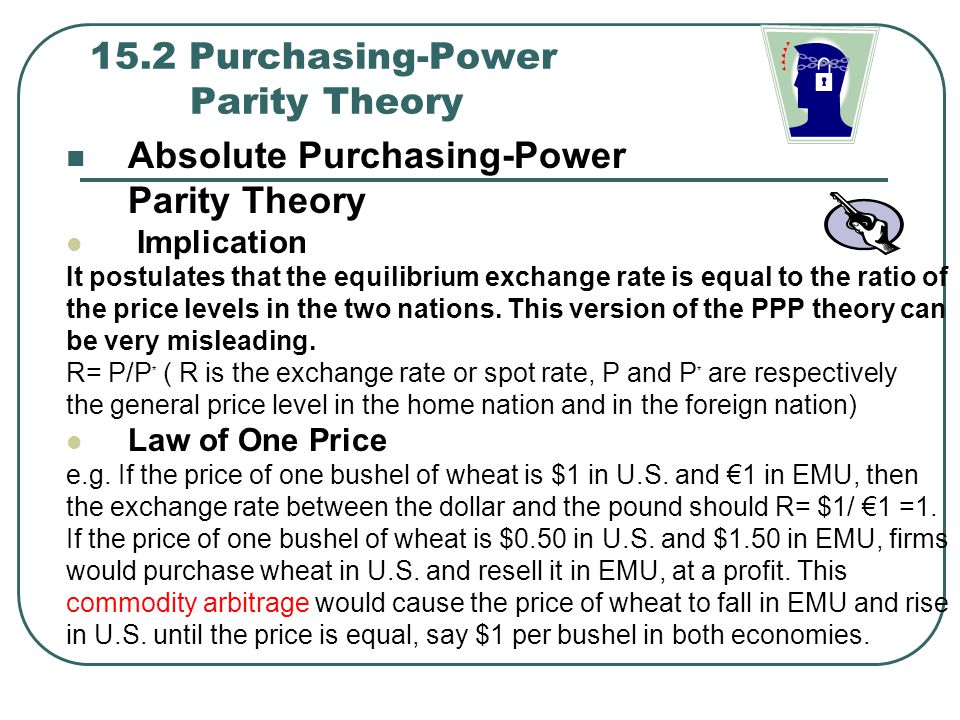
There are several different versions of PPP, including absolute PPP, relative PPP, and international PPP. Absolute PPP holds that the exchange rate between two countries should equal the ratio of the price levels of the two countries. Relative PPP, on the other hand, suggests that the exchange rate between two countries should equal the ratio of the price levels of the two countries relative to a third country. International PPP, also known as the Big Mac Index, is based on the idea that the exchange rate between two countries should be equal to the ratio of the price of a Big Mac in each country.
There are several factors that can affect the exchange rate between two countries, including differences in inflation rates, interest rates, and economic growth rates. PPP suggests that, in the long run, these factors should be taken into account when determining the exchange rate between two countries.
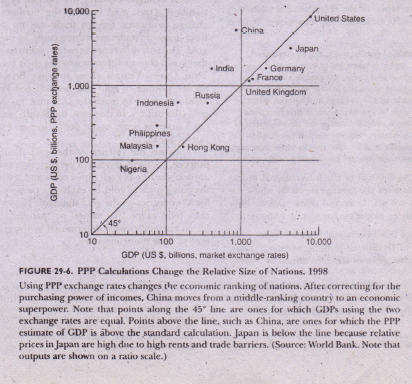
While PPP is a useful theory for understanding exchange rate determination, it is important to note that it is not always accurate. There are several factors that can cause deviations from PPP, including transportation costs, taxes, and tariffs. Additionally, PPP assumes that the exchange rate will adjust to reflect changes in the relative price levels of the two countries, but in practice, exchange rates may not always adjust as quickly as PPP would predict.
In conclusion, the purchasing power parity theory of exchange rate determination suggests that the exchange rate between two countries should be equal to the ratio of the prices of a basket of goods and services in each country. This theory is useful for understanding exchange rate determination, but it is important to recognize that there may be deviations from PPP due to a variety of factors.