Pure or perfect competition. Perfect Competition: Characteristics, Examples, Features, and Benefits 2022-12-24
Pure or perfect competition
Rating:
9,4/10
204
reviews
Pure or perfect competition is a type of market structure in which a large number of firms produce a homogenous product and compete with each other based on price. In this type of market, buyers and sellers are fully informed about the prices and quality of the products being offered, and there are no barriers to entry or exit for firms.
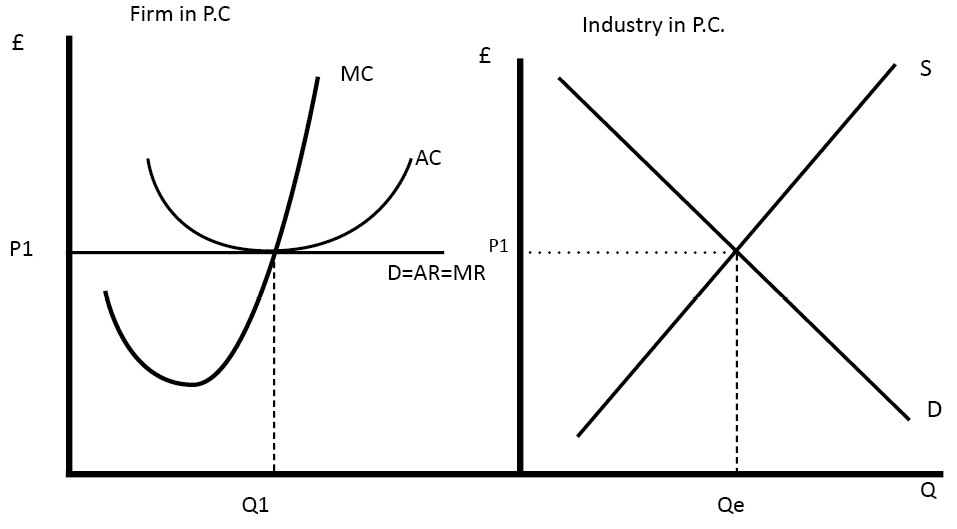
One of the key characteristics of a perfectly competitive market is that the firms are price takers, meaning they have no influence on the market price and must accept the price set by the market. This is because the firms are too small to affect the market demand for their product and must therefore accept the market price as given.
Another key characteristic of perfect competition is that there is a large number of firms in the market, each producing a small fraction of the total market output. This ensures that no single firm has a significant market share and therefore cannot influence the market price.
In a perfectly competitive market, firms aim to maximize profits by producing at the lowest possible cost and selling at the highest possible price. This results in a situation where firms are constantly trying to improve their production processes and reduce their costs in order to remain competitive.
Despite its theoretical appeal, pure or perfect competition is a rare occurrence in the real world. Most markets exhibit some degree of imperfection, such as barriers to entry, differences in product quality, or the presence of a dominant firm. However, the concept of perfect competition serves as a useful benchmark against which to compare and contrast other types of market structures.
In conclusion, pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure characterized by a large number of firms producing a homogenous product, price taking behavior, and free entry and exit. While this type of market is rare in the real world, it serves as a useful benchmark for understanding the behavior of firms and markets.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Perfect Competition

In the case of the raspberry farm, this occurs at 80 packs of strawberries. Schefold eds , Essays on Piero Sraffa, London: Unwin and Hyman, pp. Often, street vendors offer a homogeneous product, with very little variation in its features. Because you have no preference for one brand over another, and the packaging is generic on each brand, you randomly select a package. The reason is since the marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost, additional output is adding more to profit than it is taking away. If an outsider tries to sell inside their territory, he or she is likely to be threatened or even attacked, or maybe find that nobody is buying consumers are scared. It does not mean that the firm is going out of business exiting the industry.
Next
Market Forms: Pure Competition, Perfect Competition and Imperfect Competition
Also known as pure competition. For example, perfect competition may have existed in earlier centuries when commodities were the main source of economic activity. For instance, many utilities such as power companies or water authorities may be granted a monopoly status for a certain area. It is argued that perfect competition exists only in agrarian sector. Thus, perfect competition is not only pure but also free from other imperfection. Labor market monopsonies tend to be disadvantageous for workers, as firms are able to negotiate lower wages due to their market power.
Next
"Pure and Perfect" Competition? By What Standard? by Richard M Salsman

The conditions that allow oligopolies to exist include high costs of entry in capital expenditures, legal privilege license to use wireless spectrum or land for railways , and a platform that gains value with more customers such as social networks. What Is a Perfectly Competitive Market? Lesson Summary Pure competition is a market condition where the companies providing products offer the same features and price, making the difference between manufacturers minor, if not completely irrelevant. Another way to state the rule is that a firm should compare the profits from operating to those realized if it shut down and select the option that produces the greater profit. Free entry and exit of firms : There is no barrier to entry or exit from the industry. Barriers to exit are, for example, extremely high costs involved in leaving a market. In this article, we tell you what perfect competition is, its characteristics, benefits, and main examples of perfect competition.
Next
What is perfect competition? Definition and meaning
One major flaw in some types of street food vending are mafia-like behaviors. This knowledge refers not only to the prevailing conditions in the current period but in all future periods as well. This can be contrasted with the more realistic imperfect competition, which exists whenever a market, hypothetical or real, violates the abstract principles of pure or perfect neoclassical competition. Therefore, the first two criteria, homogeneous products and price takers, are far from being realistic. ADVERTISEMENTS: iv Under monopolistic competition, the demand curve or sales curve, or what is also called average revenue curve, is not a horizontal straight line. Those economists who believe in perfect competition as a useful approximation to real markets may classify those as ranging from close-to-perfect to very imperfect. They buy competitors until they are the only ones left.
Next
Does Perfect Competition Exist in the Real World?

Since customers have perfect information, they will know that the product is inferior. Entry or exit may take time, but firms have freedom of movement in and out of the industry. They are not criticizing the Another frequent criticism is that it is often not true that in the short run differences between supply and demand cause changes in price; especially in manufacturing, the more common behaviour is alteration of production without nearly any alteration of price. Because competition is much less intense in pure competition, new companies can easily enter the market and start selling products. She spent several years with Western Governor's University as a faculty member.
Next
Monopolistic Market vs. Perfect Competition: What's the Difference?

Thus, if the above two conditions, viz. Consequently, buyers exert considerable influence over sellers. Each seller and each buyer faces a price that is determined by the market forces, which are beyond his control. Since the number of firms is very large, no individual firm has the power to vary the market price. Imperfect competition was a theory created to explain the more realistic kind of market interaction that lies in between perfect competition and a monopoly. The producers can sell at that price as much as they like, and the buyers also can buy as much as they like.
Next
Perfect Competition (With 7 Assumptions)

This is called the A simple proof assuming differentiable utility functions and production functions is the following. One way to determine the most profitable quantity to produce is to see at what quantity total revenue exceeds total cost by the largest amount. Although the liberals in America, the traditional disciples of big government, have been willing accomplices in promoting this view of competition, it is the conservatives, the alleged defenders of capitalism, who are most responsible for it. The result is that each producer comes to have a hold on a clientele from whom he can charge higher prices. In this example, total costs will exceed total revenues at output levels from 0 to approximately 30, and so over this range of output, the firm will be making losses. In a monopolistic market, there is only one seller or producer of a good. It is often referred to as perfect competition.
Next
Perfect competition

The critics of the assumption of perfect competition in product markets seldom question the basic In particular, the rejection of perfect competition does not generally entail the rejection of free competition as characterizing most product markets; indeed it has been argued The issue is different with respect to factor markets. Rather, the perfectly competitive firm can choose to sell any quantity of output at exactly the same price. Since all real markets exist outside the plane of the perfect competition model, each one can be classified as imperfect. The consumers generally believe that the products are different. OX and OY are the two axes. Under perfect competition, he need not reduce the price, for he can sell any amount at the prevailing price. Mobility of labour is inhibited by a lot of obstacles like color, language and family affection.
Next
What is the difference between pure and perfect competition?

In an oligopoly, providers control the market and ultimately prices. Lockheed Martin, a US defense giant with over 120,000 workers, gets 85% of its revenue from US government contracts. They all are essentially the same. They can control the entry and exit of firms into a market by setting up rules to function in the market. Many industries also have significant barriers to entry, such as high start-up costs or strict government regulations, that limit the ability of companies to enter and exit those industries.
Next








