A quality circle is a small group of employees who voluntarily meet on a regular basis to identify, analyze, and solve work-related problems and to improve the overall effectiveness and efficiency of their work unit. The goal of a quality circle is to involve employees in the decision-making and problem-solving process, as well as to encourage continuous improvement and employee empowerment.
Quality circles were first developed in Japan in the 1950s as a way to improve quality and productivity in manufacturing organizations. Since then, they have been adopted by a wide variety of organizations around the world, including government agencies, healthcare facilities, and service organizations.
In human resource management (HRM), quality circles can be an effective tool for improving communication and collaboration among employees, as well as for promoting employee involvement and empowerment. Quality circles can also help HR managers identify and address problems or challenges within the organization, such as poor quality control, low morale, or high turnover.
To be effective, quality circles require the active participation and commitment of both management and employees. Management must provide support and resources for the quality circle program, as well as create an environment that encourages open communication and collaboration. Employees, on the other hand, must be willing to take an active role in identifying and addressing problems, as well as to share ideas and suggestions for improvement.
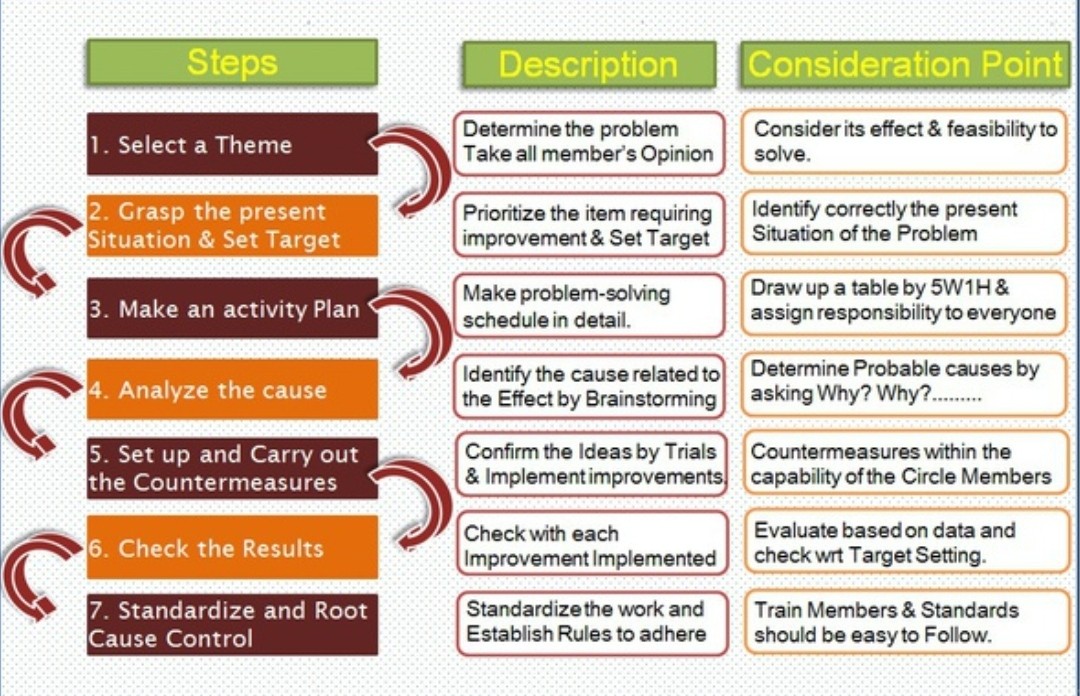
There are several key steps involved in implementing a quality circle program in HRM:
Identify the purpose and goals of the quality circle program. These should be aligned with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
Select and train facilitators to lead the quality circles. These individuals should have strong communication and problem-solving skills, as well as the ability to facilitate group discussions and decision-making.
Select and train members for the quality circles. These should be a diverse group of employees who are representative of the work unit.
Establish a schedule for quality circle meetings and determine how often they will meet.
Facilitate the first quality circle meeting, during which the purpose and goals of the program are discussed, as well as any ground rules or guidelines for participation.
Encourage open communication and collaboration during quality circle meetings. This can be achieved through activities such as brainstorming sessions, problem-solving exercises, and group discussions.
Follow up on action items and ideas for improvement that are generated during quality circle meetings. This may involve implementing changes or solutions, as well as tracking and measuring the results.
In conclusion, quality circles can be a valuable tool for HR managers looking to improve communication, collaboration, and problem-solving within their organization. By involving employees in the decision-making and problem-solving process, organizations can tap into the collective knowledge and expertise of their workforce, resulting in improved quality, efficiency, and employee satisfaction.