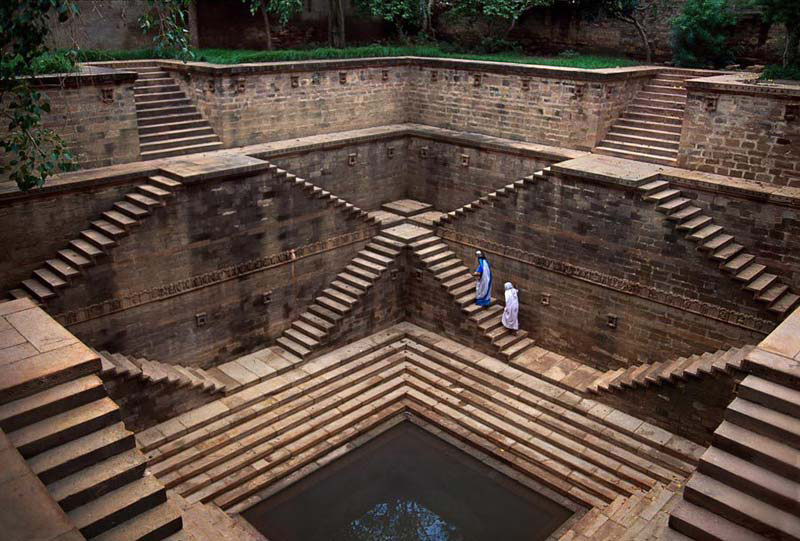
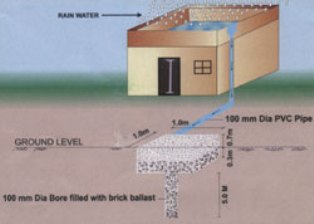
Rainwater harvesting is the collection and storage of rainwater for later use. It is a traditional technique that has been used in India for centuries, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where access to clean, potable water is limited.
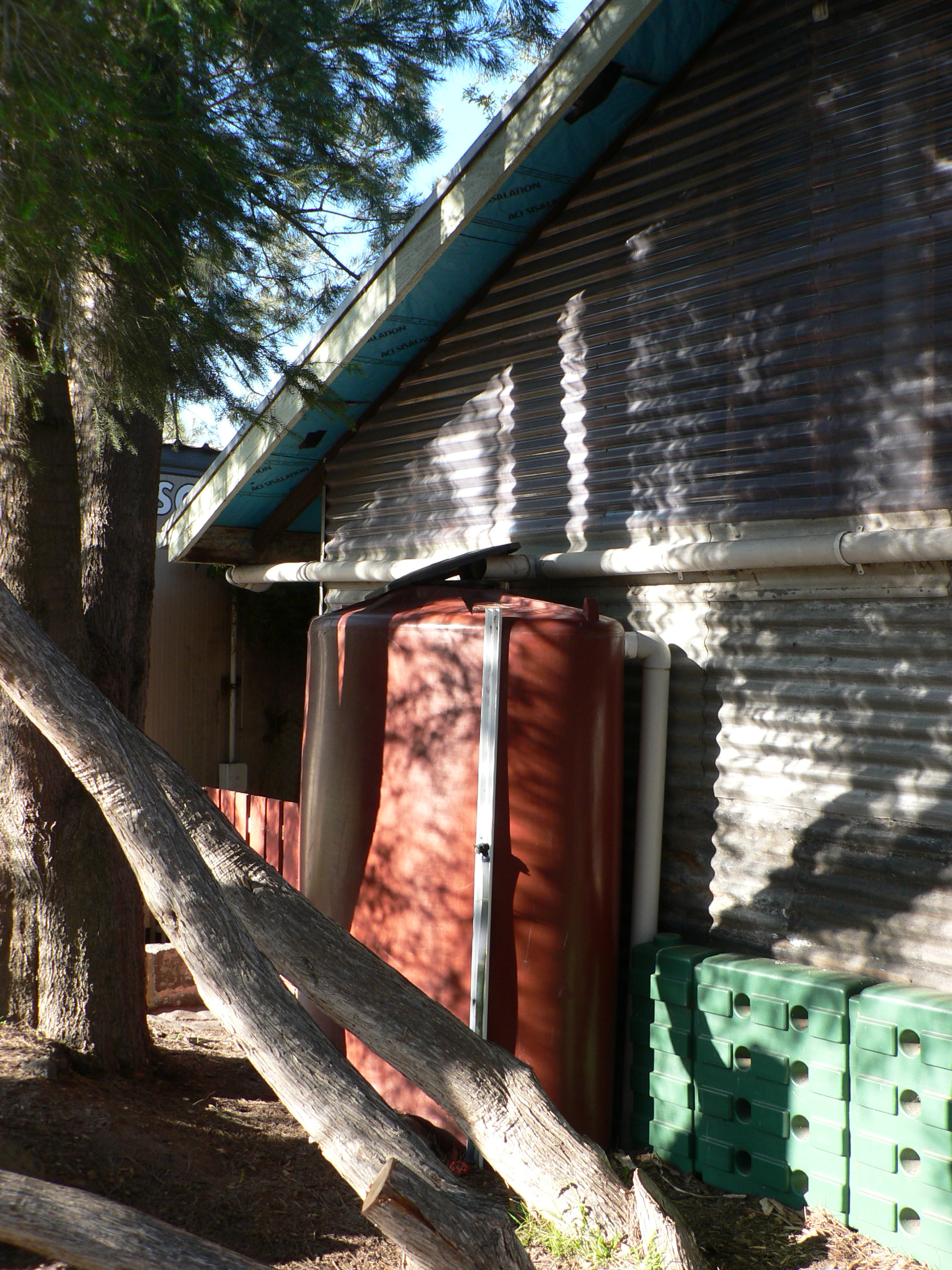
Rainwater harvesting systems typically involve the collection of rainwater from rooftops, streets, or other surfaces, which is then stored in tanks or cisterns for later use. The collected rainwater can be used for a variety of purposes, including irrigation, domestic use, and even for the production of electricity.
In India, rainwater harvesting has become increasingly popular in recent years due to growing concerns about water scarcity and the need to conserve resources. With its large population and increasing demand for water, India is facing significant water-related challenges, including pollution, overuse, and depletion of aquifers. Rainwater harvesting offers a way to address these challenges by providing a reliable source of clean, affordable water.
There are several benefits to rainwater harvesting in India. First and foremost, it helps to reduce the reliance on ground and surface water sources, which can become depleted due to overuse. By collecting and storing rainwater, communities can reduce their demand on these sources and help to preserve them for future generations.
Additionally, rainwater harvesting can help to reduce the amount of water lost through evaporation and runoff. When rainwater is collected and stored in tanks or cisterns, it can be used more efficiently and effectively, reducing the amount of water that is lost through evaporation and runoff.
Furthermore, rainwater harvesting can also help to reduce the cost of water for communities and households. By collecting and storing rainwater, households and communities can reduce their reliance on expensive, treated water from municipal sources and use the collected rainwater instead.
In conclusion, rainwater harvesting is a traditional technique that has been used in India for centuries and is becoming increasingly popular as a way to address water-related challenges such as scarcity, pollution, and overuse. It offers a reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable solution for meeting the water needs of communities and households in India.