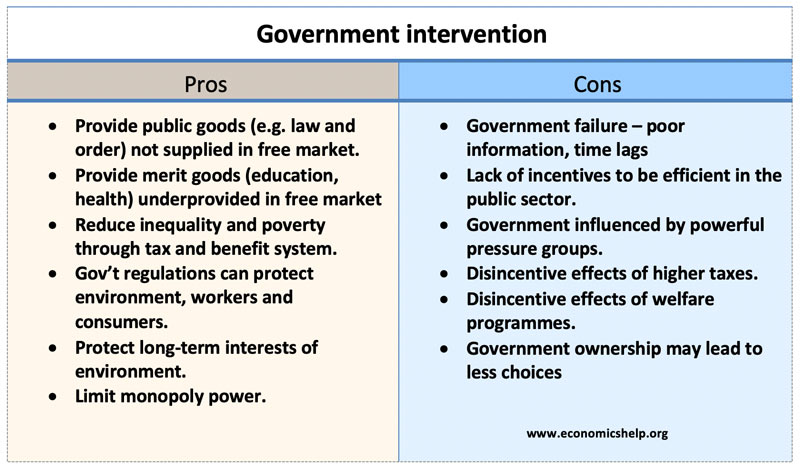
Government intervention refers to the actions taken by governments to regulate or influence economic and social activities within a country. There are several reasons why governments may choose to intervene in the functioning of markets and society.
One reason for government intervention is to promote fairness and equality. Markets can sometimes lead to unequal distribution of resources, with some individuals or groups gaining more wealth or power than others. Governments may intervene to redistribute wealth or provide access to certain goods and services to ensure that all members of society have the opportunity to thrive. For example, the government may provide healthcare, education, and social welfare programs to those in need, or implement progressive taxation to redistribute wealth from the wealthy to the less well-off.
Another reason for government intervention is to protect the public from harm. Governments may regulate businesses and industries to ensure that products and services are safe and of high quality. For example, the government may set standards for food safety, air and water quality, and consumer protection. In addition, governments may regulate certain industries, such as the pharmaceutical or financial sectors, to prevent harmful practices or protect consumers from fraud or abuse.
A third reason for government intervention is to address externalities, which are the unintended consequences of economic activities that affect third parties. Externalities can be positive or negative. Positive externalities occur when the benefits of an economic activity spill over to others, such as the way that education and healthcare provide benefits to society as a whole. Negative externalities occur when the costs of an economic activity are not fully internalized by the producers, such as the way that pollution from a factory can harm the health of people living nearby. Governments may intervene to internalize these externalities through policies such as taxes, subsidies, or regulations.
Finally, government intervention may be necessary to stabilize the economy and address market failures. Market failures occur when markets are unable to allocate resources efficiently, such as when there is a lack of competition or information. Governments may intervene to correct market failures through policies such as antitrust enforcement, regulation, or the provision of public goods. For example, the government may regulate utilities to ensure that they provide a stable and reliable service, or invest in infrastructure projects to stimulate economic growth.
In conclusion, there are several reasons why governments may choose to intervene in economic and social activities. These include promoting fairness and equality, protecting the public from harm, addressing externalities, and addressing market failures. While government intervention can be necessary to address these issues, it is important to carefully consider the costs and benefits of any policy to ensure that it is effective and efficient.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/How-governments-influence-markets_color_rev-a0f613b7ef684cba868aac7efb8818fc.jpg)