Price elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. It is calculated as the percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service divided by the percentage change in its price.
There are several different types of price elasticity, including elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic. Elastic demand occurs when the quantity demanded of a good or service is highly sensitive to changes in its price. Inelastic demand occurs when the quantity demanded is relatively insensitive to changes in price. Unit elastic demand occurs when the percentage change in the quantity demanded is equal to the percentage change in price.
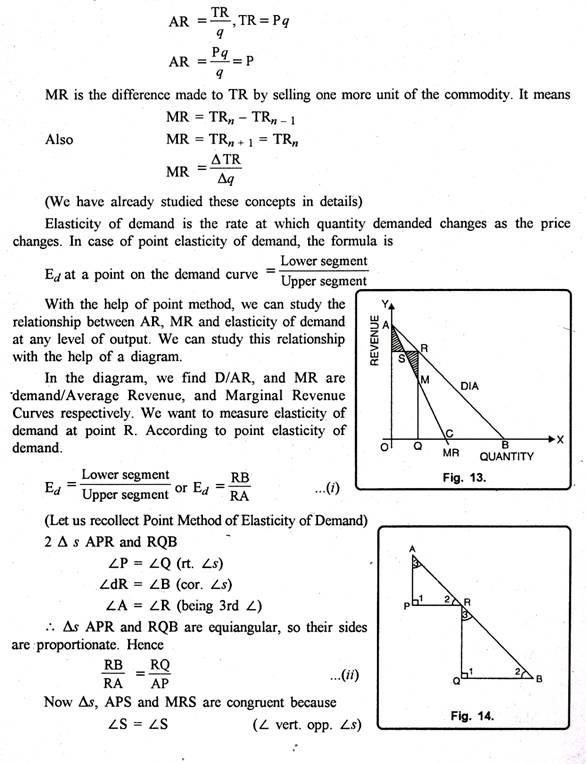
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue that a firm receives from selling one more unit of a good or service. It is calculated as the change in total revenue that results from a change in the quantity sold.
The relationship between price elasticity and marginal revenue is an important one for firms to consider when setting prices for their goods and services. If the demand for a good or service is elastic, then a small increase in price will result in a large decrease in the quantity demanded. This will lead to a decrease in total revenue, and therefore a decrease in marginal revenue. On the other hand, if the demand for a good or service is inelastic, then a small increase in price will result in only a small decrease in the quantity demanded. This will lead to an increase in total revenue, and therefore an increase in marginal revenue.
Firms need to consider the price elasticity of demand for their products when setting prices in order to maximize their profits. If the demand for a good or service is elastic, then the firm will want to set a lower price in order to maximize the quantity sold and therefore total revenue. If the demand is inelastic, then the firm will want to set a higher price in order to maximize total revenue.
In conclusion, the relationship between price elasticity and marginal revenue is an important one for firms to consider when setting prices for their goods and services. Firms need to take into account the elasticity of demand for their products in order to maximize their profits and maximize the quantity sold.
What Is the Relationship Between Elasticity & Marginal Utility?
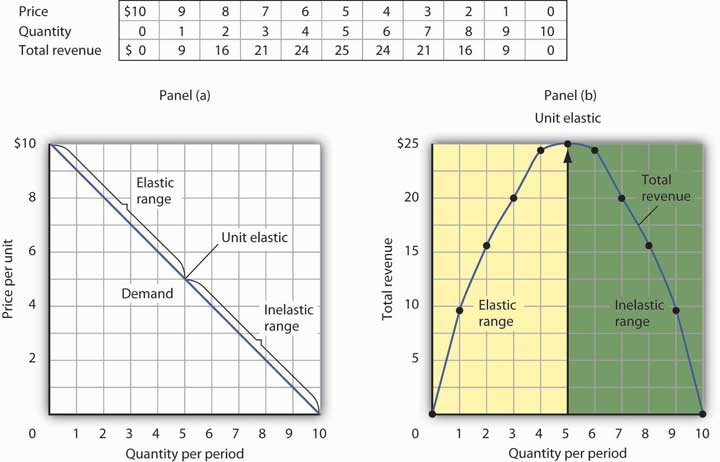
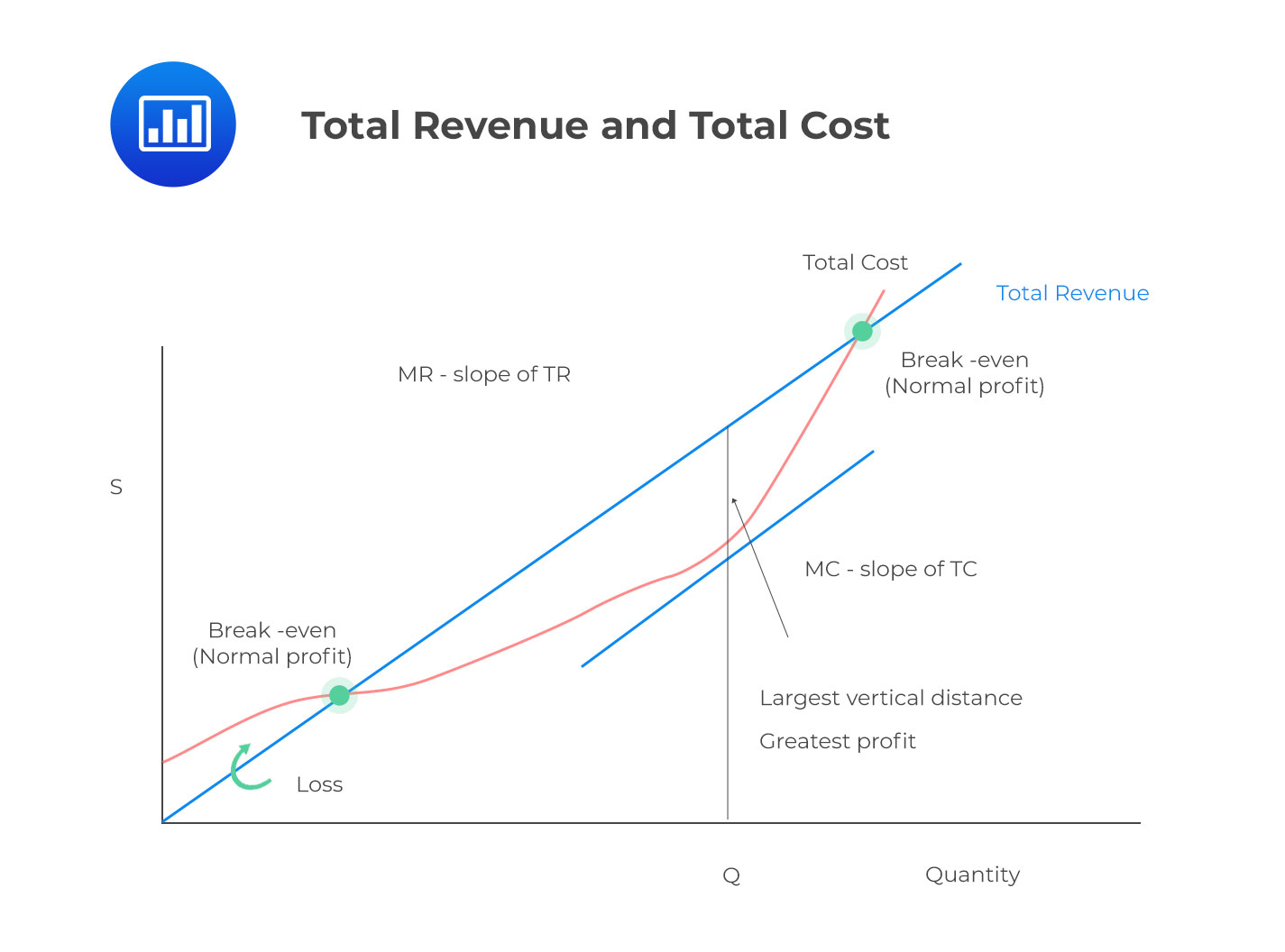
Revenue affects the profitability of the company. If, starting from the output Q 1 in Figure 6, the Board were to increase the output quota by one more unit, the increase in total revenue from selling that unit would be less than the increase in the total cost from producing it, making such an expansion of the quota not worthwhile. Turnover refers to how many times a company makes or burns through assets. It, therefore, follows that corresponding to the middle point C on the demand curve where elasticity is equal to one the total revenue will be maximum. .
4.2 Elasticity and Revenue
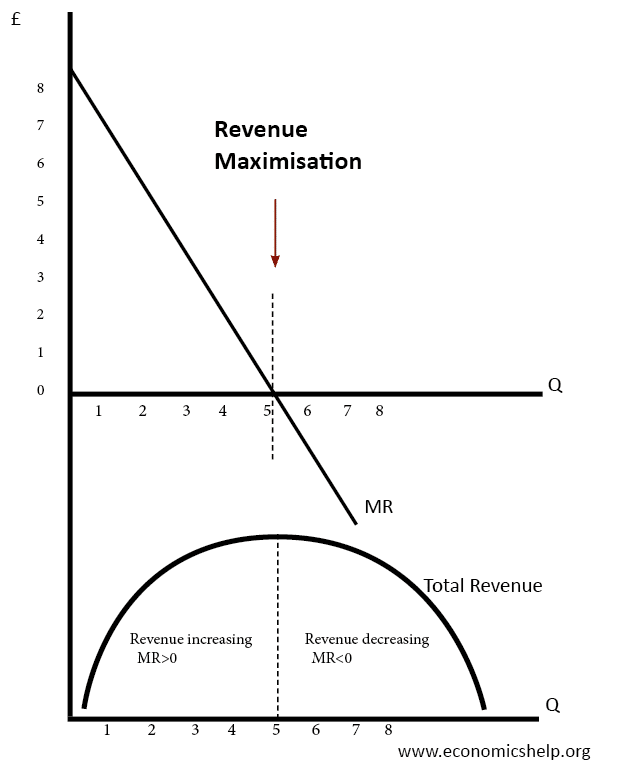
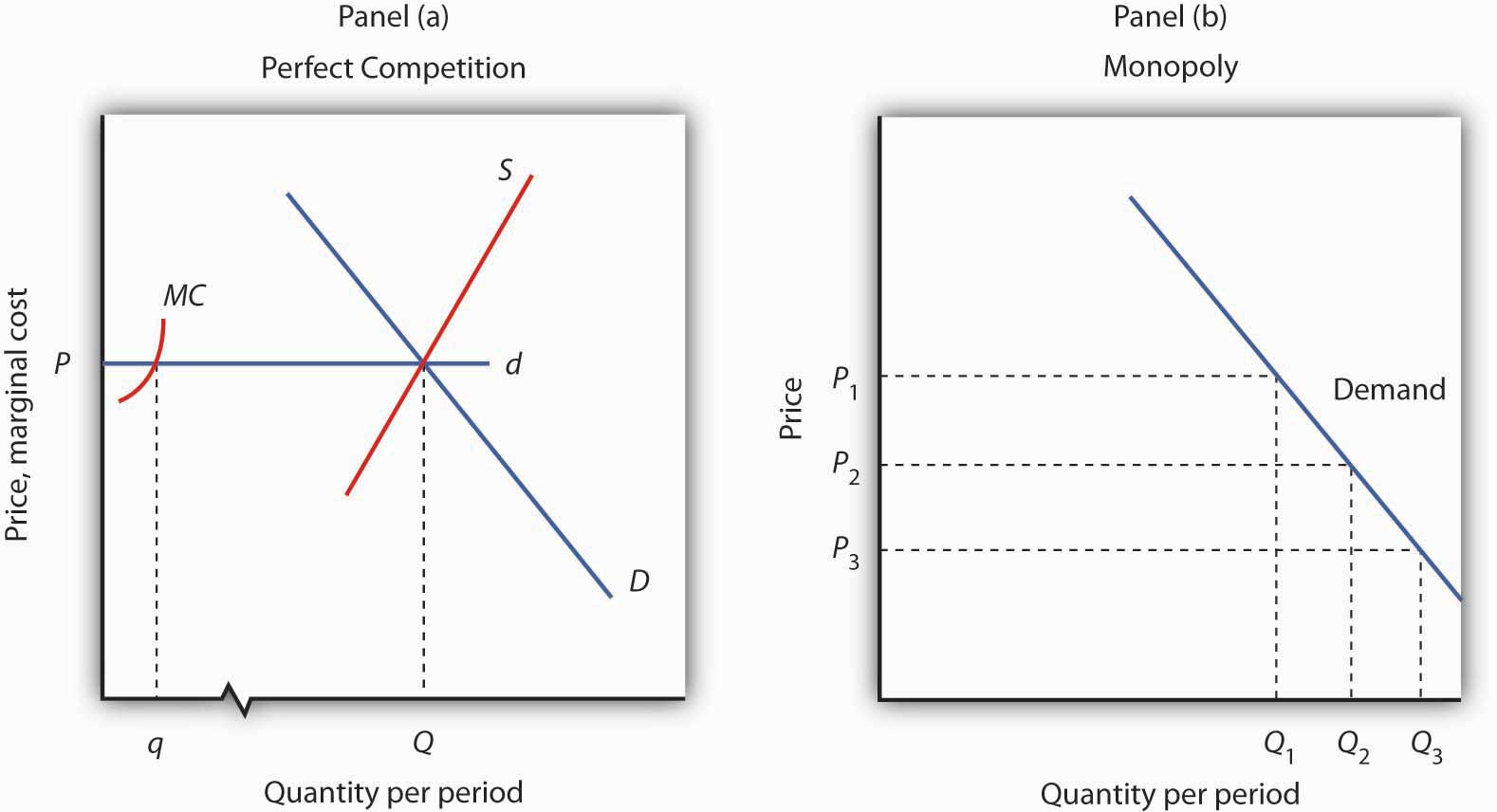
This section will answer these questions. When marginal revenue is positive, demand is elastic; and when marginal revenue is negative, demand is inelastic. Answer: By definition, The elasticity of demand is the change in demand due to the change in one or more of the variable factors that it depends on. A legal monopoly is created by the exclusive right to use a patent, copyright or intangible asset. Then we can write 2. As seen before, each firm does not make any economic profit in the long run. So this possibility is also ruled out.
3.3: Marginal Revenue and the Elasticity of Demand
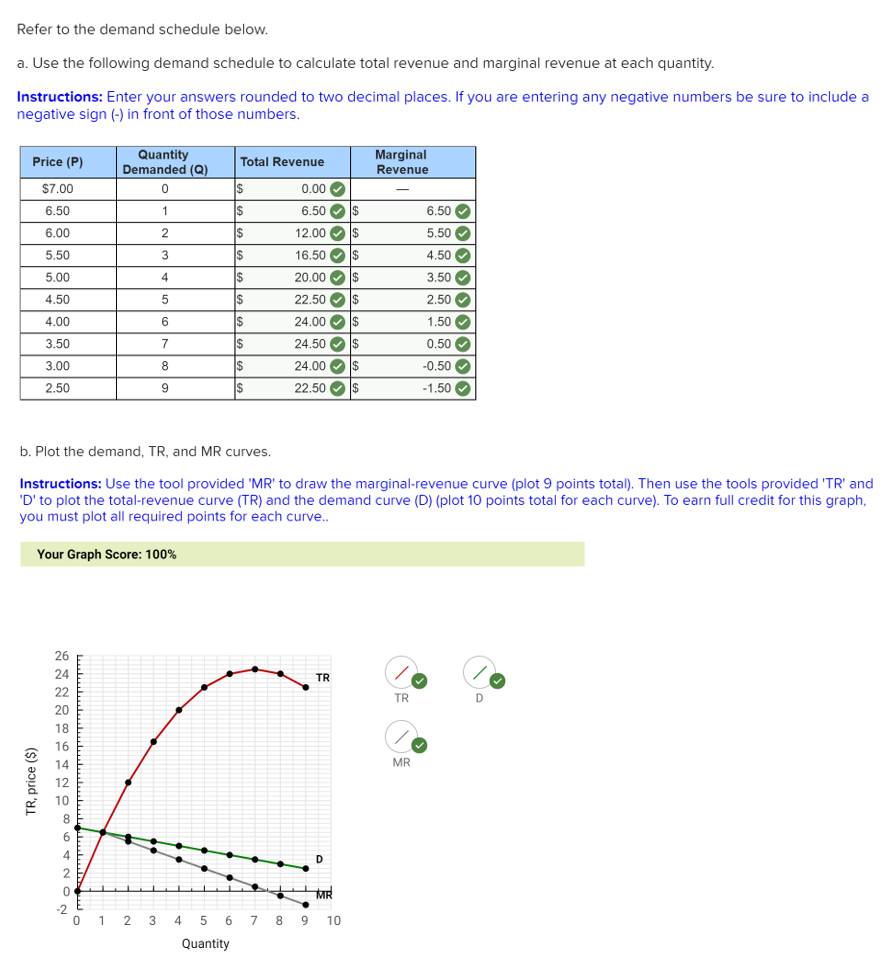
Starting from zero, therefore, the Board will increase the quota, unit by unit, until the marginal revenue curve crosses the marginal cost curve in this case, supply curve. They keep their old car longer and make the necessary repairs. At a quantity of three units, consumers are willing to pay Rs. Luxuries are optional; they aren't necessary to live. We can use this expression to identify the revenue gains and losses in Fig. In this context we may refer to the inverse elasticity rule. Our mission is to provide an online platform to help students to discuss anything and everything about Economics.
What is the relationship between price elasticity and total revenue?
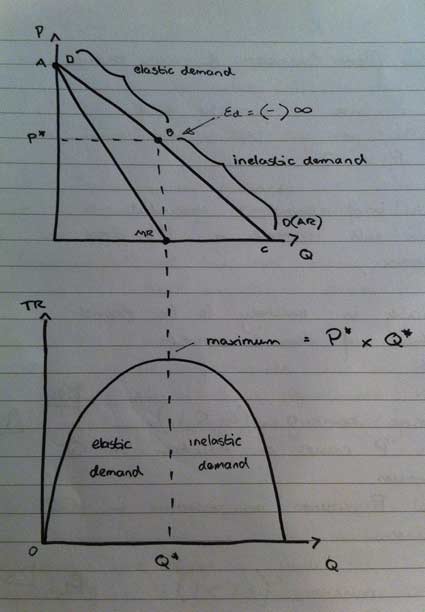
Alternatively, if it were to reduce the quota by one unit, the reduction in total revenue from selling one less unit would be greater than the reduction in the total cost from producing one unit less, making the reduction in the quota not worthwhile. Elasticities can be divided into three broad categories: elastic, inelastic, and unitary. I usually watch the videos before going into more in-depth reading and they are a good way to avoid being overwhelmed by the sheer volume of content when you look at the readings. On balance, total revenue increases by only Rs. A car is a good example. Total revenue is maximized when marginal revenue is zero; hence total revenue will only decrease when marginal revenue becomes zero. We can then express the slope of the demand curve, denoted by the greek symbol δ, as 1.