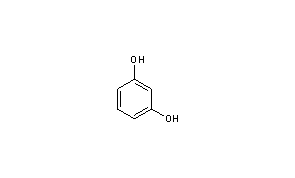
Resorcinol, also known as 1,3-dihydroxybenzene, is a aromatic compound that is commonly used in the production of resins, dyes, and pharmaceuticals. It is a white crystalline solid with a sweet, bitter taste and a characteristic sweet, pungent odor.
The condensed structural formula of resorcinol is C6H6O2. This formula represents the molecular structure of resorcinol, which is made up of six carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms. The carbon atoms are connected to each other and to the hydrogen atoms by single covalent bonds, forming a six-membered ring. The oxygen atoms are bonded to two of the carbon atoms in the ring, one of which is bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
The aromatic nature of resorcinol is due to the presence of the six-membered ring of carbon atoms, which is held together by alternating single and double bonds. This ring is conjugated, meaning that the electrons in the bonds are delocalized over the entire ring, giving the molecule enhanced stability.
Resorcinol has a number of important uses in various industries. It is used as a starting material for the synthesis of resins, such as phenol-formaldehyde resins, which are used in the production of adhesives, plastics, and coatings. It is also used as an intermediate in the production of dyes, such as sulfur dyes and vat dyes, which are used to color textiles, leather, and paper.
In the pharmaceutical industry, resorcinol is used as an active ingredient in a number of skin care products, such as acne medications and skin lighteners. It is also used as a disinfectant and astringent, and has been found to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Overall, resorcinol is a versatile chemical compound with a wide range of uses in various industries. Its condensed structural formula, C6H6O2, represents the molecular structure of this aromatic compound, which is characterized by a six-membered ring of carbon atoms held together by alternating single and double bonds.