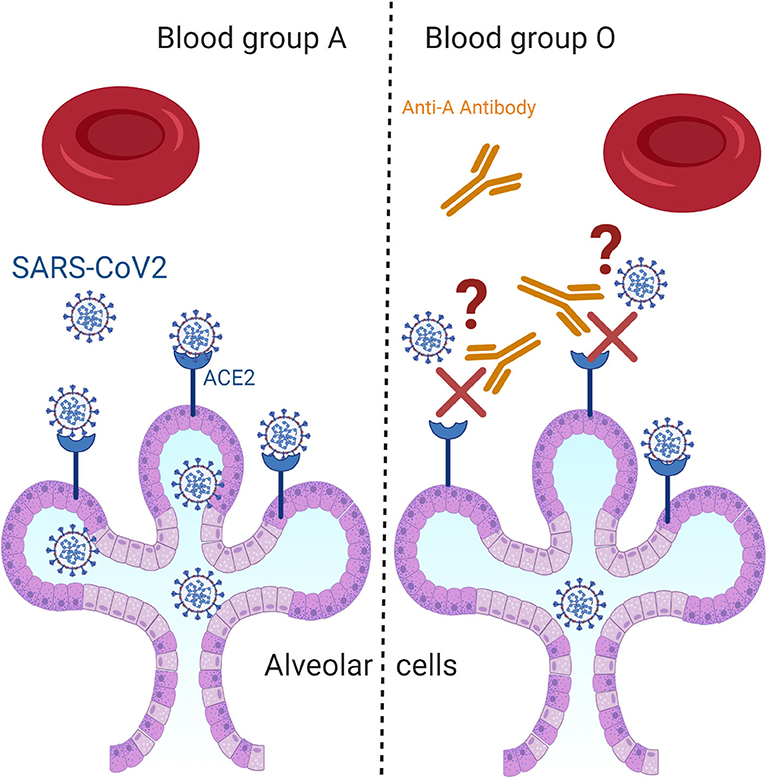
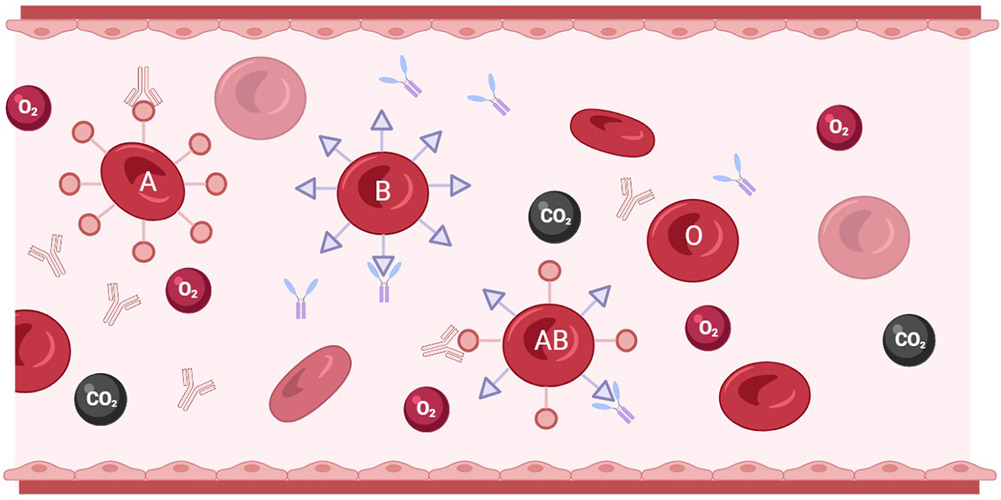
The Rh blood group system, also known as the Rh factor, is a classification system for red blood cells based on the presence or absence of a specific protein, called the RhD antigen, on the surface of the cells. The Rh factor is one of the most important blood group systems in transfusion medicine, as it can cause serious problems if mismatched during a transfusion.
The Rh blood group system is named after the rhesus monkey, in which the protein was first discovered. The presence of the RhD antigen is denoted by the positive (+) blood type, while the absence of the RhD antigen is denoted by the negative (-) blood type. Approximately 85% of people are RhD positive, while 15% are RhD negative.
One of the main issues with the Rh blood group system is the potential for hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), also known as erythroblastosis fetalis. This condition occurs when an RhD negative mother carries a fetus that is RhD positive, and the fetal red blood cells enter the mother's circulation during pregnancy or delivery. The mother's immune system recognizes the fetal RhD positive red blood cells as foreign and produces antibodies against them. If the mother becomes pregnant with another RhD positive fetus, these antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the fetal red blood cells, leading to anemia and other serious complications.
To prevent HDN, pregnant women who are RhD negative are given a prophylactic treatment called Rh immune globulin, which prevents the production of antibodies against the RhD antigen. This treatment is usually given after delivery, abortion, or miscarriage, and in some cases, it may be given during pregnancy to prevent the mother from developing antibodies in the first place.
In addition to HDN, mismatched Rh blood transfusions can also cause problems. If an RhD negative individual receives an RhD positive transfusion, they may develop antibodies against the RhD antigen, leading to hemolytic transfusion reactions. These reactions can be severe and may result in kidney damage, shock, and even death.
Overall, the Rh blood group system is an important factor to consider in transfusion medicine and pregnancy. It is essential that blood transfusions and prophylactic treatments are matched correctly to avoid serious complications.