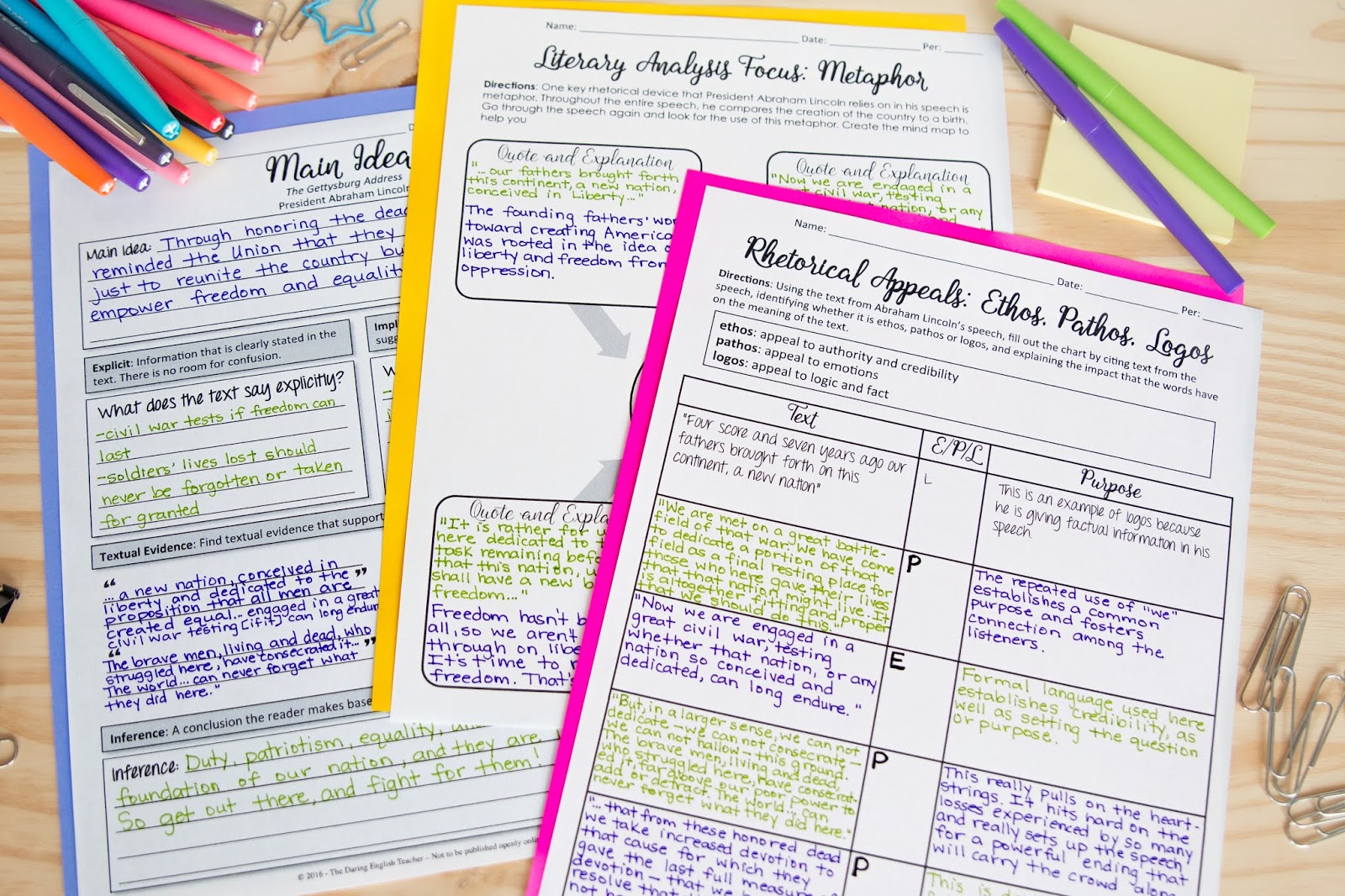
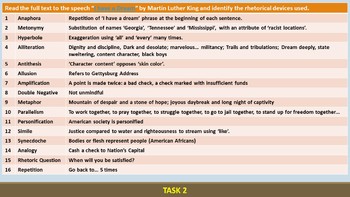
A rhetorical speech is a type of speech that is designed to persuade or influence an audience through the use of language and rhetorical techniques. Rhetorical speeches are often used in political campaigns, public debates, and other situations where it is important to sway the opinions of others.
One of the most important elements of a rhetorical speech is the use of rhetorical devices. These are language techniques that are used to appeal to the audience's emotions, values, and logic. Some common rhetorical devices include metaphors, analogies, and rhetorical questions.
Metaphors are figures of speech that compare two seemingly unrelated things in order to make a point. For example, a politician might say "our country is a ship, and I am the captain who will steer us to safety." This metaphor compares the country to a ship and the politician to a captain, in order to convey the idea that the politician is capable of leading the country.
Analogies are similar to metaphors, but they use more explicit comparisons between two things. For example, a speaker might say "just like a tree needs water to grow, a child needs love and support to thrive." This analogy compares the needs of a tree to the needs of a child, in order to make a point about the importance of nurturing and caring for children.
Rhetorical questions are questions that are asked for the purpose of making a point, rather than seeking an answer. For example, a speaker might say "how can we expect our children to succeed if we don't invest in their education?" This rhetorical question is meant to appeal to the audience's sense of fairness and justice, in order to persuade them to support educational policies.
Another important element of rhetorical speeches is the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. Ethos refers to the credibility or authority of the speaker. If a speaker is perceived as trustworthy and knowledgeable, they will be more likely to persuade their audience. Pathos refers to the emotional appeal of a speech. If a speaker can tap into the emotions of their audience, they will be more likely to persuade them. Logos refers to the logical appeal of a speech. If a speaker can present a well-reasoned argument, they will be more likely to persuade their audience.
In conclusion, rhetorical speeches are a powerful tool for persuasion and influence. By using rhetorical devices, appealing to ethos, pathos, and logos, and carefully crafting their language, speakers can effectively persuade their audience to support their ideas and take action.