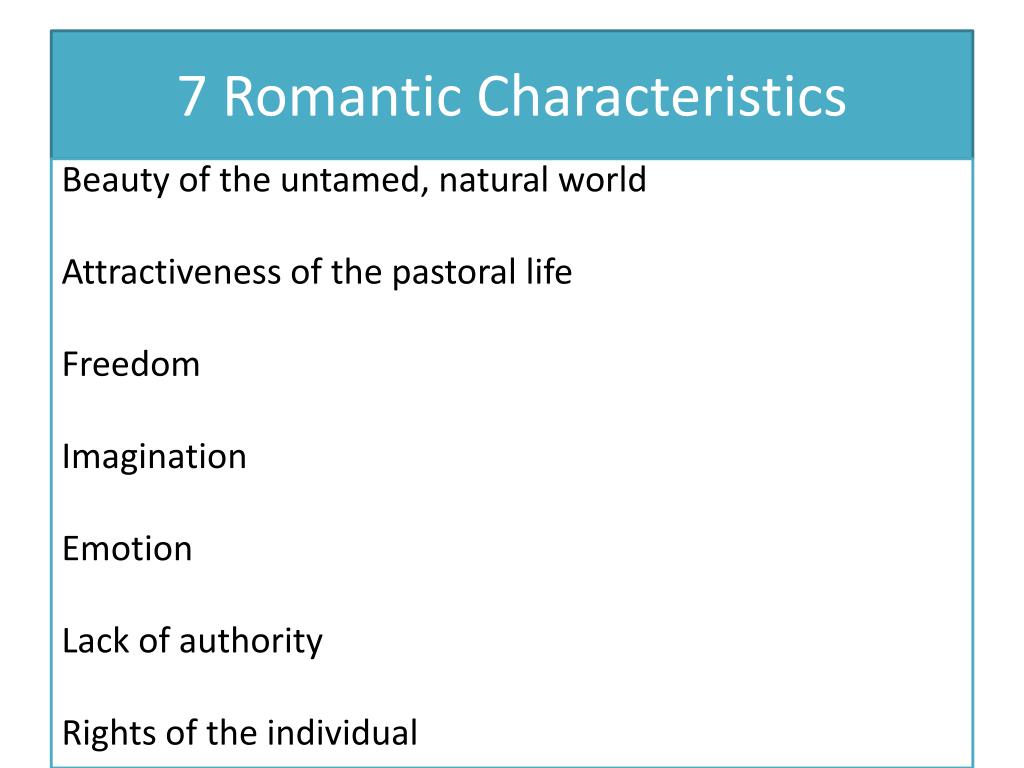
Romanticism was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It emphasized emotion, imagination, and individualism, as well as a reverence for nature and a belief in the inherent goodness of humanity. The Romantic movement had a significant influence on the arts and humanities, and it continues to shape contemporary culture and thought.
One of the defining characteristics of Romanticism was an emphasis on emotion and feelings. Romantic artists, writers, and musicians sought to capture and express intense emotional experiences, such as love, passion, longing, and sadness. They believed that emotions were a powerful force that could be harnessed to create art that was deeply moving and evocative.
Another key characteristic of Romanticism was a focus on the imagination and the creative process. Romantic artists and writers believed that the imagination was a limitless source of inspiration and that it should be given free rein in the creative process. They valued originality and creativity, and they often drew on their own personal experiences and emotions as the basis for their works.
In addition to its emphasis on emotion and imagination, Romanticism was also marked by a strong sense of individualism. Romantic artists and writers often celebrated the unique perspective and voice of the individual, and they rejected the strict rules and conventions that had governed art and literature in the past. They believed that each person had the right to express themselves freely and to create art that reflected their own experiences and viewpoints.
Romanticism was also characterized by a reverence for nature and a belief in its inherent goodness. Romantic artists and writers often depicted nature in their works as a source of beauty, peace, and inspiration. They saw nature as a reflection of the divine and believed that it had the power to heal and uplift the human spirit.
Overall, Romanticism was a movement that celebrated emotion, imagination, individualism, and nature. Its influence can still be seen in contemporary art, literature, and culture, and it continues to shape our understanding of the world and our place in it.