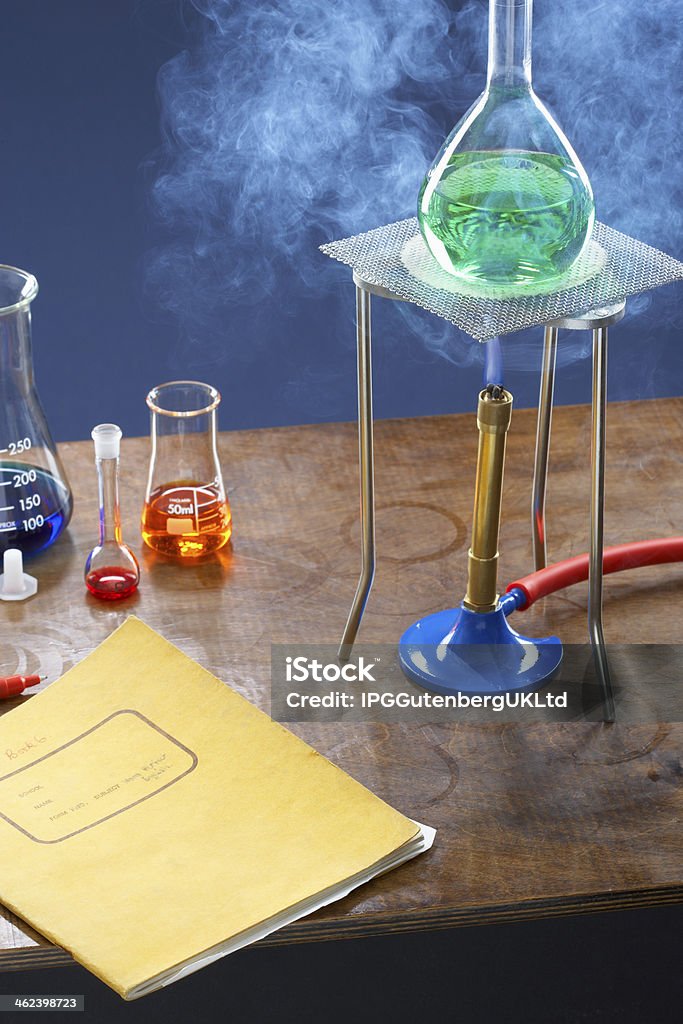
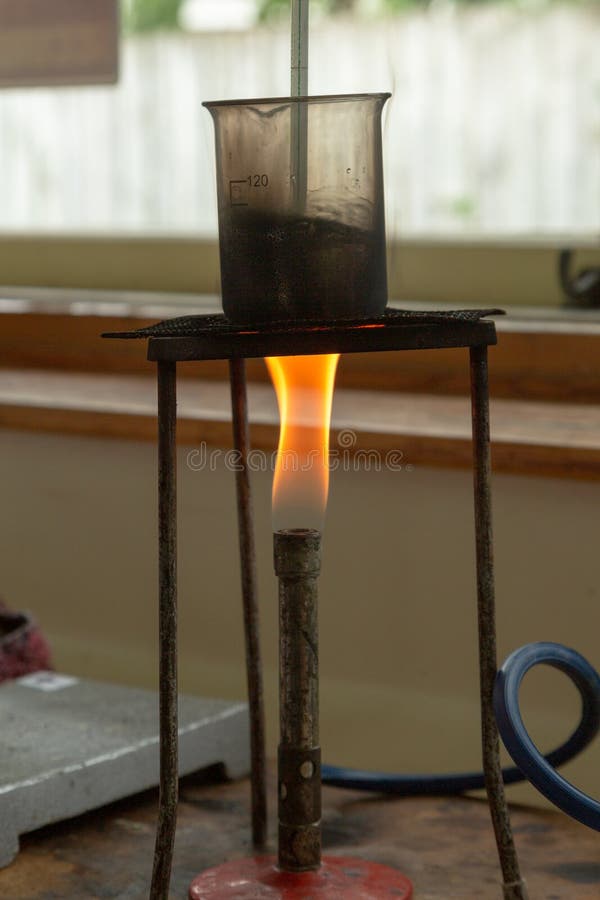
A Bunsen burner is a common piece of laboratory equipment that is used to heat substances for a variety of scientific purposes. It is named after its inventor, German chemist Robert Bunsen, who developed the burner in the mid-19th century.
The Bunsen burner is a simple but effective device that consists of a gas nozzle, a cylindrical barrel, and a metal base. The gas nozzle is connected to a gas line, which can be either natural gas or propane, and the barrel is used to adjust the flame size and shape. The metal base serves as a support for the burner and also helps to stabilize the flame.
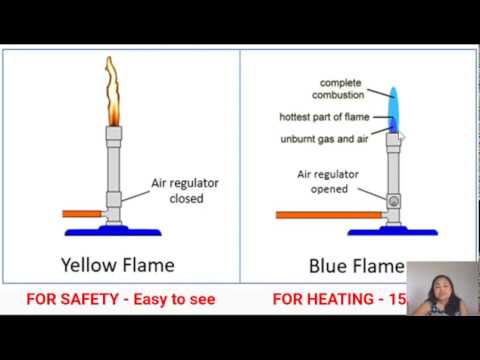
To use a Bunsen burner, the gas nozzle is first turned on and the barrel is adjusted to the desired flame size. The flame is then lit using a sparker or a lighter. Once lit, the Bunsen burner can be used to heat a variety of substances, including chemicals, metals, and glassware.
One of the main advantages of the Bunsen burner is its versatility. It can be used for a wide range of scientific experiments, including distillation, sterilization, and the preparation of solutions. It is also a useful tool for demonstrating chemical reactions, such as the combustion of a substance.
In addition to its scientific uses, the Bunsen burner has also found applications in other areas, such as cooking and metalworking. However, it is important to note that the Bunsen burner should be used with caution, as it produces high temperatures and can be a fire hazard if not used properly.
Overall, the Bunsen burner is an essential piece of equipment in the scientific community, and its simple design has made it a valuable tool for researchers and students for over 150 years.