Sensation, perception, and attention are three interconnected psychological processes that allow us to interact with the world around us. Sensation refers to the process by which our sensory receptors detect physical stimuli, such as light, sound, and touch, and transmit this information to the brain. Perception refers to the process by which the brain interprets and organizes this sensory information, giving it meaning and context. Attention, on the other hand, is the process by which we selectively focus on certain stimuli and filter out distractions.
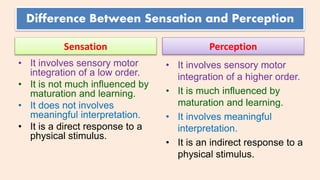
Sensation begins with the detection of physical stimuli by our sensory receptors, which are specialized cells that are sensitive to specific types of stimuli. For example, the retina in the eye contains photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to light, while the skin contains sensory receptors that are sensitive to touch, temperature, and pressure. When these receptors are stimulated by a physical stimulus, they generate an electrical signal that is transmitted to the brain through sensory nerves.
Once the brain receives this sensory information, it begins the process of perception, which involves organizing, interpreting, and giving meaning to the sensory data. This process is influenced by a number of factors, including past experiences, expectations, and attention. For example, if you see a picture of a familiar object, such as a chair, your brain will quickly recognize it as such because you have seen similar objects before and have stored this information in your memory. However, if you see an unfamiliar object, your brain may have to work harder to interpret and understand it.
Attention is the process by which we selectively focus on certain stimuli and filter out distractions. It is a limited resource, meaning that we can only pay attention to a certain amount of information at a time. We use attention to prioritize and process the most important or relevant stimuli, while ignoring or filtering out less important or irrelevant stimuli. For example, if you are trying to concentrate on a difficult task, you may use attention to filter out distractions such as background noise or irrelevant thoughts.
In conclusion, sensation, perception, and attention are important psychological processes that allow us to interact with the world around us. Sensation involves the detection of physical stimuli by our sensory receptors, perception involves the interpretation and organization of this sensory information, and attention involves the selective focus on certain stimuli and the filtering out of distractions. Together, these processes enable us to perceive and make sense of the world around us.