A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi.
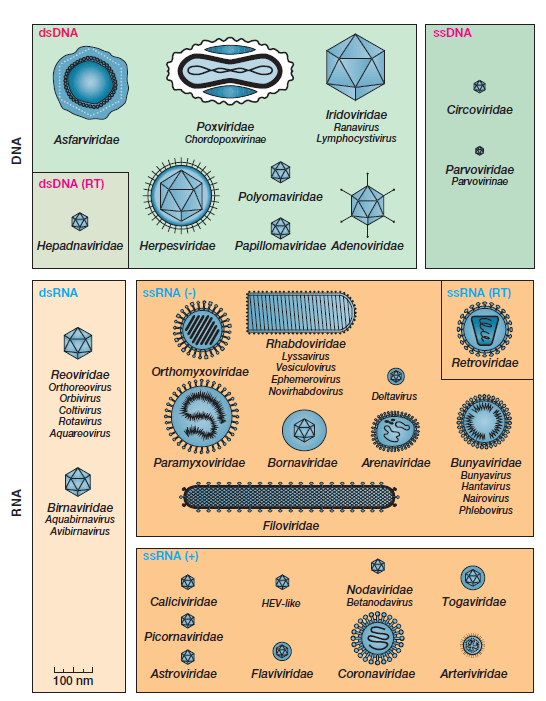
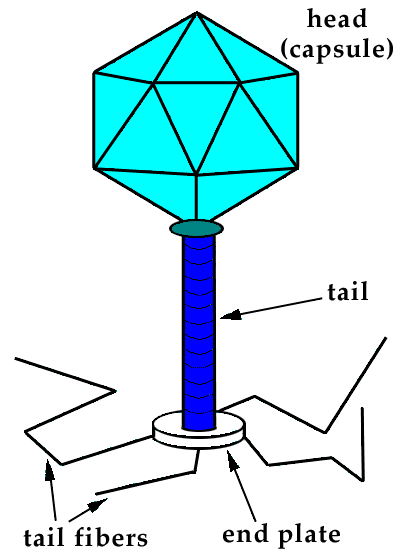
Viruses are much smaller than cells and can only be seen with the aid of a microscope. They are usually composed of a protein coat, called the capsid, which surrounds their genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA.
Viruses can cause a wide range of diseases in humans, ranging from the common cold to more serious illnesses such as AIDS and Ebola. They can also cause diseases in animals and plants.
Viruses are transmitted from one host to another through various means, including direct contact, respiratory droplets, and through vectors such as mosquitoes and ticks.
Vaccines are a crucial tool in preventing viral infections and are available for many viruses. Antiviral drugs can also be used to treat viral infections, although the effectiveness of these drugs can vary depending on the specific virus.
In conclusion, viruses are small infectious agents that can cause a wide range of diseases in humans and other organisms. They are transmitted through various means and can be prevented through vaccination and treated with antiviral drugs.
Notes on Viruses: Meaning, Size and Structure

A head with large capsomeres individual protein subunits of capsids at each apex of the hexagon; it has no tail Fig. Papova Viruses: Papova from pa, papilloma, po, polyoma, va, vacuolaling agent Viridae family comprises of papilloma virus of man and rabbits, polyoma virus of mice and simian virus 40 SV 40 — the vacuolating agent virus of rhesus monkeys. ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides a short note on Miscellaneous Viruses. Xylem is generally less affected by virus than is parenchyma or phloem, but tyloses and formation of gum have been described in the xylem of plants infected with viruses. The protein coat of the phage remains outside the cell.
Virus

Viruses are composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. Cyanophages: These are viral agents that attack a wide range of blue-green algae. These viral particles, also known as virions, consist of: i the genetic material made from either DNA or RNA, long molecules that carry genetic information; ii a protein coat, called the capsid, which surrounds and protects the genetic material; and in some cases iii an envelope of lipids that surrounds the protein coat. The persistent viruses retain infectivity for a long period of time and there is delay in the development of infective power. Host range and symptoms are studied. Matthews' Plant Virology Fourthed.