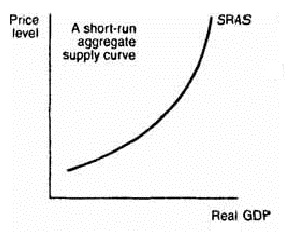
The short run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price level of goods and services in an economy and the quantity of output produced by firms in that economy. In the short run, firms are able to adjust the prices of their goods and services, but they are unable to alter the quantity of labor and capital they have available for production.
The SRAS curve slopes upward, indicating that as the price level increases, firms are willing to produce and sell more goods and services. This is because as the price of goods and services rises, firms can expect to earn higher profits, which incentivizes them to increase production. However, the SRAS curve is not perfectly elastic, meaning that there is a limit to the extent to which firms can increase production in response to higher prices.
One key determinant of the slope of the SRAS curve is the degree of price stickiness in the economy. Price stickiness refers to the reluctance of firms to adjust their prices in response to changes in demand or supply conditions. If firms are unwilling to adjust their prices in the short run, the SRAS curve will be relatively steep, indicating that only a significant increase in the price level will lead to a significant increase in production. On the other hand, if firms are more willing to adjust their prices in the short run, the SRAS curve will be relatively flat, indicating that even a small increase in the price level will lead to a significant increase in production.
In addition to price stickiness, the slope of the SRAS curve can also be influenced by the availability of production inputs such as labor and capital. If these inputs are in short supply, firms may not be able to increase production as quickly in response to higher prices, leading to a steeper SRAS curve. On the other hand, if production inputs are abundant, firms may be able to increase production more quickly in response to higher prices, leading to a flatter SRAS curve.
Overall, the SRAS curve is an important tool for understanding the relationship between the price level and the quantity of output produced in an economy in the short run. It is a useful tool for policymakers and analysts who want to understand how changes in the price level might affect the level of economic activity in the short run.
Aggregate Supply Explained: What It Is, How It Works

An increase in labor force participation helps the economy produce more over time. The short run may be two months or an entire year. On the other hand, a drop in the economy's capital stock affects productivity and the number of goods and services provided, pushing the long-run aggregate- supply curve to the left. When an economy experiences a rise in its capital stock, this enhances productivity, and as a result, more products and services can be delivered. An increase in the price of raw materials meant that the cost for many firms increased as well. Thus, it will become a short run production based on production planning by the firm. A decrease can imply inflation.
Aggregate Supply Curve and Definition
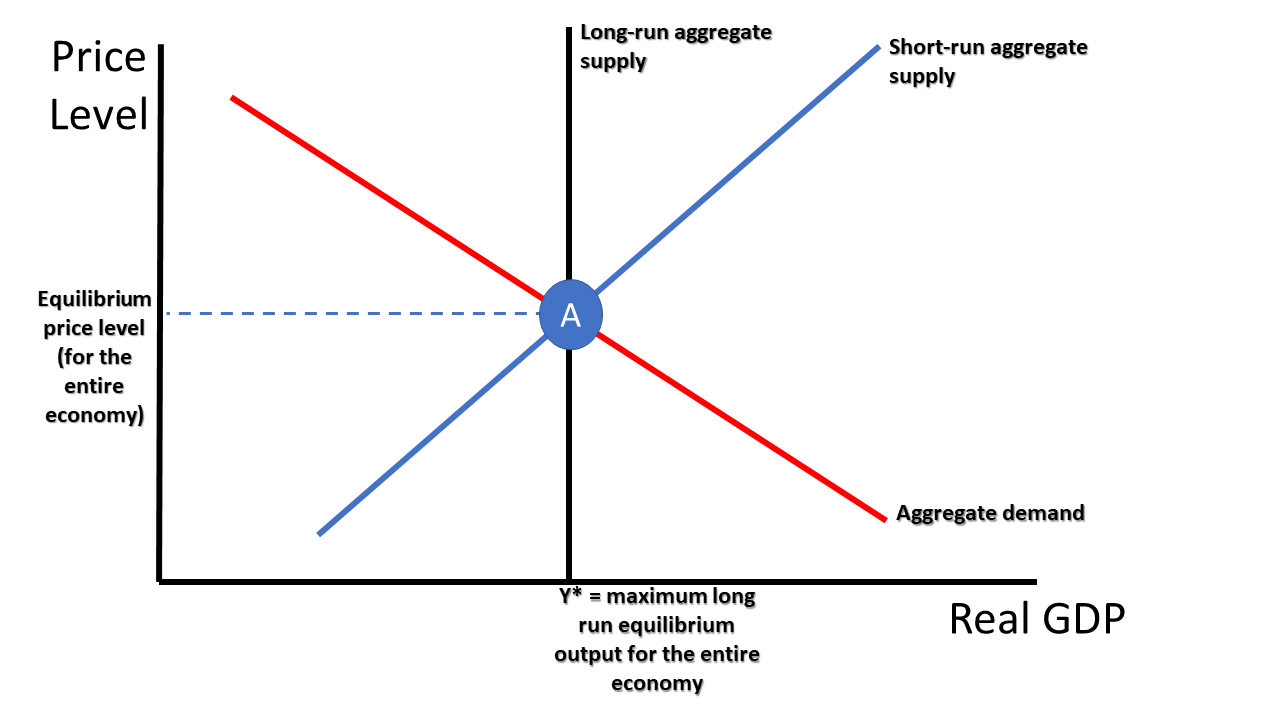
Thus, the supply curve of an industry depicts the various quantities of the product offered for sale by the industry at various prices at a given time. The reason for that is that firms do not change their output in the long run, as resources adjust to the change in price. Misperception theory: This theory holds that when a seller sees the price of its products decline, it makes an erroneous assumption that their relative prices have also declined. Thus, advancements in technology can help boost the production of goods. Determine the effect on the supply of Good X for 2022-2023. Vertical Long Run of Slope As said earlier, the aggregate supply curve is completely vertical in the long run.
Aggregate Supply (AS) Curve
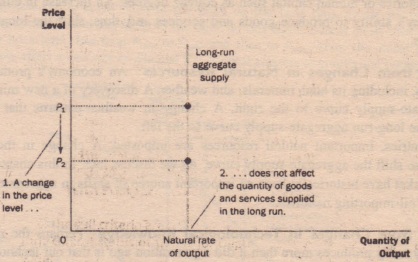
Natural Resources If new natural resources are discovered, the aggregate supply curve will shift to the right because production can increase. Short run aggregate supply is the overall production in an economy during the short run. Shifts in the aggregate supply curve include changes in the labor, capital, natural resources, technological knowledge, and expectation of price levels. When an economy experiences technological advancement, it will cause the long-run aggregate supply. So the However, there is an overall surge of 1% in the UK price level, which also increases the selling prices of perfumes to £101. Both the SRAS and LRAS will increase. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment.
Short Run Aggregate Supply Concept & Curve

Long-run aggregate supply refers to the total amount of production in an economy given that its full resources are employed. The LSC slopes downwards to the right which means that the additional supplies of the output are forthcoming at lower prices, since both the marginal cost and average cost have fallen owing to cheaper supplies of the productive resources. With that in mind, we can then define the long-run aggregate supply LRAS as a concept that represents the optimum output that can be produced by an economy when it utilizes all its factors of production and therefore operates at full employment. It consists of four main components: labor force, capital, natural resources, entrepreneurial ability, and technological progress. However, the demand for cakes increases to approximately 1000 a day during the Christmas week.
Short
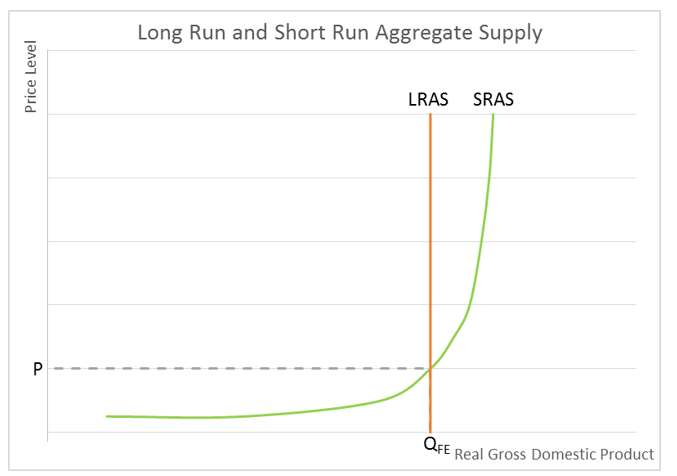
This means that whatever the output along the X-axis, price is the same OP where the marginal cost and average cost are equal. A Right or Downward Shift When that curve shifts to the right or downwards, supply increases. In this example, the lower aggregate supply could lead to demand exceeding output. That is because it directly improves productivity allowing for more goods and services to be produced using the same labor and capital. The amount of capital in the bank, the space and machines where sunglasses are made and possibly the vendor arrangements that provide materials to build the glasses are all things that require time to change. These include technological innovations, changes in labor size and quality, changes in production costs, availability of resources, subsidies, changes in wages and taxes, and the current inflation level.
Long Run Aggregate Supply: Definition, Examples & Curve
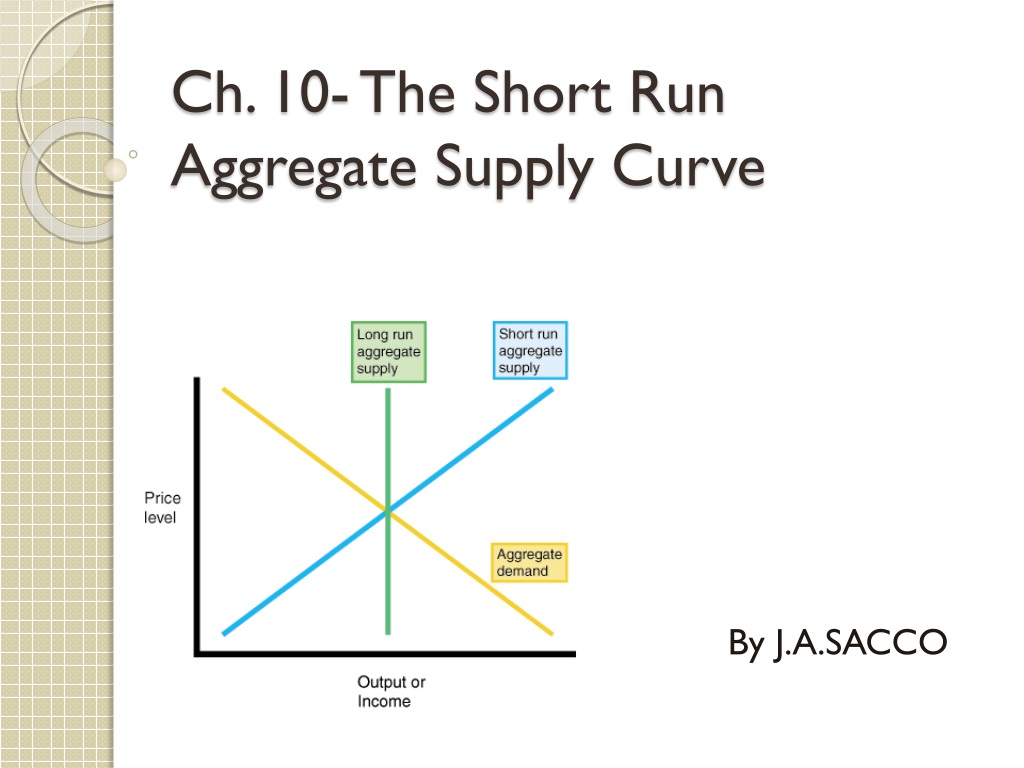
In the long run, the aggregate supply curve is vertical, but the aggregate supply curve will be upward sloping in the short run. On the other hand, depleting natural resources will result in lower potential output shifting the LRAS to the left. The shape of supply curve, in the long run, will depend on whether the industry is subject to the law of constant return i. This goes back to the notion that the short-run curve is upward sloping. It will convert the whole production arrangement into a long run production. Figure 2 shows the shifts in the SRAS curve. Short-run AS determines the output while the price is constant.