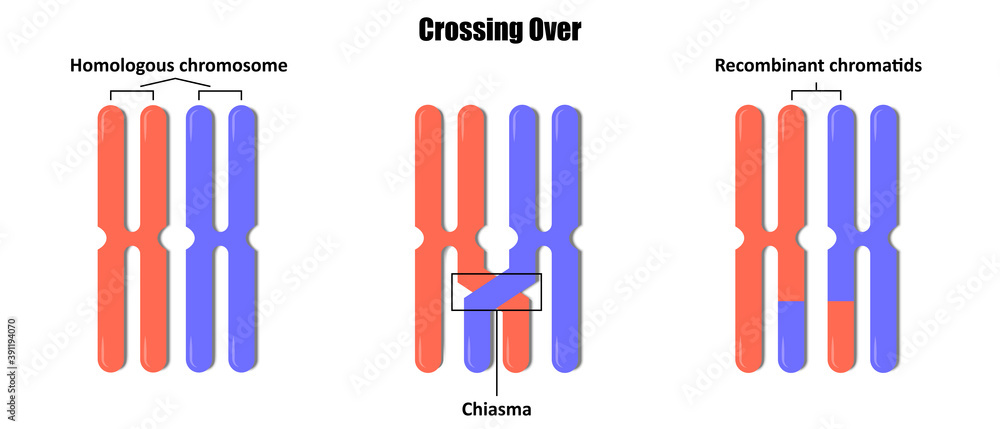
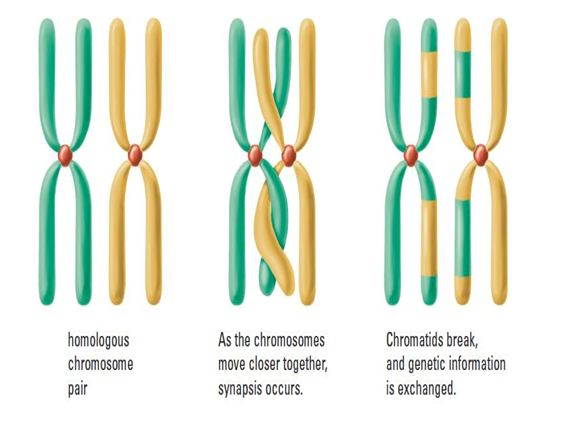
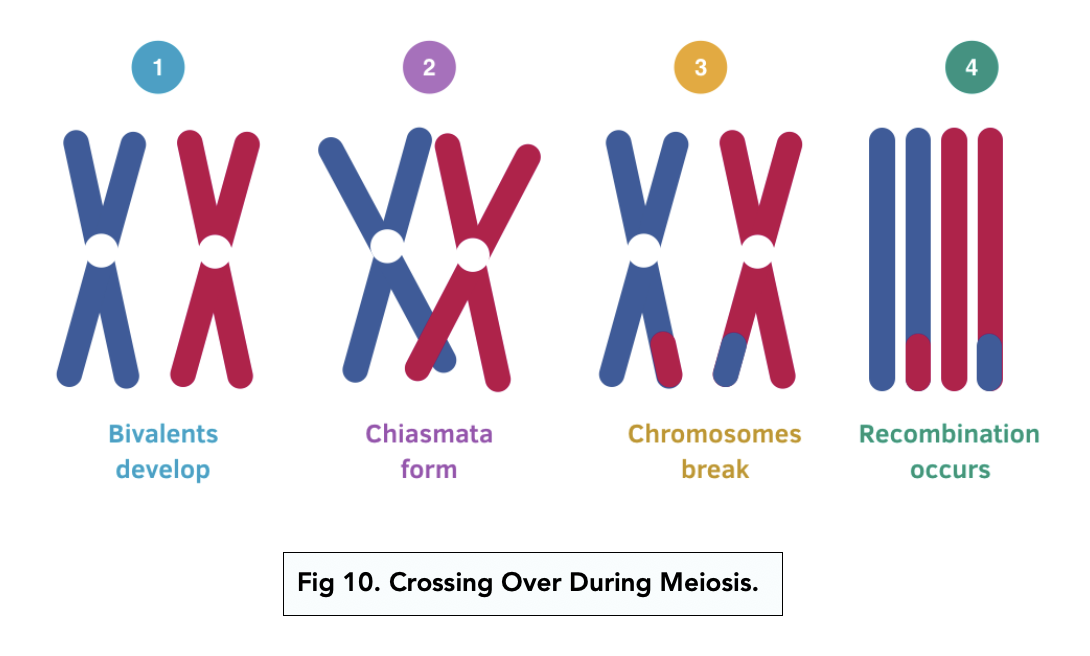
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, including animals and plants. One of the key features of meiosis is the process of crossing over, which plays a crucial role in the production of genetically diverse offspring.
During meiosis, cells divide into four genetically unique daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. This is accomplished through two rounds of cell division, known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Crossing over occurs during meiosis I, and involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that contain the same genes, but may have different versions of those genes, known as alleles.
During crossing over, a segment of DNA from one chromosome is exchanged with a corresponding segment from the other chromosome. This process creates new combinations of alleles on the resulting chromosomes, increasing the genetic diversity of the daughter cells.
The significance of crossing over cannot be overstated. Without this process, the genetic diversity of a population would be greatly reduced, leading to a decrease in the overall health and fitness of the population. This is because crossing over allows for the creation of new combinations of alleles, which can provide a selective advantage in different environments.
For example, in a population of plants that is exposed to a new insect pest, some individuals may have alleles that provide resistance to the pest, while others may not. If crossing over did not occur, all of the offspring would have the same combination of alleles as their parents, and it is unlikely that any of them would have the alleles for pest resistance. However, if crossing over does occur, it is possible that some of the offspring will have the alleles for pest resistance, increasing the chances of survival for those individuals.
In addition to increasing genetic diversity, crossing over also plays a role in the repair of genetic errors. If a mistake occurs during DNA replication, it can result in a genetic mutation that may have negative consequences for the organism. Crossing over allows for the correction of these errors by exchanging the incorrect DNA segment with a correct one from the homologous chromosome.
In conclusion, crossing over is a crucial process in meiosis that plays a significant role in the production of genetically diverse and healthy offspring. Its importance cannot be understated, as it allows for the creation of new combinations of alleles that can provide a selective advantage in different environments, as well as the repair of genetic errors.