Social change refers to the transformation of culture, behavior, social institutions, and social structure over time. It can refer to small or large-scale changes, and can be driven by various factors such as technological advances, economic shifts, political movements, or cultural and social movements.
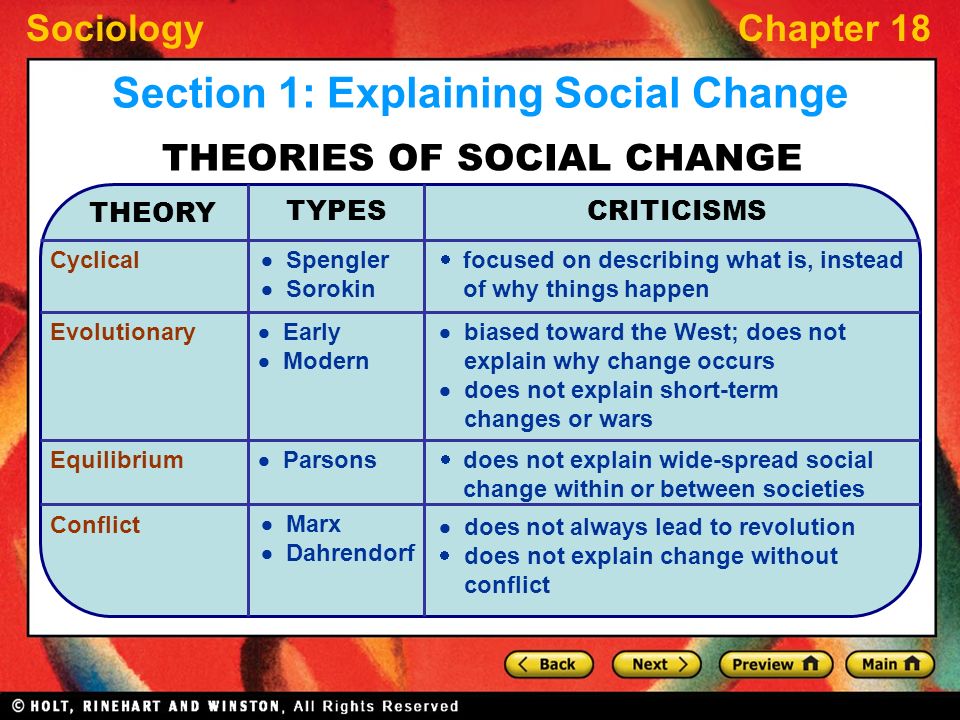
There are many different theories that have been developed to explain the process of social change. One of the most well-known theories is the theory of evolution, which suggests that social change occurs gradually over time through a process of natural selection. According to this theory, societies change in response to changing environmental conditions and through competition with other societies.
Another theory of social change is the theory of social evolution, which suggests that societies progress through a series of stages, from simple to complex, as they adapt to changing environmental and technological conditions. This theory is often associated with the work of 19th-century sociologist Herbert Spencer, who argued that societies evolve from a state of "barbarism" to a state of "civilization."
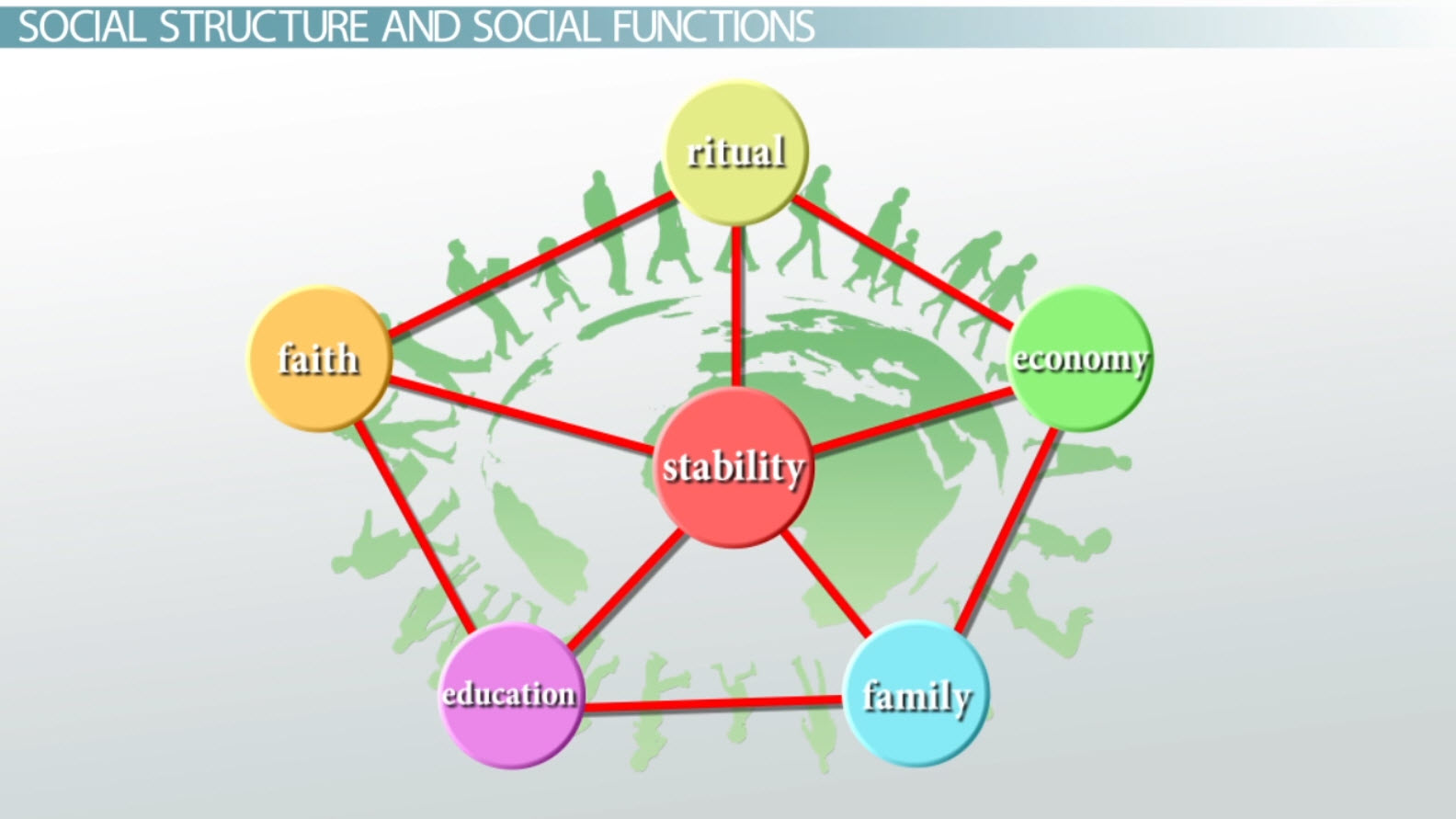
A third theory of social change is the theory of structural functionalism, which suggests that social change occurs as a result of the balance of opposing forces within a society. According to this theory, social change is driven by conflicts and tensions within a society, as different groups compete for resources and power.
Another important theory of social change is the theory of social conflict, which suggests that social change is driven by power struggles between different groups within a society. According to this theory, social change is the result of the struggle between dominant and subordinate groups, as the dominant group tries to maintain its power and the subordinate group tries to challenge and change the existing social order.
There are also many other theories of social change, including the theory of modernization, the theory of social construction, and the theory of cultural diffusion. Each of these theories offers a different perspective on the process of social change and the factors that drive it.
Overall, social change is a complex and multifaceted process that is influenced by a wide range of factors. Understanding the different theories of social change can help us to better understand the ways in which societies change and adapt over time.
Theories of Social Change: Meaning, Nature and Processes

Years ago, when checking out at a grocery store, the cashier would ask, 'Paper or plastic? This later led to more complex theories since social change is ever-present , by people like Karl Marx, which expanded on social change to ideas like communism, socialism, and slavery. Some suggest that since social exchange theory was crafted based on the White middle class, it neglects the realities of other race groups. Most mammals are equipped by heredity with special talents, skills, and instincts which enable them to meet their basic needs, and to adapt themselves to their environment. If an employee doesn't feel that their effort is being reciprocated from higher-ups, this can affect their work. It is not enough to say that social change has occurred because such a vague statement does not indicate anything beyond what is inevitable. Benefits Rewards are the amount of benefit that someone receives from a relationship. When putting together a ToC, you must clearly define what you desire to achieve.
What is the Theory of Change? Definition & Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/definition-of-social-construct-1448922_final1-6fe378481ec5483ea8d61e1ca1d20234.png)
But eventually, as a result of forces that are internal within the culture itself, there will be a shift of direction and a new period of development will be ushered in. For decades, sociologists have grappled with different models and ideas. These indicators help operationalize the outcomes. Principle 3: Social interaction involves two parties, each exchanging a reward needed by the other person: in order to get rewards, people must exchange something better Burns, 1973. You may think that's great, but wonder why you should care, why you should take time out of your incredibly busy schedule to take action and more importantly, how you can even go about helping to create positive social change. Thus, in the development of languages where the process of differentiation has been stressed we have many disconcerting facts. These institutions question how you can serve your community, and how your community fits into society-and if your society needs to change to serve your community, what tools you'll need to make that dream a reality.
Lewin’s Change Theory (Definition + Examples)

He challenges the widespread belief that the development of productive forces is by itself a threat to the environment, arguing that only specific technologies, not technology as such, lead to environmental degradation. Principle 2: People seek to maximize rewards and minimize costs in pursuit of the greatest profit: this reflects a belief that people are generally motivated by their own self-interest, regardless of the decision. In order to make a sweeping change throughout an organization, you need planning, communication, and consistency. For example, an employer can withhold a bonus from an employee until he has met a particular work standard. Walking into the pool slowly will be a painful and much longer process.
Social Change

They are of the opinion that change disrupts the orderly functioning of the system. This meant that the domains no longer restricted their production to meet their own needs. That particular perspective may single out those conditions which are, so to say, decisive. In addition, we learned that there are many sources of social change, such as culture, ideas, inequality, conflict, and demographic change. Most often we do not recognise the change taking place because at that point in time it is not very significant or observable. It seems that even the newest technology is outdated a few days after you purchase it! The first assumption is that humans tend to seek out rewards and avoid punishments.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/definition-of-social-construct-1448922_final1-6fe378481ec5483ea8d61e1ca1d20234.png)