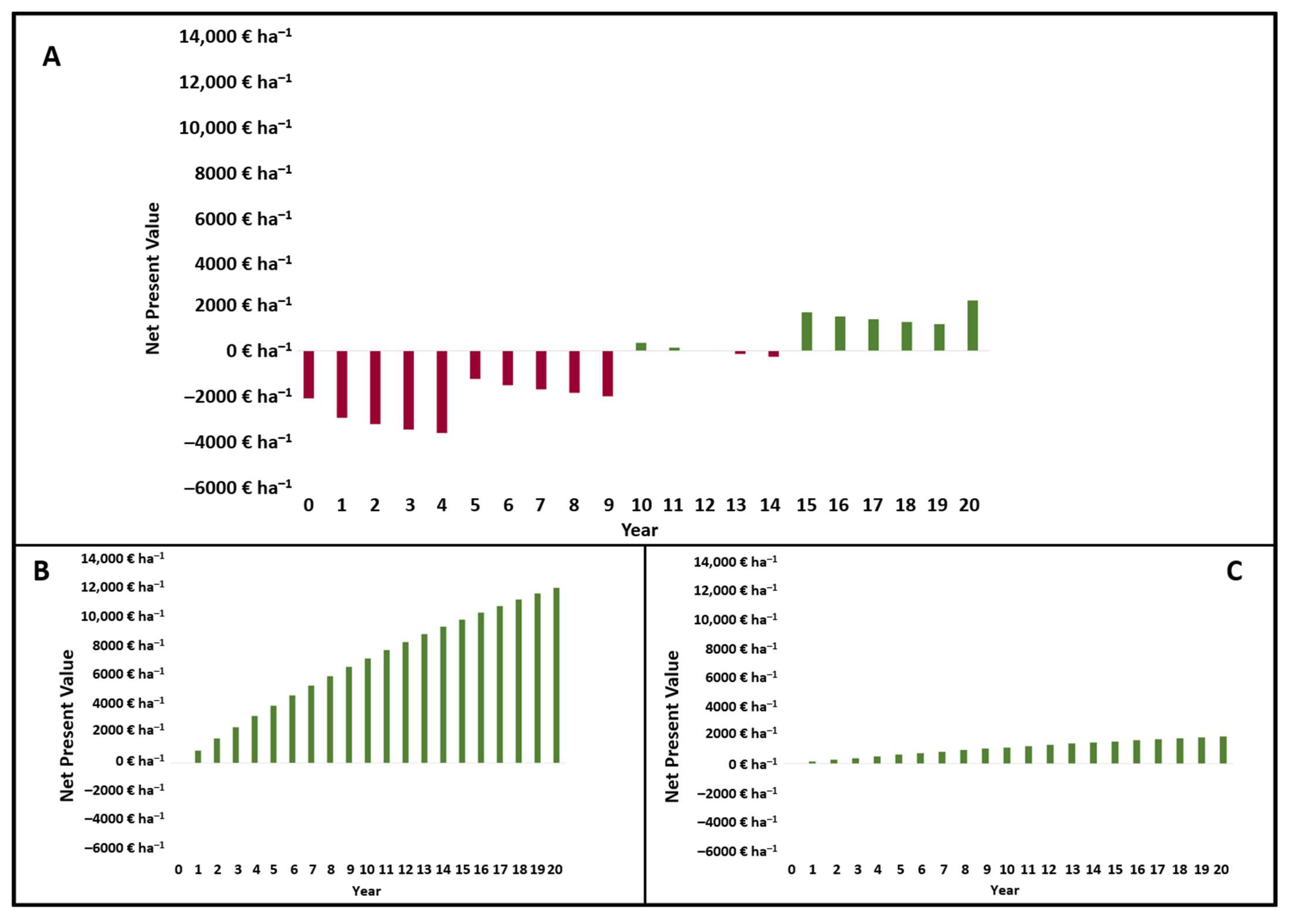
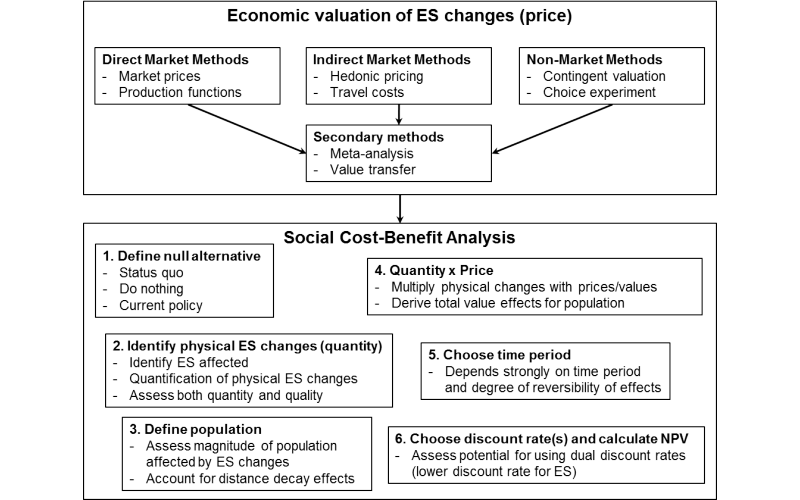
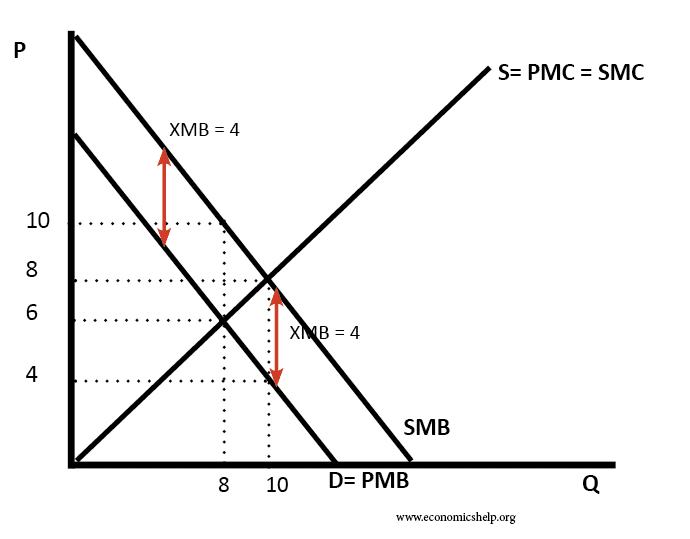
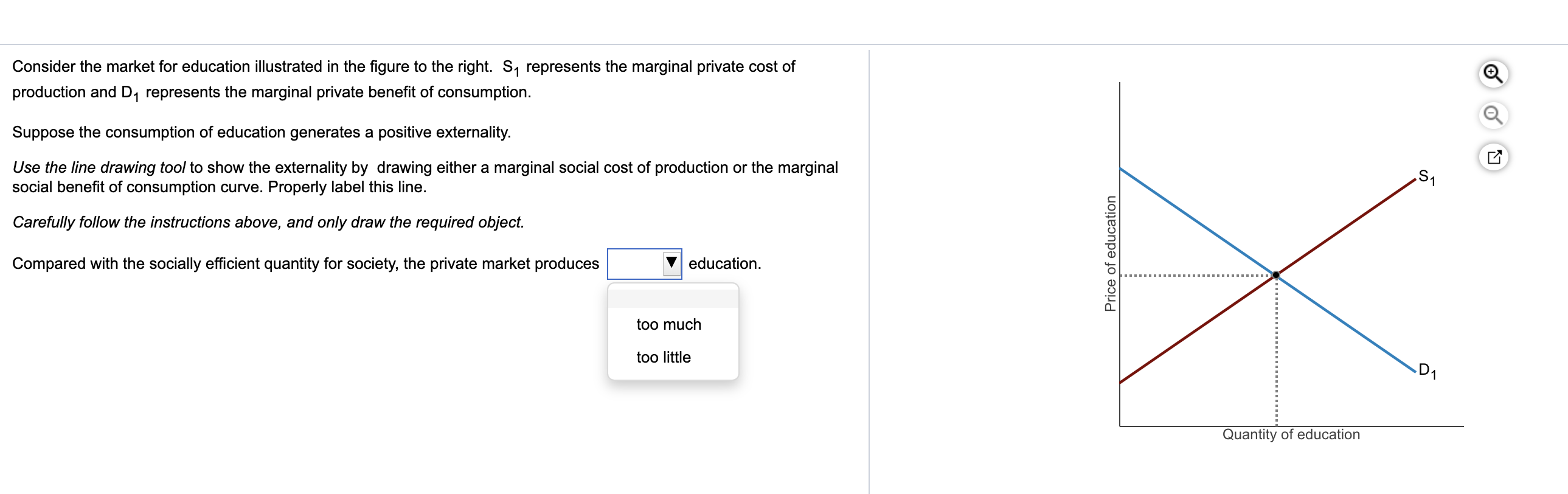
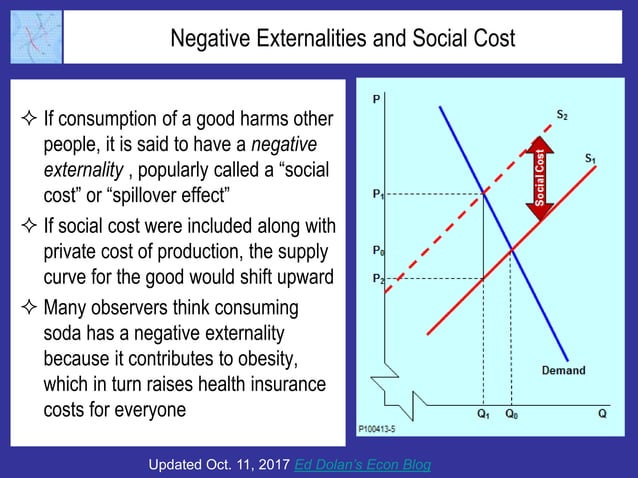
The social cost of production refers to the total cost of producing a good or service, including both private costs incurred by the producer and external costs imposed on society. These external costs, also known as externalities, can include environmental damage, negative impacts on public health, and other consequences that are not reflected in the market price of the good or service.
One example of a social cost of production is the environmental damage caused by certain forms of energy production. For instance, the extraction and use of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas can have significant negative impacts on the environment, including air and water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. These externalities are not typically taken into account when the market price of fossil fuels is determined, leading to a misalignment between the true cost of production and the price paid by consumers.
Another example of a social cost of production is the negative impact of certain manufacturing processes on public health. For example, the production of chemicals and other toxic substances can have negative effects on the health of workers and local communities, as well as on the environment. These costs are not typically reflected in the market price of the goods produced, leading to an undervaluation of the true cost of production.
The social cost of production can also include indirect costs, such as the cost of traffic congestion and accidents resulting from the production and transportation of goods. These costs may not be directly incurred by the producer, but they can still have significant impacts on society and the environment.
To address the social cost of production, governments and policymakers may use a variety of tools, such as taxes, subsidies, and regulations. For example, a government may impose a tax on goods or activities that have significant negative externalities, such as a carbon tax on fossil fuel use. This can help to internalize the external costs of production and encourage producers to adopt more sustainable practices.
In conclusion, the social cost of production refers to the total cost of producing a good or service, including both private costs and external costs imposed on society. These externalities can have significant negative impacts on the environment, public health, and other areas, and can be addressed through a variety of policy tools. By taking into account the full cost of production, governments and policymakers can help to ensure that the market reflects the true cost of goods and services, and encourage more sustainable and responsible production practices.