APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association) are two of the most commonly used citation styles in academic writing. While both styles provide guidelines for citing sources and formatting papers, there are some key differences between the two.
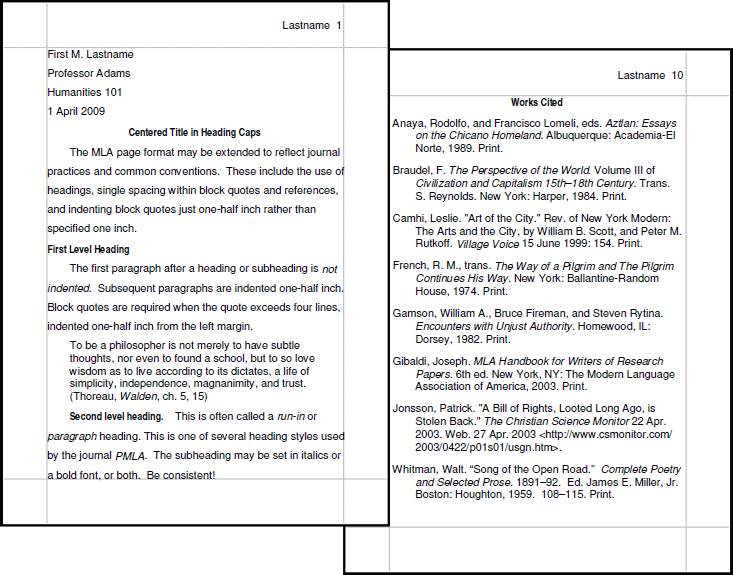
One of the main differences between APA and MLA is the way they format in-text citations. In APA style, in-text citations include the author's last name and the year of publication, with the page number in parentheses if quoting directly from a source. For example: (Smith, 2020, p. 34). In MLA style, in-text citations include the author's last name and the page number, with the year of publication in parentheses if quoting directly from a source. For example: (Smith 34).
Another difference between APA and MLA is the way they format the reference list at the end of a paper. In APA style, the reference list is alphabetized and the entries include the author's last name, first initial, publication year, title of the work, and publication information. The reference list is double-spaced and the entries are formatted with a hanging indent. In MLA style, the reference list is also alphabetized, but the entries include the author's last name, first name, title of the work, and publication information. The reference list is also double-spaced, but the entries are not formatted with a hanging indent.
In terms of the overall format of a paper, APA style requires a title page with a running head, an abstract, and a reference list. It also has specific guidelines for headings and the use of statistics. MLA style does not require a title page or abstract, and it has specific guidelines for the use of headings and the formatting of quotes.
Ultimately, the choice of which citation style to use depends on the specific requirements of the assignment or the preferences of the instructor or publication. It is important for writers to be familiar with both APA and MLA style and to use the appropriate style consistently throughout their work.
Plot segmentation is a technique used in storytelling to divide a story into distinct parts or segments. This can be done for a variety of reasons, including to increase suspense, to reveal character development, or to provide a sense of structure to the story.
One common method of plot segmentation is to divide a story into three acts. The first act introduces the main characters and sets the stage for the conflict that will drive the rest of the story. The second act is typically where the conflict reaches its climax, and the third act is where the resolution is achieved.
Another way to segment a plot is to use a series of flashbacks or flash-forwards to reveal information about the characters or events that have occurred in the past or will occur in the future. This can be a useful tool for adding depth and complexity to a story, as it allows the reader to see how events in the present are connected to events in the past or future.
Plot segmentation can also be used to create tension and suspense in a story. By breaking the story into smaller segments, the writer can build up the tension gradually, leaving the reader wondering what will happen next. This can be especially effective in mysteries or thrillers, where the reader is trying to piece together the puzzle of what happened or who is responsible for a particular event.
Overall, plot segmentation is a powerful tool for writers to create a sense of structure and build tension in a story. By dividing the story into distinct parts, writers can reveal information at the right moments, creating a sense of momentum and keeping the reader engaged.
A song analysis paper example might involve analyzing the lyrics of a particular song in order to understand its deeper meaning or message. To begin, it would be helpful to provide some background information about the song, including the artist, the album it appears on, and the year it was released. This context can help to provide a better understanding of the cultural and historical influences that may have shaped the song's themes and content.
Next, the essay could delve into a detailed analysis of the lyrics themselves. This might involve breaking down the lyrics line by line and examining their individual meanings and symbolism. It might also involve looking at the overall structure and flow of the song, including the use of repetition, imagery, and figurative language.
In addition to analyzing the lyrics, it might be helpful to consider the music itself, including the instrumentation, tempo, and overall tone of the song. The way that the music and lyrics work together can often add depth and meaning to the song, and can help to convey the artist's intended message in a more powerful way.
Finally, the essay could discuss the broader themes or messages that the song conveys, and how it connects to the artist's overall body of work or to broader social or cultural issues. This might involve examining the song in the context of the artist's personal experiences or perspectives, as well as considering how it speaks to broader themes or issues that are relevant to the world at large.
Overall, a song analysis paper example might be a detailed and thoughtful exploration of a particular song, examining its lyrics, music, and overall message in order to understand its deeper meaning and significance.