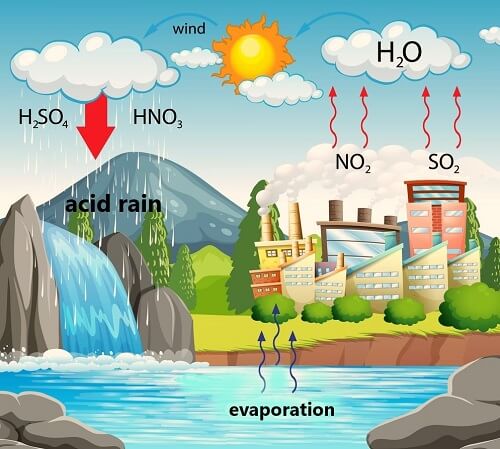
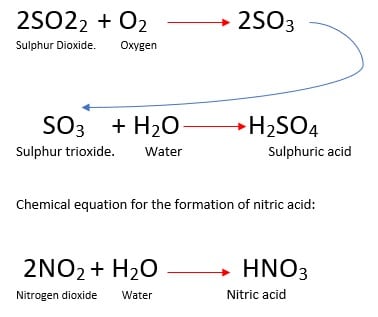
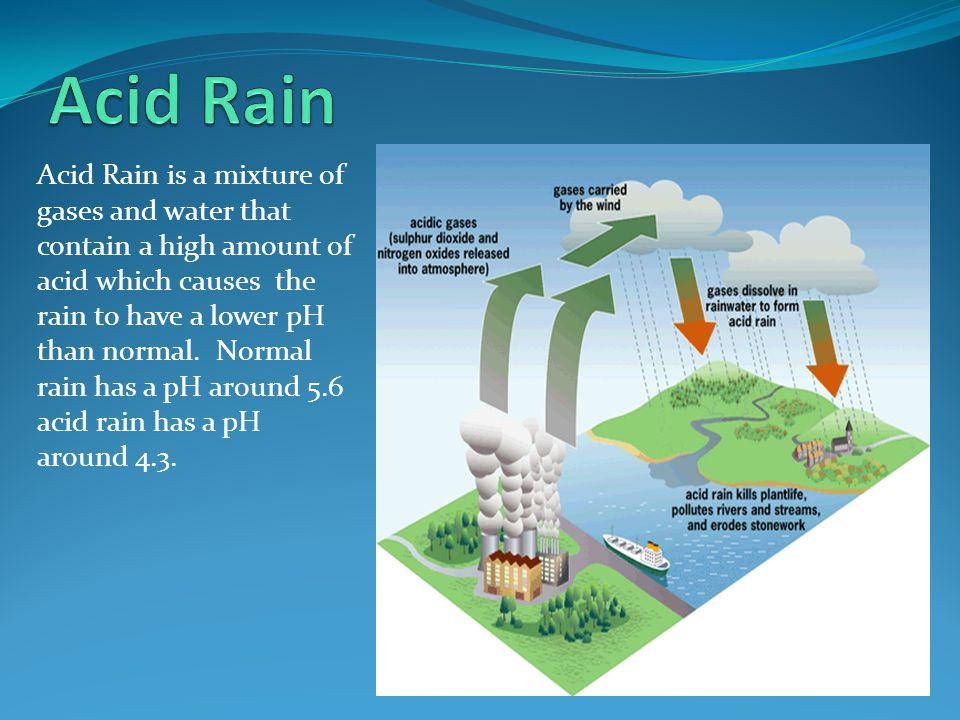
Acid rain is a type of air pollution that occurs when sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are released into the atmosphere and react with water, oxygen, and other substances to form acidic compounds. These compounds can then be carried by wind and precipitation and deposited onto the land and into bodies of water, causing significant damage to the environment and human health.
One of the main causes of acid rain is the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, which releases large amounts of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the air. The transportation sector, particularly the use of automobiles, is a major contributor to acid rain, as is the electricity generation industry. In addition, industrial processes, such as the production of cement and the processing of metal ores, also contribute to the emission of these pollutants.
The effects of acid rain are wide-ranging and can have serious consequences for the environment and human health. Acid rain can damage forests, crops, and other vegetation, as well as harm wildlife. It can also contaminate and degrade bodies of water, reducing their pH level and making them toxic to aquatic life. Acid rain can also corrode buildings and other infrastructure, causing significant financial damage.
In addition to these environmental impacts, acid rain can also have negative health effects on humans. The inhalation of acid rain can irritate the respiratory system and cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis. It can also damage crops and reduce crop yields, leading to food shortages and increased food prices.
There are several measures that can be taken to reduce the occurrence of acid rain and mitigate its effects. One of the most effective ways to do this is by reducing the emission of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which can be achieved through the use of cleaner technologies and the implementation of stricter emissions standards. Governments and industries can also work to promote the use of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, which do not produce the pollutants that contribute to acid rain.
In conclusion, acid rain is a significant environmental and public health issue that is caused by the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. Its effects on the environment and human health can be severe, and it is important that steps are taken to reduce its occurrence and mitigate its effects. By working together, governments, industries, and individuals can take action to protect the environment and improve public health.