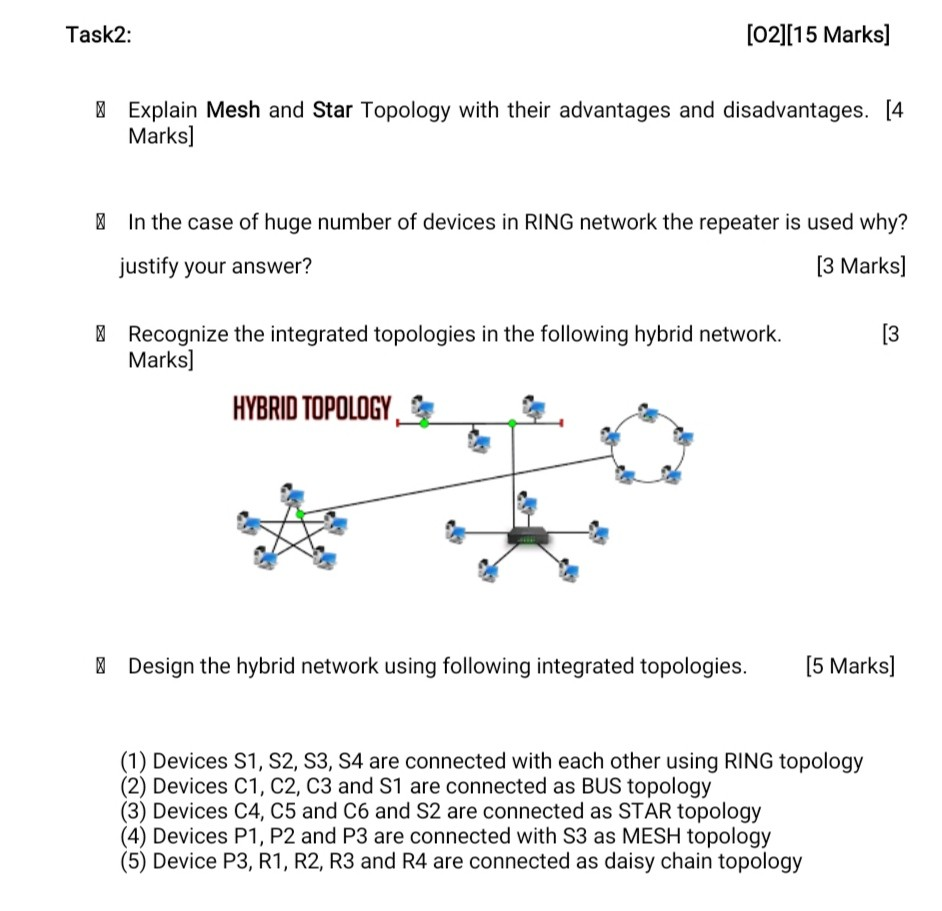
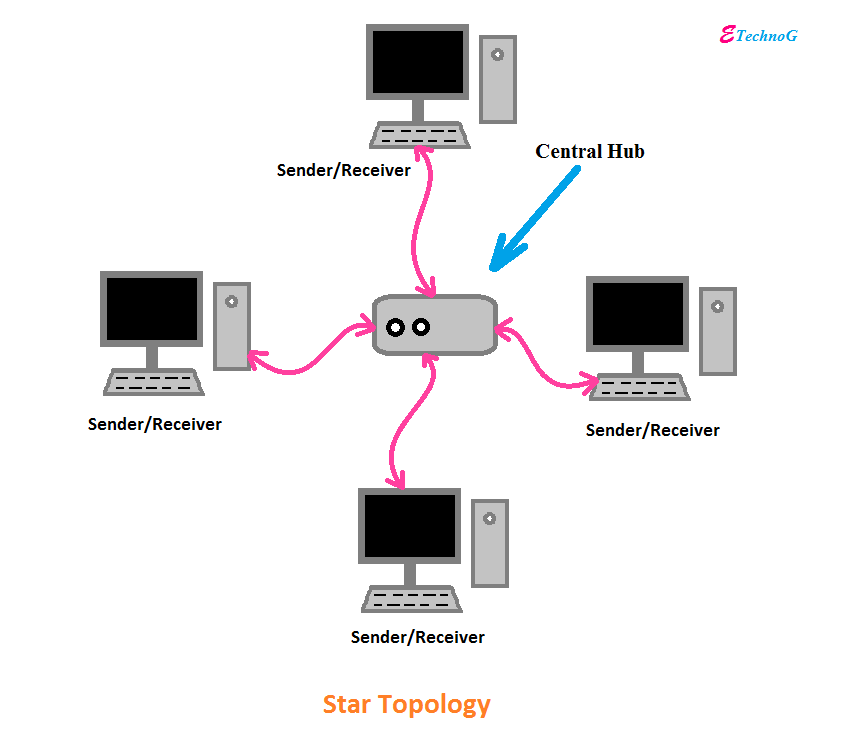
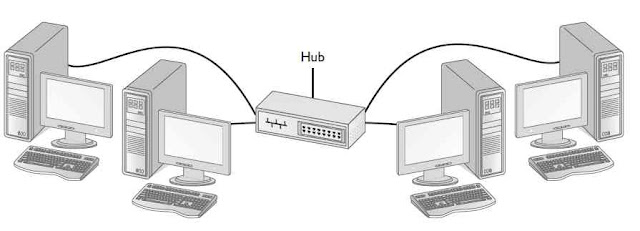
A star topology is a type of network configuration in which all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. In this arrangement, each device has its own dedicated point-to-point connection to the central hub, rather than being connected to each other in a linear fashion like a bus topology or a ring topology.
One of the main advantages of a star topology is that it is relatively easy to install and configure. Since each device has a dedicated connection to the central hub, it is simple to add or remove devices from the network without disrupting the entire system. This makes it an ideal choice for small to medium-sized networks where the number of devices is likely to change over time.
Another advantage of a star topology is that it is relatively robust and resistant to failure. If one device fails or is disconnected from the network, it will not affect the other devices, since they are all connected to the central hub rather than to each other. This makes it a good choice for mission-critical networks that need to be highly reliable.
A star topology also has the advantage of being relatively easy to troubleshoot and maintain. Since each device has a dedicated connection to the central hub, it is easy to identify and fix problems with individual devices. This makes it a good choice for networks that need to be carefully monitored and maintained.
Despite these advantages, there are also some disadvantages to using a star topology. One disadvantage is that it can be relatively expensive to set up and maintain, since each device requires a separate connection to the central hub. This can be a major drawback for large networks or for organizations with limited budgets.
Another disadvantage of a star topology is that it can be less efficient than other types of networks. Since all traffic passes through the central hub, it can become congested and slow down the entire network if there is a high volume of traffic. This can be a major issue for networks that need to handle large amounts of data or support real-time applications.
In summary, a star topology has several advantages, including ease of installation and maintenance, robustness, and ease of troubleshooting. However, it can also be relatively expensive to set up and maintain, and it may not be as efficient as other types of networks in certain situations. As with any type of network configuration, the choice of a star topology should be carefully evaluated based on the specific needs and resources of the organization.