Starbucks is a global coffee company and coffeehouse chain with more than 30,000 locations in over 80 countries. The company has achieved significant economies of scale in its operations, which have contributed to its success and helped it maintain a leading position in the highly competitive coffee industry.
Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that a company can achieve by increasing the scale of its operations. In the case of Starbucks, the company has been able to achieve economies of scale in several ways.
First, Starbucks has achieved economies of scale through the expansion of its operations. By opening new stores in various locations around the world, Starbucks has been able to increase its customer base and revenue. This has allowed the company to spread its fixed costs, such as rent and utilities, over a larger number of units, resulting in lower costs per unit.
Second, Starbucks has achieved economies of scale through the use of technology and automation in its operations. The company has implemented automated systems for tasks such as order taking and payment processing, which have helped to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. Starbucks has also invested in technology such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize its supply chain and improve its operations.
Third, Starbucks has achieved economies of scale through its partnerships and collaborations with other companies. For example, the company has formed partnerships with major airlines and hotel chains to offer its products in these locations, which has allowed Starbucks to tap into new markets and increase its customer base.
Overall, Starbucks has been able to achieve significant economies of scale through its expansion, use of technology and automation, and partnerships with other companies. These economies of scale have helped the company to maintain its competitive advantage and become a leading player in the global coffee industry.
Economics of Starbucks

The businesses involved are constantly fighting to outdo one another in order to satisfy a larger market or demand, which results in a hugel conflict. Furthermore, according to Starbucks Chief Marketing Officer Mr. This can be seen from the diagram. For instance, the Starbucks Rewards loyalty program enables the brand to stay connected with its customers through the Starbucks app. When firms and industries increase the scale of their operation there can be advantages which reduce the average unit cost of their output. Delivering beverage innovation : To improve partner and customer experiences, Starbucks has developed the Siren System, a proprietary new equipment innovation designed to meet the growing demand for customization of hot and cold beverages and warm foods. At the point when there is a little cost increment, it may be a huge effect on their edges as their clients aren't that delicate into value changes.
How Starbucks Built a Global Coffee Empire

However if Starbucks shut down its stores, its loss would be just the total fixed cost. The costs of goods sold, depreciation and amortization expenses, and store operating expenses have declined over the last six years, with only general and administrative expenses rising. Furthermore, Panera does not have the same scale advantages that Starbucks enjoys thanks to Starbucks' amazing global supply chain. This is in Managerial Economics Starbucks Case Study Managerial Economics Starbucks Case Study Abstract This paper will explore the science of Managerial Economics, the cost effective management of scarce resources, through an exploration of the Starbucks Company. One factor that will change supply is the price of factors of production. Consumers want the best coffee at affordable prices and they would rather go to a business they already know or trust.
Effects of the Expansion of Starbucks

As a result, those who wish to become Starbucks partners must adhere to its explicit guidelines. Q-quantity, P-price, E-equilibrium point, S-supply 3. In the east, it associates with Uni-President and in the South, Maxim Caterers. Since 1971, Starbucks Coffee Company has been committed to ethically sourcing and roasting high-quality arabica coffee. Edited by Naomi Santiago. This will include an assessment of relevant market forces, market structure and the economic theories that guide business decisions for this company. This allows Starbucks to minimize its operating risks.
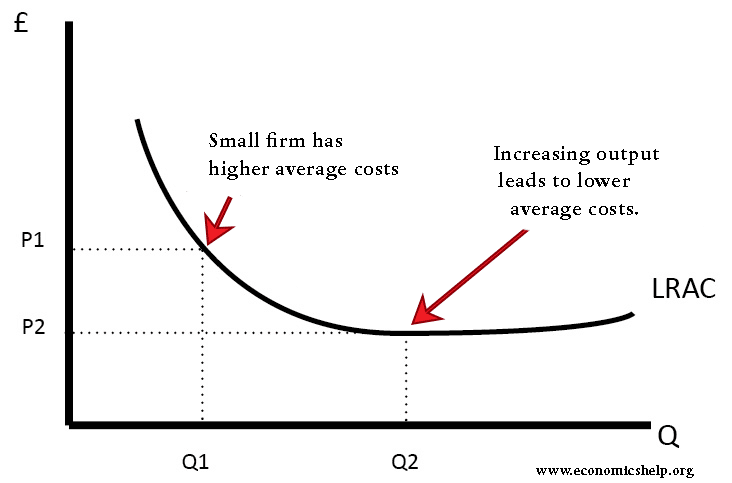
Over the long haul Starbucks encounters economies of scale The alleged economies

Furthermore, although Starbucks has thousands of locations all over the world, the market does not seem saturated. An analysis of Starbucks international strategy Starbucks' success in its internationalization process comes down to its cultural mindfulness and intensive research of the host market. Starbucks business strategy is based on the following four pillars: 1. Cost of Production There are various costs that Starbucks® faces within the company: fixed costs, direct and indirect costs, and operating costs. Overhead costs fixed are spread over more units produced. This is mainly because of the amount of Starbucks® stores open across the globe, more than 24,000. This also has enabled Starbucks to increase its operating profit margins from 0.