Structural ambiguity, also known as syntactic ambiguity, is a type of linguistic ambiguity that occurs when a sentence or phrase can be interpreted in more than one way due to its syntax, or the way the words are arranged in a sentence. This type of ambiguity can arise when a sentence contains words or phrases that can be interpreted in multiple ways, or when a sentence has more than one possible structure.
For example, consider the following sentence: "The old man the boat." This sentence is structurally ambiguous because it can be interpreted in two different ways. The first interpretation is that the old man owns the boat, while the second interpretation is that the old man is located in the boat. The presence of the word "the" before both "old man" and "boat" makes it difficult to determine which interpretation is correct.
Structural ambiguity can also occur when a sentence contains words or phrases that can be interpreted in multiple ways. For example, the word "bank" can refer to a financial institution or to the edge of a river. In the sentence "I deposited my money in the bank," the word "bank" could refer to either a financial institution or the edge of a river, depending on the context in which it is used.
Structural ambiguity can be a source of confusion and can lead to misunderstandings in communication. However, it can also be used as a literary device to add depth and complexity to written or spoken language. For example, poets and writers may use structural ambiguity to create multiple layers of meaning in their work, or to encourage readers or listeners to think critically about the words and phrases they use.
Overall, structural ambiguity is a common occurrence in language and can have a significant impact on the way we interpret and understand communication. By understanding the concept of structural ambiguity, we can better navigate the complexities of language and improve our communication skills.
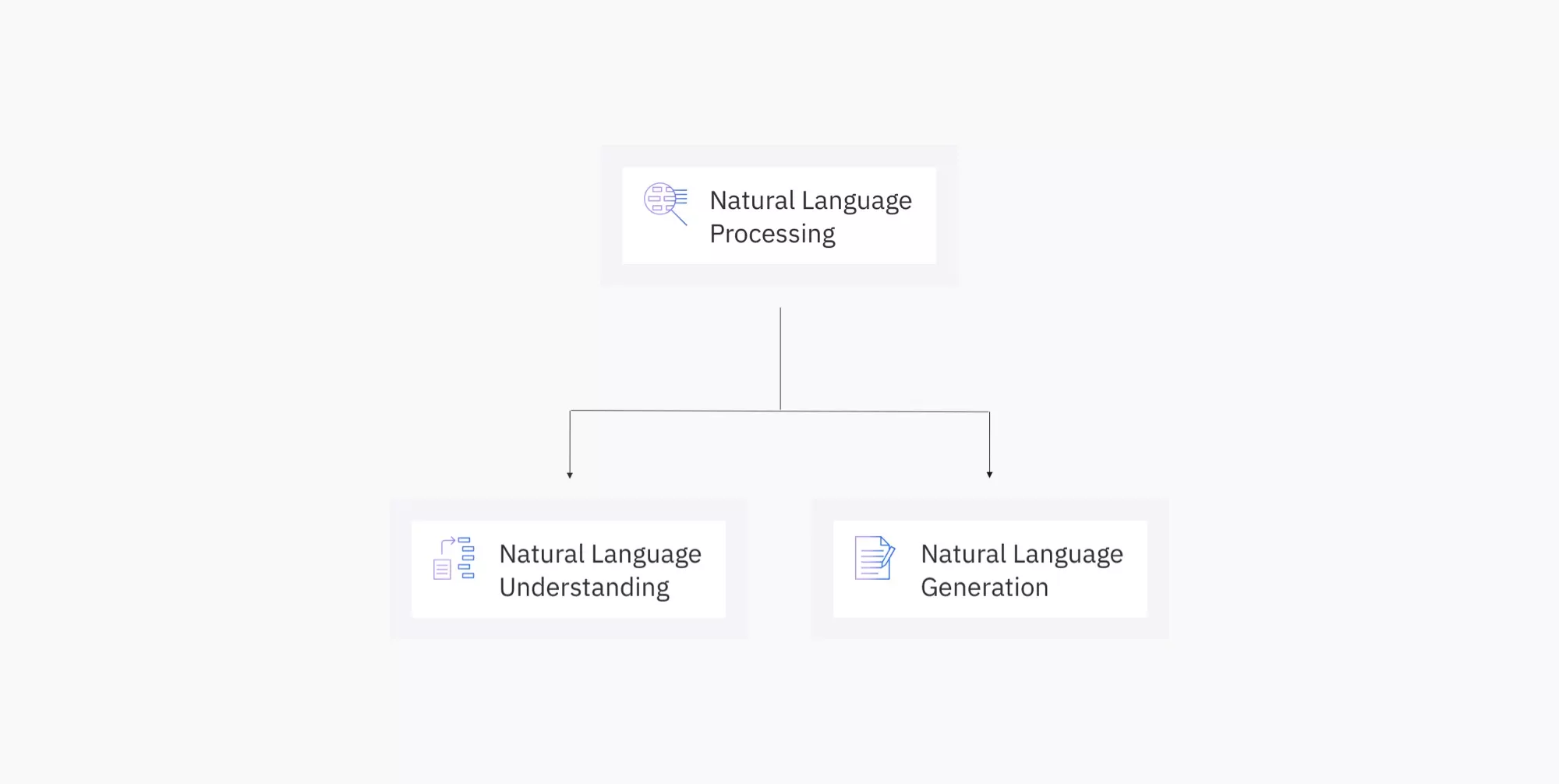
structural ambiguity

The dominant strain of current syntactic theory takes the lexicon as primitive and studies the rule-governed derivation of syntactic forms, which are structures known as LFs or, more misleadingly, Logical Forms. Because there is no singular, clear explanation of the sentence, people attempting to make sense of it are hampered by ambiguity. Dissertation, with 1991 preface. Giving an account of ambiguity and disambiguation requires one to discern the bearer s of ambiguity. On the other hand, in philosophical discourse, distinctions that are quite fine can be made that may well be missed by normal users of the language who are inclined to miss differences in meaning that are slight.
Examples Of Structural Ambiguity
Henry James, during the middle part of his career, incorporated this type of vagueness into his writing. In general, under- determination and generality may leave open many possibilities without being ambiguous between those possibilities. Example 1 : I invited the person with the microphone. Expression and Meaning: Studies in the Theory of Speech Acts, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. We can formulate another test 9 for constituency. Imagination and Convention: Distinguishing Grammar and Inference in Language.
What is linguistic ambiguity?
Third, ambiguity in art can intentionally or unintentionally increase the interest in a work of art by refusing to allow easy categorization and interpretation. Logical Form: Its Structure and Derivation, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. It helps to provide a paraphrase afterwards to bring out the distinct senses. When there is ambiguity between two words, this is referred to as structural ambiguity or grammatical ambiguity. Philosophy Without Ambiguity: A Logico-Linguistic Essay, Oxford: Oxford University Press. This test has led people some philosophers to surprising results.
Structural Ambiguity In Linguistics

However, upon learning that there is a car by the same name made by Volkswagen, it will be much less clear to me that I know what she bought. Example 1 : My sister saw bat. Read also The English Phonemic System English Language Essay Structural ambiguity happens if there is a sentence which is ambiguous because its words relate each other in different ways, even though none words are ambiguous Hufford 129 — 130. In newspapers today, we are witnessing the latest linguistic accommodation to changing social and commercial pressures. Simpler Syntax, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ambiguity in Language — The Writing Center

Lexical ambiguity occurs when a word has more than one possible meanings. For example, in the sentence She really loves these dates, the word dates could have the following meanings: 1 days of the month 2 the fruit 3 romantic social appointments Structural ambiguity arises when a sentence has more than one meaning due to the way words are arranged in that sentence. In linguistics, structural ambiguity is the phenomenon whereby a phrase, sentence, or text can be interpreted in more than one way due to its grammatical structure. LFs can be represented as trees, and the terminal nodes of the branches are taken from the lexicon. Peter saw his neighbour with binoculars. This case may be far-fetched; but we have a real live cases of it. A lexicon is a repository of lexical items, which need not look like words and they certainly need not correspond to our intuitions about words.