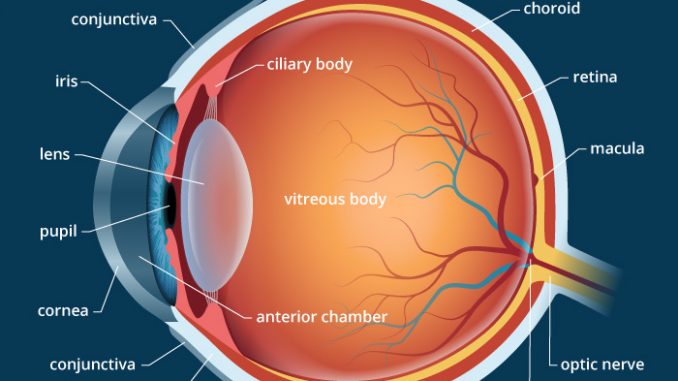
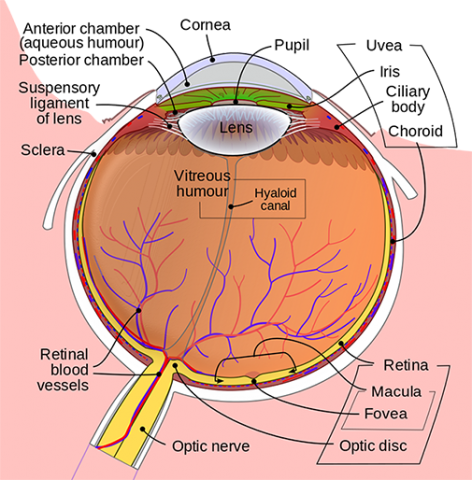
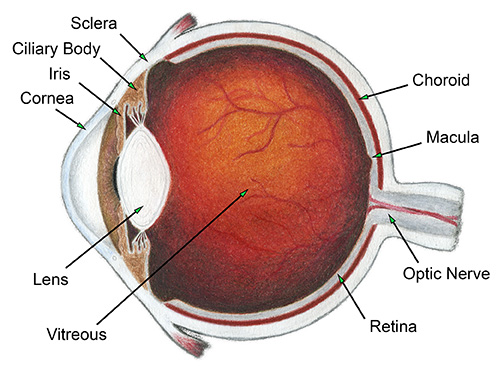
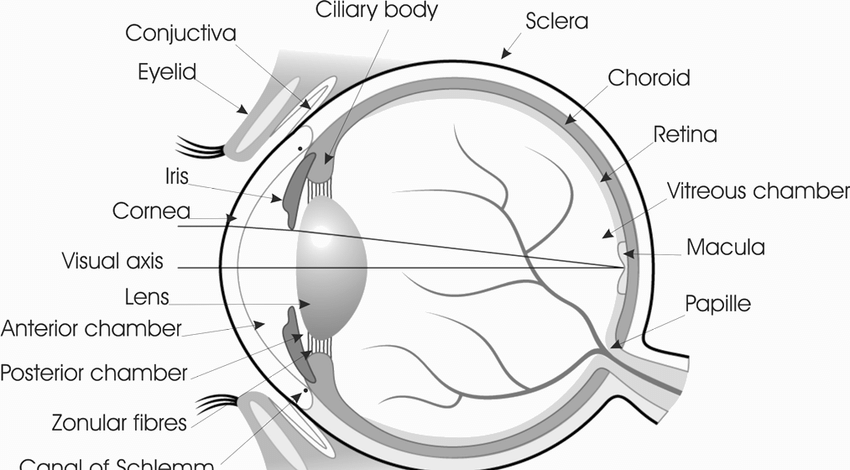
The human eye is a complex and intricate organ that plays a vital role in our ability to see and perceive the world around us. The structure of the eye is designed to allow light to enter and be focused onto the retina, which is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. The retina is responsible for converting light into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as images.
The eye is divided into two main parts: the front part, which is called the anterior chamber, and the back part, which is called the posterior chamber. The front part of the eye is made up of the cornea, the iris, and the lens. The cornea is the transparent outer layer that covers the front of the eye and helps to protect it from dirt, dust, and other foreign objects. It is also responsible for bending the light that enters the eye, which helps to focus it onto the retina.
The iris is the colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil, which is the small opening in the center of the iris. The size of the pupil can be adjusted to control the amount of light that enters the eye. This is important because too much light can damage the retina, while too little light can make it difficult to see.
The lens is a transparent structure located behind the iris that helps to focus light onto the retina. The lens is held in place by the ciliary muscles, which can change the shape of the lens to help focus on objects at different distances.
The posterior chamber of the eye is made up of the vitreous humor, the retina, and the optic nerve. The vitreous humor is a clear, gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina. It helps to maintain the shape of the eye and provides a clear path for light to reach the retina.
The retina is a thin layer of cells located at the back of the eye that is responsible for converting light into electrical signals. The retina is made up of several different types of cells, including rods and cones, which are specialized cells that are sensitive to light. The rods are responsible for detecting light and dark, while the cones are responsible for detecting colors.
The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that carries the electrical signals from the retina to the brain. The optic nerve is located at the back of the eye and is responsible for transmitting the information that the retina has collected to the brain, which then interprets it as an image.
In conclusion, the structure of the human eye is a complex and intricate system that is designed to allow us to see and perceive the world around us. The various parts of the eye work together to allow light to enter the eye, be focused onto the retina, and be converted into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as images.