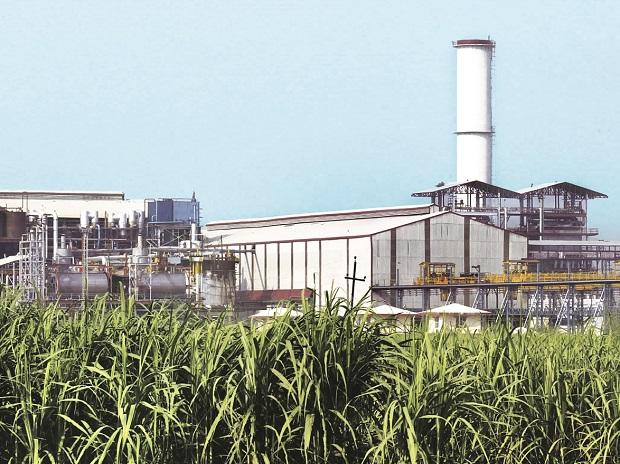
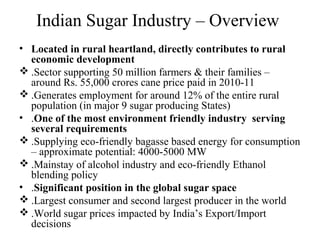
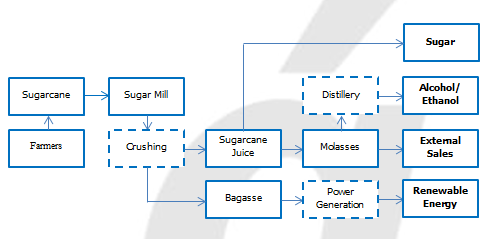
The sugar industry in India is a significant contributor to the country's economy and employs millions of people. It is one of the largest industries in India, with more than 50 million metric tons of sugar produced annually. The industry is concentrated in the northern and western regions of the country, particularly in the states of Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka.
The history of the sugar industry in India dates back to the colonial era, when the British introduced sugarcane cultivation and established sugar mills in the country. The industry has grown significantly since then, with a number of technological advancements and government policies supporting its growth.
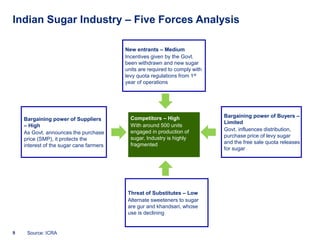
India is the world's second-largest producer of sugar, with a significant portion of the industry being owned by cooperatives and small-scale producers. However, the industry has also faced a number of challenges, including low prices, fluctuating demand, and competition from imported sugar.
One of the major challenges faced by the sugar industry in India is the fluctuating demand for sugar. The demand for sugar in India is largely influenced by the country's monsoon season, as well as the availability of other sweeteners such as honey and jaggery. The industry has also faced competition from imported sugar, which has led to a decline in domestic prices.
To address these challenges, the government has implemented a number of policies and schemes to support the sugar industry. These include the Sugar Development Fund, which provides financial assistance to sugar mills, and the Sugarcane Control Order, which regulates the production and sale of sugarcane in the country.
Despite these challenges, the sugar industry in India continues to play a significant role in the country's economy and employs millions of people. It is a vital source of income for small farmers and rural communities, and it is likely to continue to be an important industry in the country in the future.