Supplementary genes are a type of genetic material that is present in some organisms but not in others. These genes are often referred to as "accessory" or "supernumerary" genes, as they are not essential for the basic functioning of an organism. However, they can play important roles in the evolution, adaptation, and variation of a species.
Supplementary genes can be found in a variety of organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals. They are typically found in the genome alongside the "core" genes that are essential for an organism's survival and reproduction. However, supplementary genes are not necessary for the basic functioning of an organism and may be present in some individuals but not others.
One of the key roles of supplementary genes is in the evolution and adaptation of a species. These genes can provide a source of genetic variation that allows a species to adapt to changing environments or to develop new traits. For example, some supplementary genes may encode proteins that help an organism to resist diseases or environmental stresses. Others may enable an organism to utilize new sources of food or to adapt to new habitats.
In addition to their role in adaptation, supplementary genes can also contribute to the variation within a species. This variation can be beneficial for a population as it allows for the development of different strategies for survival and reproduction, leading to increased fitness and evolutionary success.
There are several ways in which supplementary genes can be acquired by an organism. One way is through horizontal gene transfer, which is the transfer of genetic material from one organism to another. This can occur through mechanisms such as bacterial conjugation, transduction, and transformation. Another way is through the process of gene duplication, where a gene is copied and then becomes free to evolve independently of the original gene.
In conclusion, supplementary genes are a type of genetic material that is not essential for the basic functioning of an organism but can play important roles in the evolution, adaptation, and variation of a species. These genes can be acquired through horizontal gene transfer or gene duplication and can provide a source of genetic variation that allows a species to adapt to changing environments and develop new traits.
Difference Between Complementary and Supplementary Genes
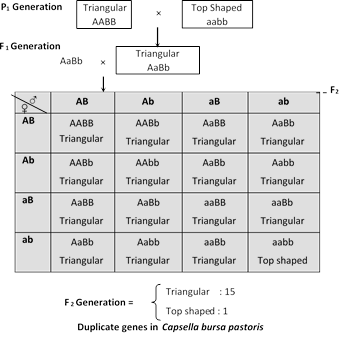
Research Involving Plants Experimental research on plants either cultivated or wild including collection of plant material, must comply with institutional, national, or international guidelines. These minor mutations of the SIRT6 gene increase its ability to better repair DNA and then to delay aging. It's a long, long way off — if we get there at all — but perhaps one day, Borg-packed microbes could be engineered to make a sizeable dent Field work is being undertaken in parallel with lab analysis to reveal more about how these extraordinary Borgs work, and to trace back a history that could potentially extend to billions of years. In this instance, a single phenotype is produced by the genotype aaBB, aaBb, Aabb, aabb. All reviewer comments should be responded to in a point-by-point fashion. A phenotype is a characterized trait that can be determined upon observation. It is transcribed by your cytoplasm and contains a code and instructions that make every single one of us unique and separate humans, animals, and plants alike.
Types Of Genes: What Are They. & What Do They Do?

In fact some Borgs have all the mechanisms required to eat up methane on their own, provided they're within a cell that is able to express the Borg's genes. Authors are expected to comply with the best ethical publication practices when publishing with MDPI. It should explain why the manuscript fits the scope of the journal. When gene or protein names are included, the abbreviated name rather than full name should be used. Dataset title; Data repository or archive; Version if any ; Persistent identifier e. Authors should not copy references from other publications if they have not read the cited work. Methods used to generate the proteomics data should be described in detail and we encourage authors to adhere to the " Research Ethics Research Involving Human Subjects When reporting on research that involves human subjects, human material, human tissues, or human data, authors must declare that the investigations were carried out following the rules of the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975 Example of an ethical statement: "All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
Weird 'Borg' DNA May Have Assimilated Microbes For Billions of Years : ScienceAlert

If the required revision time is estimated to be longer than 2 months, we will recommend that authors withdraw their manuscript before resubmitting so as to avoid unnecessary time pressure and to ensure that all manuscripts are sufficiently revised. When any of the two factors is present independently, its dominant Complementary Factor 9:7 The interaction of two or more genes inhabiting distinct loci acquired from different parents results in the development of specific characteristics. Authors are responsible for correctness of the statements provided in the manuscript. Polymeric or Additive Genes : Duplicate Genes with Cumulative Effect Two independent dominant genes, whether present in homozygous or heterozygous condition, have similar phenotypic effect when present individually but produce a cumulative or double effect when found together. In other words, both genes must be present together, or else the desired phenotype will not appear.








