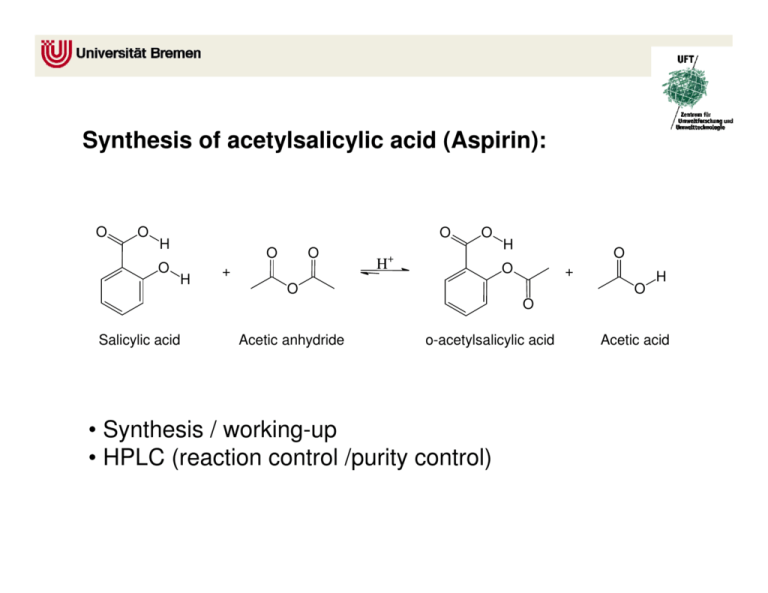
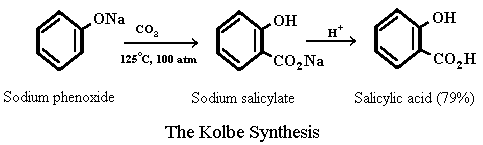
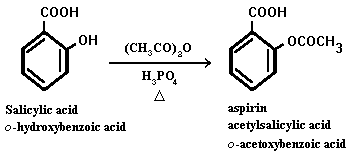
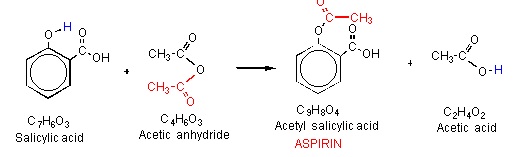
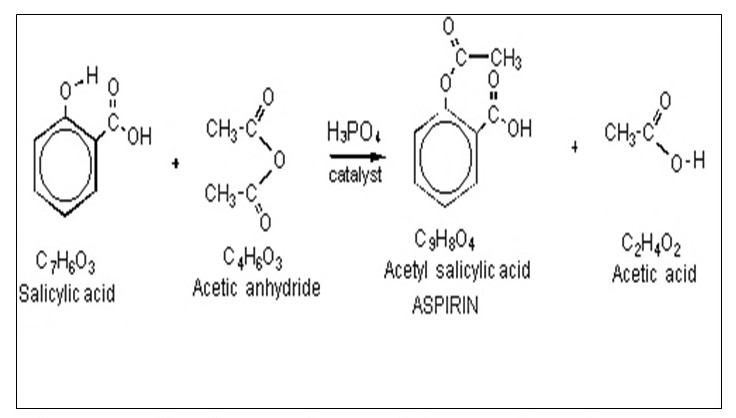
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, is a common over-the-counter pain reliever and anti-inflammatory medication. It is used to treat a variety of ailments, including headaches, muscle pain, and fever. Aspirin is synthesized through a chemical reaction known as esterification, which involves the combination of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. The synthesis of aspirin involves the following equation:
Reactants:
- Salicylic acid
- Acetic anhydride
- Phosphoric acid (catalyst)
Products:
- Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid)
- Acetic acid
The synthesis of aspirin begins with the reactant salicylic acid, which is derived from plants such as willow trees and meadowsweet. Salicylic acid is a natural compound that has been used for centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including pain and inflammation.
Next, the reactant acetic anhydride is added to the salicylic acid. Acetic anhydride is a chemical compound that is used as a reagent in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including aspirin.
Phosphoric acid is added as a catalyst to speed up the reaction between the salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. The combination of these reactants results in the production of aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, and acetic acid.
The synthesis of aspirin is an important chemical reaction that has numerous applications in the medical field. Aspirin is a widely used pain reliever and anti-inflammatory medication that is effective in treating a variety of ailments. The synthesis of aspirin involves the combination of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol through the process of esterification, resulting in the production of acetylsalicylic acid and acetic acid.
What is the balanced chemical equation of aspirin?

We hope this article on the aspirin formula is helpful to you. Weigh the dried recrystallized product on the filter paper and record the mass to 0. The theoretical yield is rarely obtained because of sources of error, side reactions, or other complications. This compound is stable in dry air but gets hydrolysed to acetic acid and salicylic acid when it comes in contact with moist air. Place a small amount of yield around 0. Conclusion: The main objective of the synthesis of aspirin lab was so produce aspirin acetylsalicylic acid through the reaction of salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. Ensure that your waste is disposed of correctly either in the "Non-halogenated" or "Halogenated" waste containers -"Non-halogenated"- chemicals containing ONLY C, H, and O -"Halogenated" - chemicals containing C, H, O, and halogens Any waste generated from either acid or base must first be neutralized with NaHCO3 and then poured down the sink -Flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid can form an ignitable mixture in the air near the surface of a liquid -The lower the flash point, the easier it is to ignite the material -For example, gasoline has a flash point of approximately -40 degrees C and is more flammable than ethylene glycol antifreeze , which has a flash point of 111 degrees C -4 diamonds - blue, red, yellow, and white -Blue: Health hazard 4 Deadly 3 Extreme danger 2 Hazardous 1 Slightly hazardous 0 No health threat -Red: Fire Hazard Flashpoints 4 Below 73 F 3 Below 100 F 2 Below 200 F 1 Above 200 F 0 Will not burn -White: Specific Hazard W - Water reactive OX - Oxidizing agent ACID - Acid CORR- Corrosive -Yellow: Reactivity hazard 4 May detonate 3 Shock or heat may detonate 2 Violent chemical reaction; water reactive 1 Unstable if heated 0 Stable.
Aspirin Formula: Structure, Properties, Side Effects

Zinc oxide also acts as a base in this reaction, giving zinc acetate as a by-product. After the 6 minutes elapsed, 10 mL of distilled water was added to the Erlenmeyer flask and placed in the ice water, avoiding getting any of the ice water in the Erlenmeyer flask. When you are finished with this step, stop data collection. Aspirin Synthesis As we know Aspirin is also known as Acetylsalicylic acid, this compound can be synthesised by the action of salicylic acid on acetic anhydride through an esterification reaction. Start the data-collection program, then choose New from the File menu.