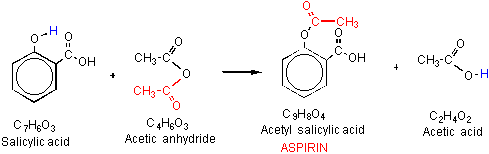
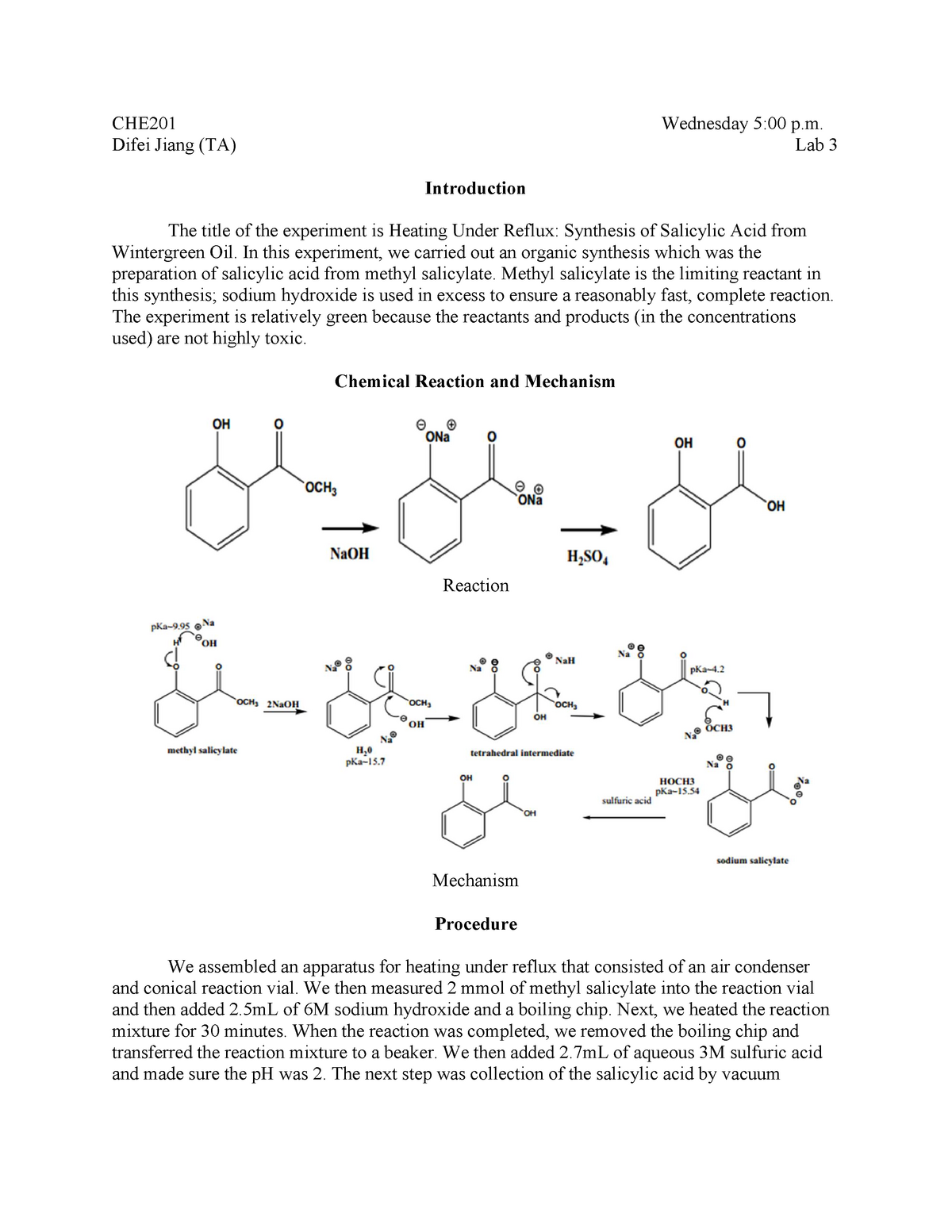
Salicylic acid is a widely used organic compound that has a variety of applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries. It is a white, crystalline solid that is derived from the metabolism of salicin, which is found in plants such as willow and meadowsweet. Salicylic acid has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, making it an effective treatment for a range of conditions such as acne, dandruff, and warts. It is also used as a preservative and a pH adjuster in a variety of personal care products.
There are several methods for synthesizing salicylic acid, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. One common method is the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction, which involves the electrochemical reduction of phenol using an electrolytic cell. This method is efficient and cost-effective, but it produces a low yield of salicylic acid and requires the use of hazardous chemicals such as concentrated sulfuric acid.
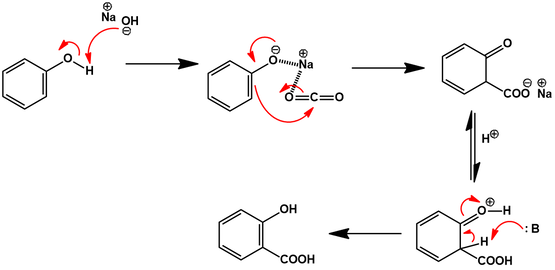
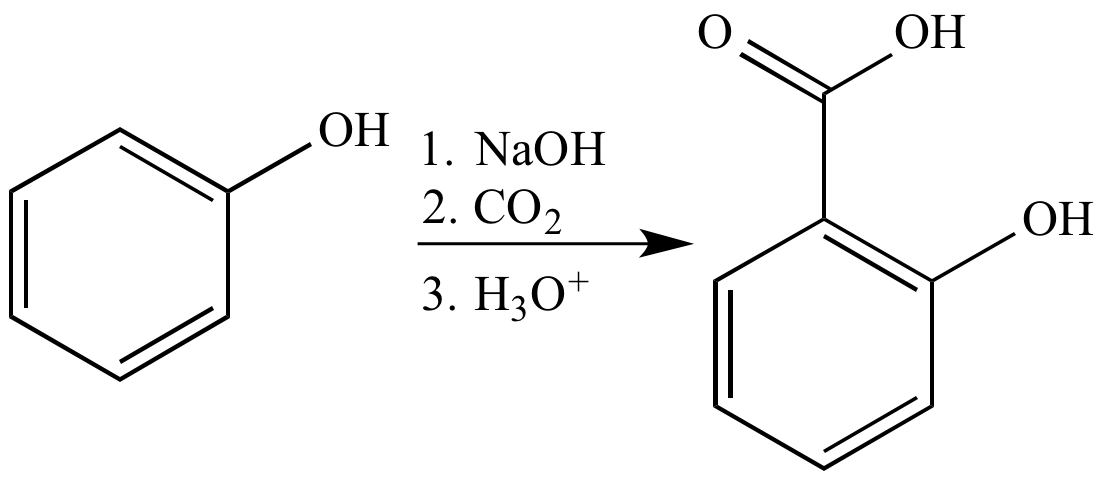
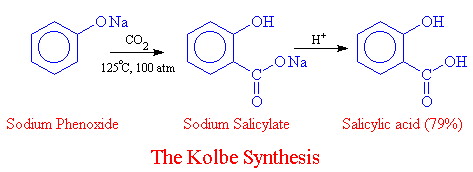
Another method for synthesizing salicylic acid is the Hock reaction, which involves the treatment of sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide and water. This method is less hazardous and produces a higher yield of salicylic acid, but it requires the use of specialized equipment such as a high-pressure reactor.
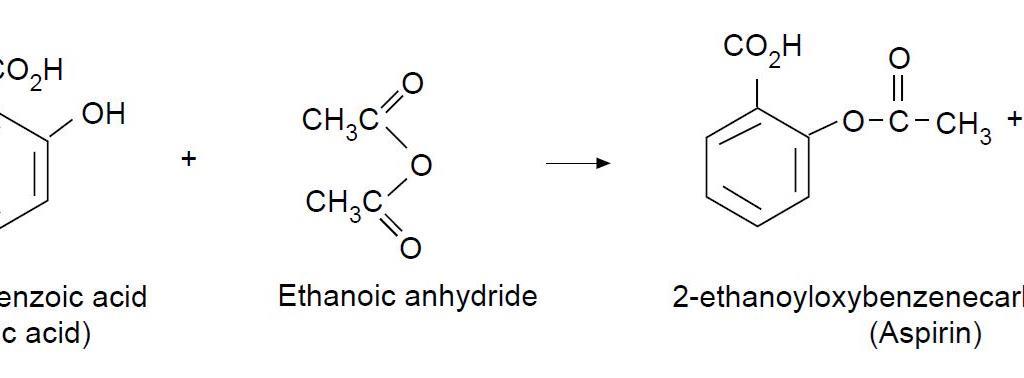
A third method for synthesizing salicylic acid is the hydrolysis of acetylsalicylic acid, also known as aspirin. This method is simple and cost-effective, but it produces a lower yield of salicylic acid compared to the other methods.
Regardless of the method used, the synthesis of salicylic acid requires careful control of the reaction conditions to ensure that the desired product is obtained in high purity. Impurities can affect the physical and chemical properties of the final product, which can impact its effectiveness and safety.
In conclusion, salicylic acid is an important organic compound that has a wide range of applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries. There are several methods for synthesizing salicylic acid, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The selection of a synthesis method depends on the desired yield, cost, and safety considerations. Regardless of the method used, it is important to carefully control the reaction conditions to ensure that the final product is of high purity.